Abstract
1 The kinetics of metformin were studied after i.v. and oral administration in four healthy subjects and after oral administration in twelve maturity onset (Type II) diabetic patients.
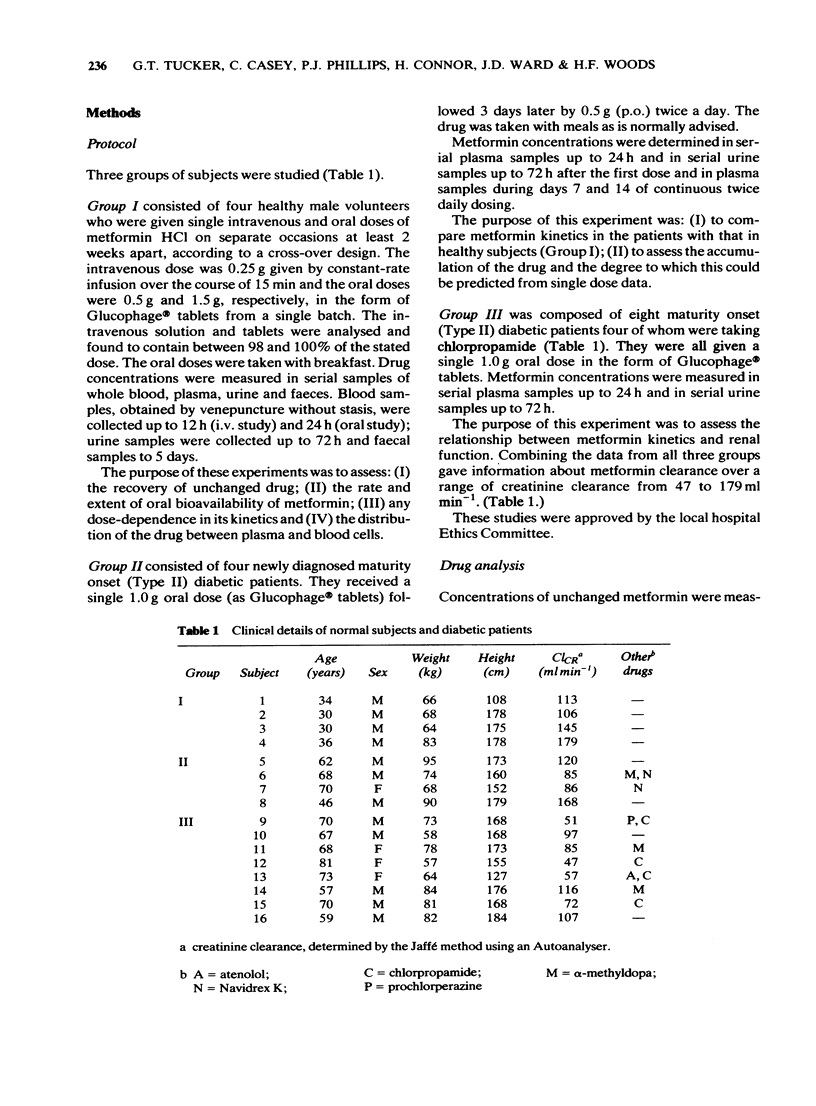
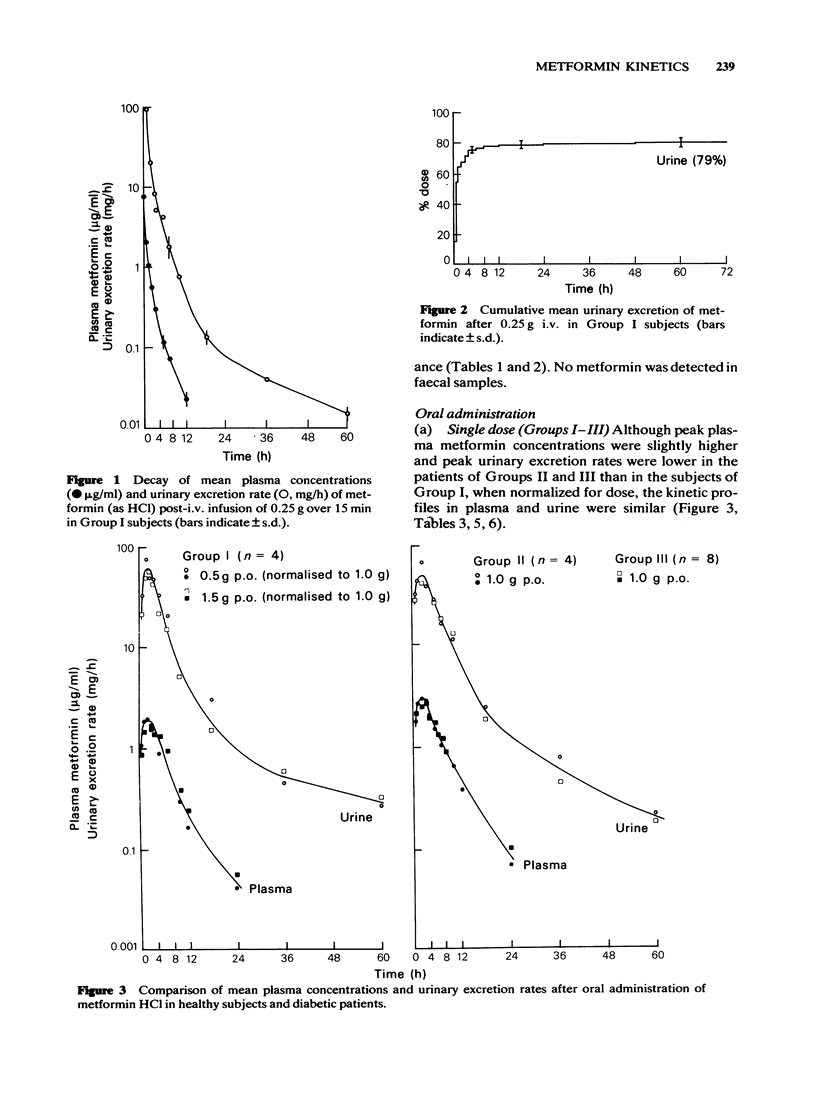
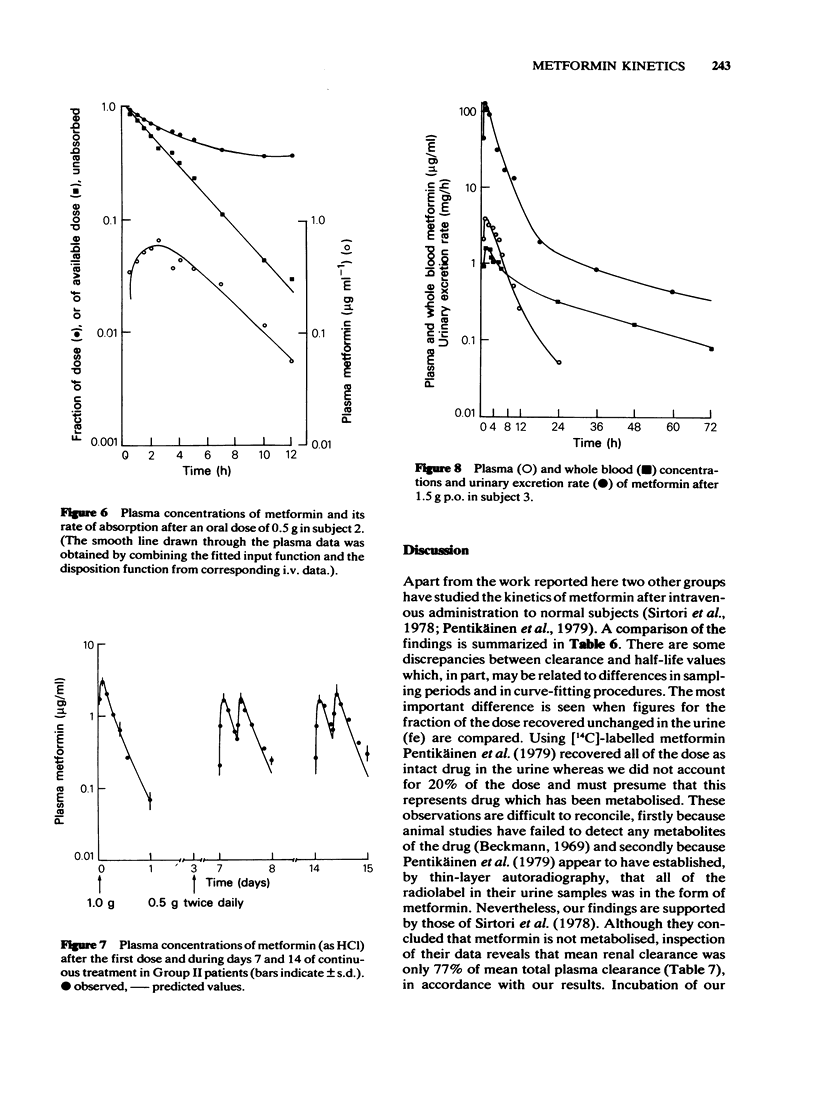
2 After i.v. administration most of the dose was rapidly eliminated but with a mean `terminal' T1/2 of 4 h measured up to 12 h in plasma and of 16 h measured up to 60 h from the urinary excretion rate. On average, 80% of the dose was recovered as unchanged drug in the urine with none detected in the faeces.
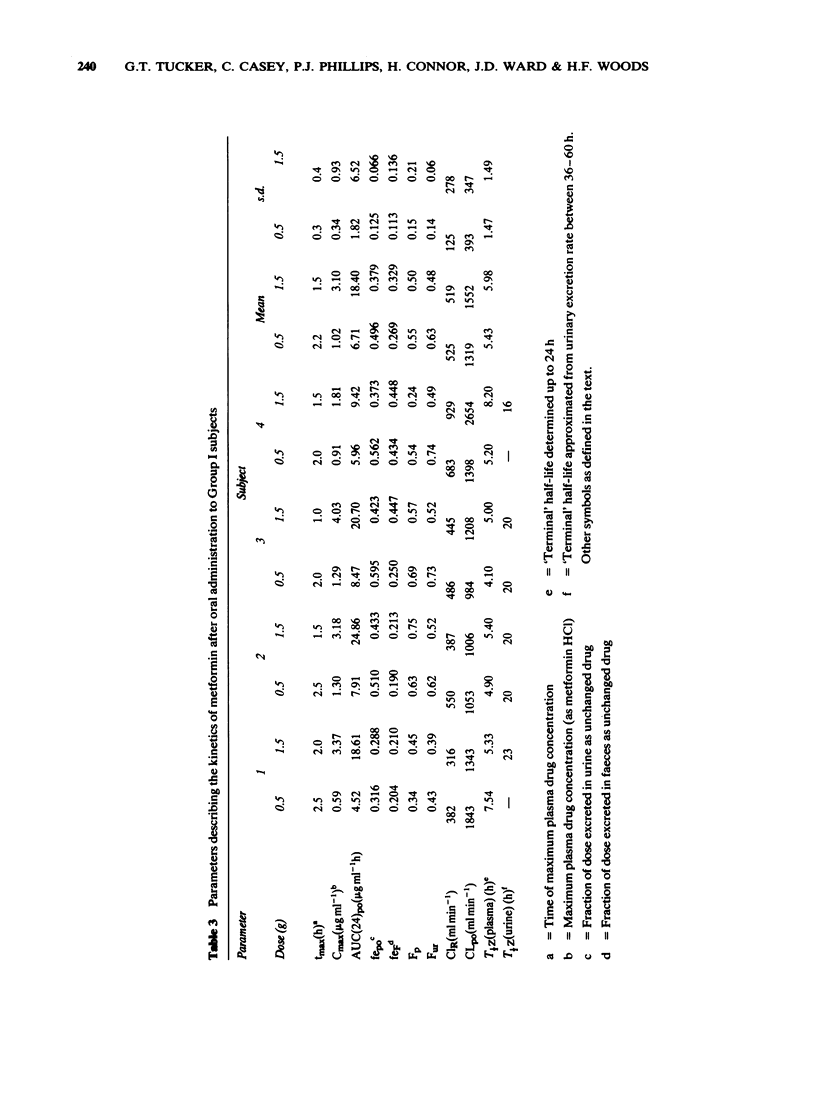
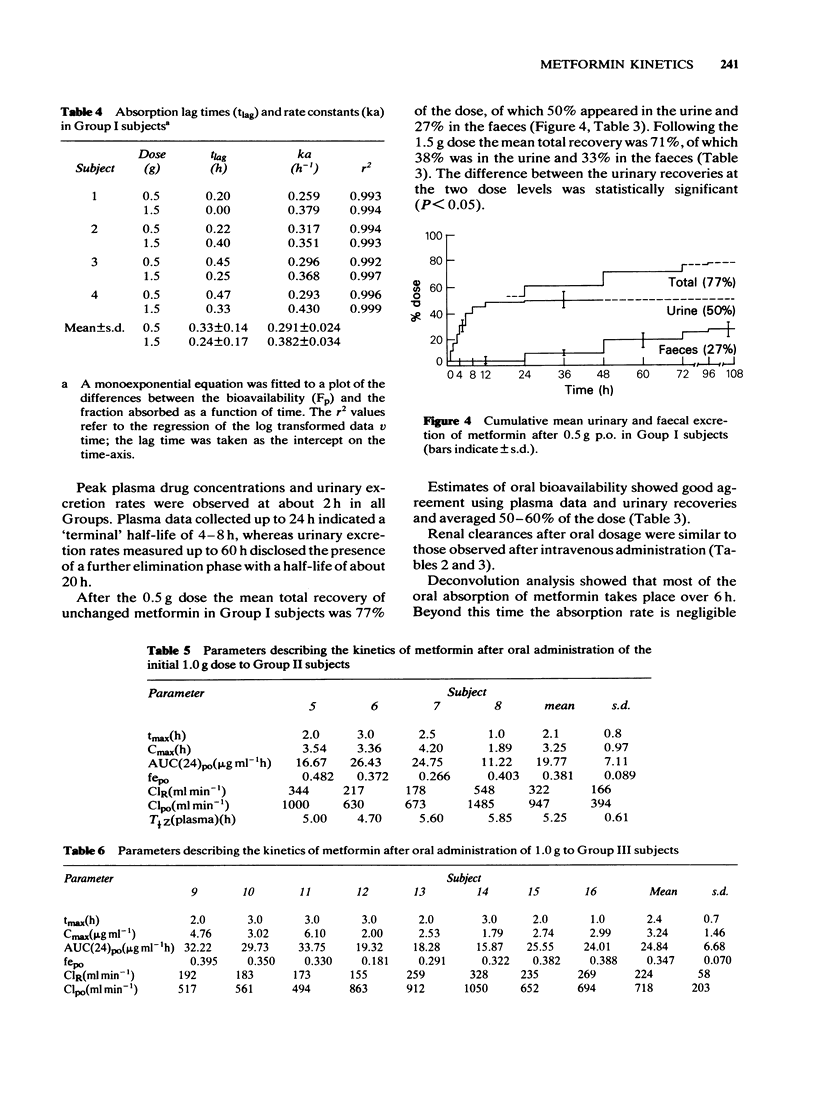
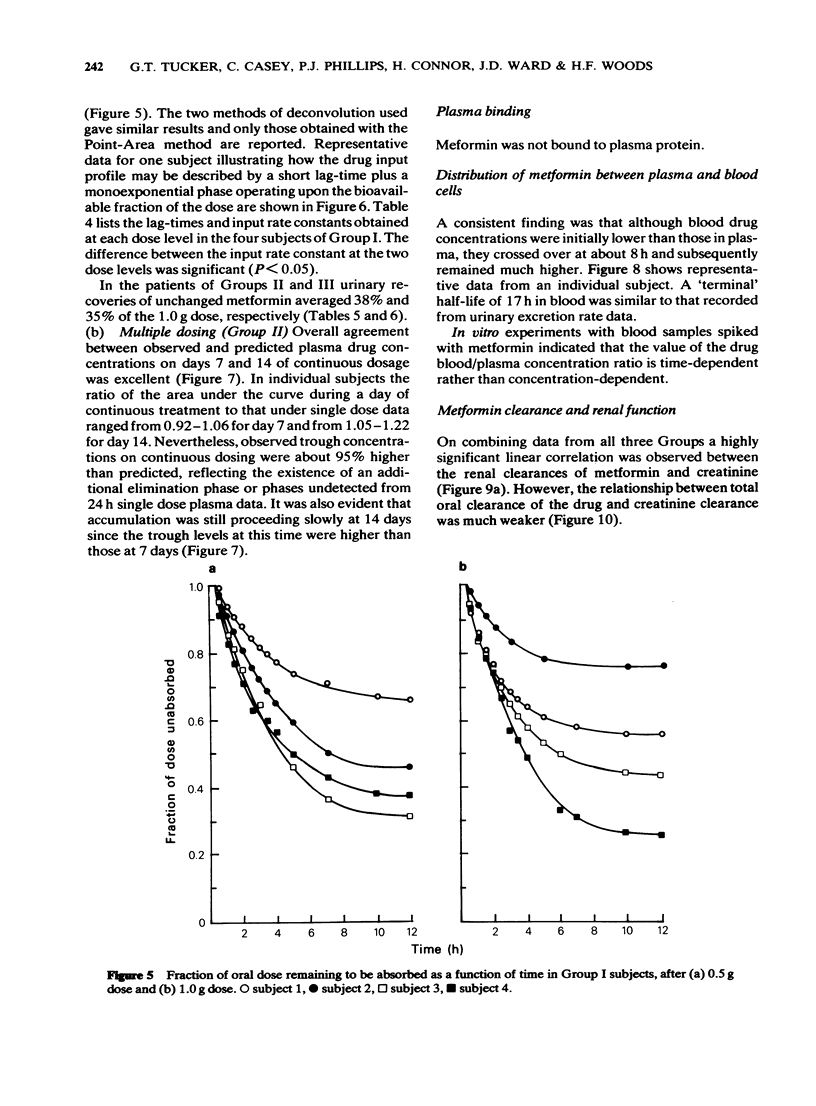
3 After single oral doses (0.5 and 1.5 g), maximum plasma concentrations and urinary excretion rates were observed at about 2 h with urinary recoveries of unchanged drug of 35-50% and faecal recoveries of about 30%. Urinary recoveries were significantly lower after the higher dose. Absolute oral bioavailability was 50-60% of the dose.
4 Deconvolution analysis showed that after a short lag-time, the available oral dose was absorbed at an exponential rate over about 6 h. Implications for the design of prolonged release dosage forms are discussed.
5 Plasma metformin concentrations measured throughout the seventh and fourteenth days of continuous 0.5 g twice daily treatment were accurately predicted from single dose data, although a discrepancy between observed and predicted trough levels reflected the existence of a slow elimination phase. Implications of the latter for a gradual accumulation of metformin in peripheral tissues and a possible association with lactic acidosis are discussed.
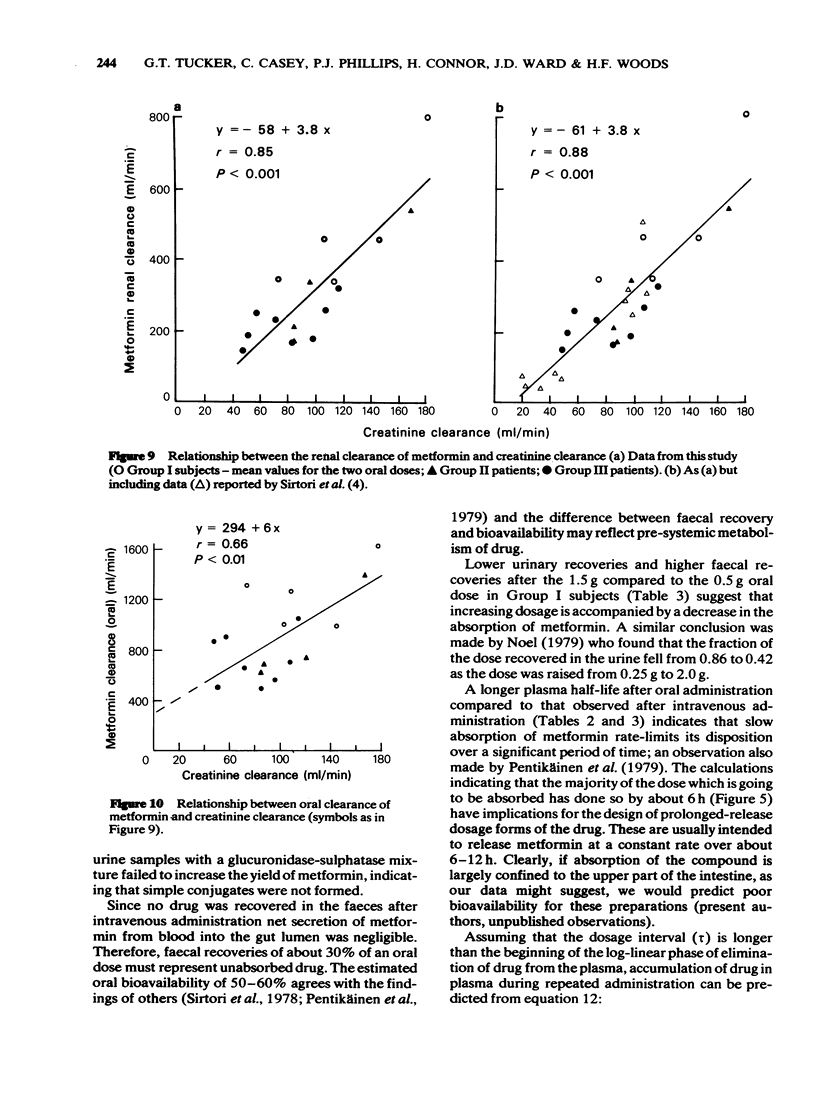
6 Renal clearance of metformin was highly correlated with creatinine clearance. However, a weaker relationship between total oral clearance of the drug and creatinine clearance suggests that the latter may not always be a reliable indicator of potential metformin accumulation owing to variability in absorption and possibly non-renal clearance of the drug,
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assan R., Heuclin C., Ganeval D., Bismuth C., George J., Girard J. R. Metformin-induced lactic acidosis in the presence of acute renal failure. Diabetologia. 1977 May;13(3):211–217. doi: 10.1007/BF01219702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R. Resorption, Verteilung im Organismus und Ausscheidung von Metformin. Diabetologia. 1969 Oct;5(5):318–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00452906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman U., Boman G., Wiholm B. E. Epidemiology of adverse drug reactions to phenformin and metformin. Br Med J. 1978 Aug 12;2(6135):464–466. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6135.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxenbaum H. G., Riegelman S., Elashoff R. M. Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1974 Apr;2(2):123–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomeni C., Gomeni R. IGPHARM: interactive graphic package for pharmacokinetic analysis. Comput Biomed Res. 1978 Aug;11(4):345–361. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(78)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda I., Harpur E. S. Accumulation in the peripheral compartment of a linear two-compartment open model. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1980 Feb;8(1):99–104. doi: 10.1007/BF01059451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irsigler K., Kritz H., Regal H., Kaspar L. Biguanid-induzierte und Biguanid-assoziierte Laktazidose. Serum- und Gewebsspiegel der Biguanide bei Hyperlaktämie und Laktazidose. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1979 Jan 19;91(2):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard M. S., Casey C., Tucker G. T., Woods H. F. Determination of metformin in biological samples. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;6(2):183–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb00852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. New method for calculating the intrinsic absorption rate of drugs. J Pharm Sci. 1968 Jun;57(6):918–928. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600570602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentikäinen P. J., Neuvonen P. J., Penttilä A. Pharmacokinetics of metformin after intravenous and oral administration to man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(3):195–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00562061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P. J., Thomas D. W., Harding P. E. Biguanides and lactic acidosis. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 22;1(6055):234–234. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6055.234-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirtori C. R., Franceschini G., Galli-Kienle M., Cighetti G., Galli G., Bondioli A., Conti F. Disposition of metformin (N,N-dimethylbiguanide) in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Dec;24(6):683–693. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978246683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan D. P., Dennis M. Mathematical basis of point-area deconvolution method for determining in vivo input functions. J Pharm Sci. 1978 May;67(5):663–665. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600670524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


