Abstract
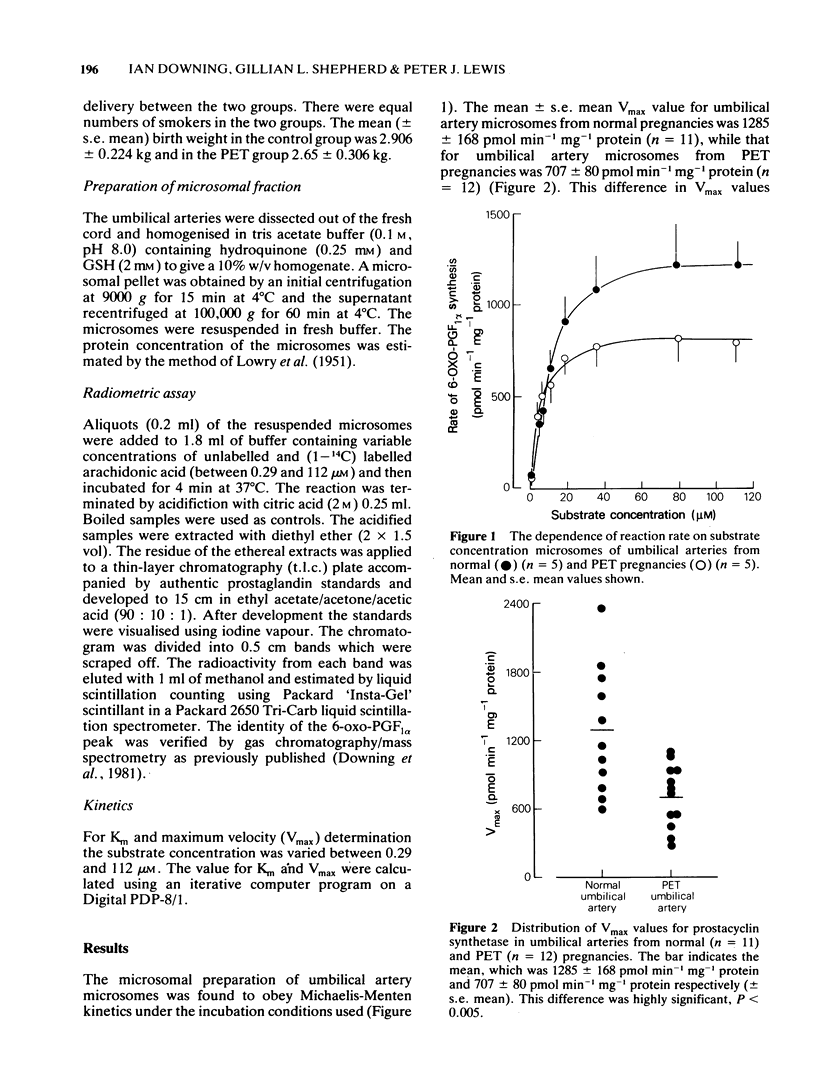
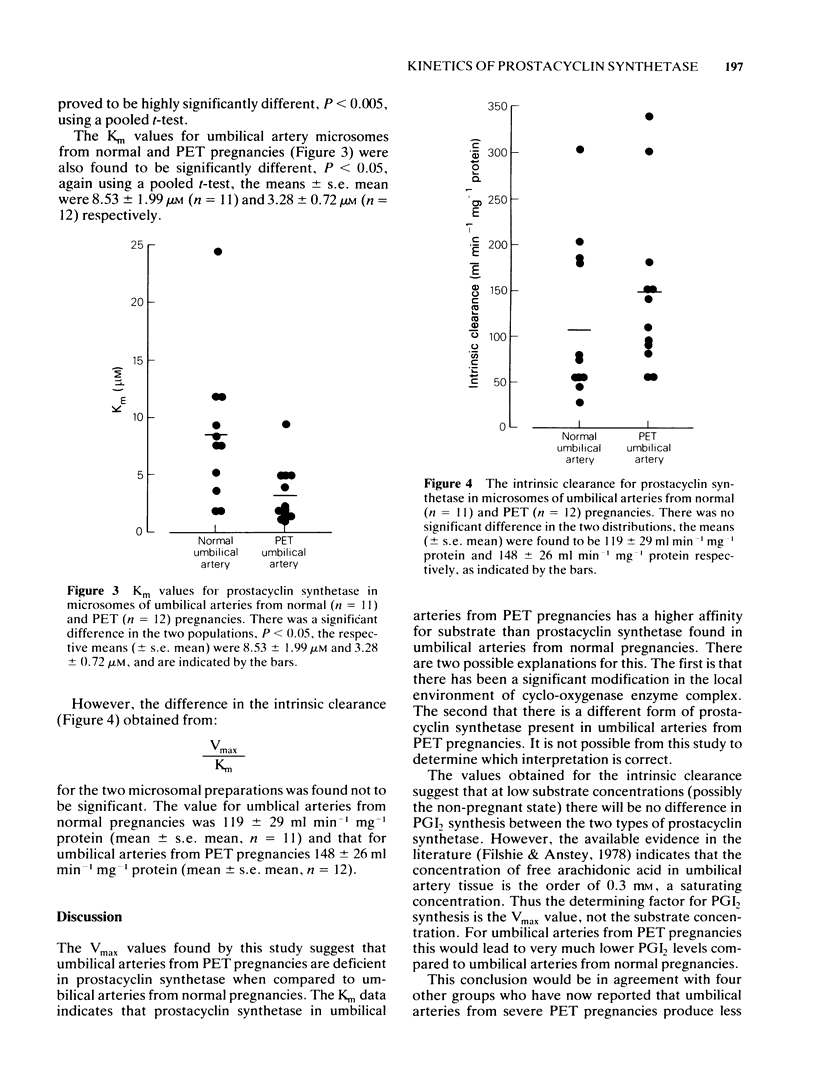
1 Prostacyclin synthetase in umbilical artery microsomes obeys Michaelis-Menten kinetics. 2 The maximum velocity (Vmax) of prostacyclin synthetase prepared from normal umbilical arteries was significantly higher than the Vmax of prostacyclin synthetase in umbilical arteries taken from pre-eclamptic pregnancies. 3 The Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) of the two prostacyclin synthetase preparations was significantly different with the synthetase from pre-eclamptic arteries have a higher affinity for substrate. 4 The limiting factor for prostacyclin synthesis is Vmax at high substrate concentrations which appears to be the case in umbilical arteries. However, at low substrate concentration there would be no difference in prostacyclin synthesis by the two forms of prostacyclin synthetase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodzenta A., Thomson J. M., Poller L. Prostacyclin activity in amniotic fluid in pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 1980 Sep 20;2(8195 Pt 1):650–650. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Benedetto C., Massobrio M., Camussi G. Maternal vascular prostacyclin activity in pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 1980 Sep 27;2(8196):702–702. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreras L. O., Defreyn G., van Houtte E., Vermylen J., van Assche A. Prostacyclin and pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 1981 Feb 21;1(8217):442–442. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91822-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. B., Worley R. J., MacDonald P. C., Gant N. F. Effect of prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors on pressor response to angiotensin II in human pregnancy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Jun;46(6):1007–1010. doi: 10.1210/jcem-46-6-1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filshie G. M., Anstey M. D. The distribution of arachidonic acid in plasma and tissues of patients near term undergoing elective or emergency Caesarean section. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1978 Feb;85(2):119–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1978.tb10464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Boylan P., Friedman L. A., Hensby C. N., Downing I. Prostacyclin in pregnancy. Br Med J. 1980 Jun 28;280(6231):1581–1582. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6231.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi G., Marchesi D., Zoja C., Muratore D., Mecca G., Misiani R., Rossi E., Barbato M., Capetta P., Donati M. B. Reduced umbilical and placental vascular prostacyclin in severe pre-eclampsia. Prostaglandins. 1980 Jul;20(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remuzzi G., Misiani R., Muratore D., Marchesi D., Livio M., Schieppati A., Mecca G., de Gaetano G., Donati M. B. Prostacyclin and human foetal circulation. Prostaglandins. 1979 Sep;18(3):341–348. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(79)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terragno N. A., Terragno A., McGiff J. C. Role of prostaglandins in blood vessels. Semin Perinatol. 1980 Apr;4(2):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terragno N. A., Terragno A. Prostaglandin metabolism in the fetal and maternal vasculature. Fed Proc. 1979 Jan;38(1):75–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


