Abstract
1 Dose-dependent increments of plasma noradrenaline were observed during graded infusions of (±)isoprenaline (3.5-35 ng kg-1 min-1 i.v.) in seven normal subjects and in ten subjects with borderline hypertension. At the highest dose of isoprenaline, noradrenaline rose by 166 ± 16 pg/ml in normals and by 169 ± 34 pg/ml in hypertensives (mean ± s.e. mean).
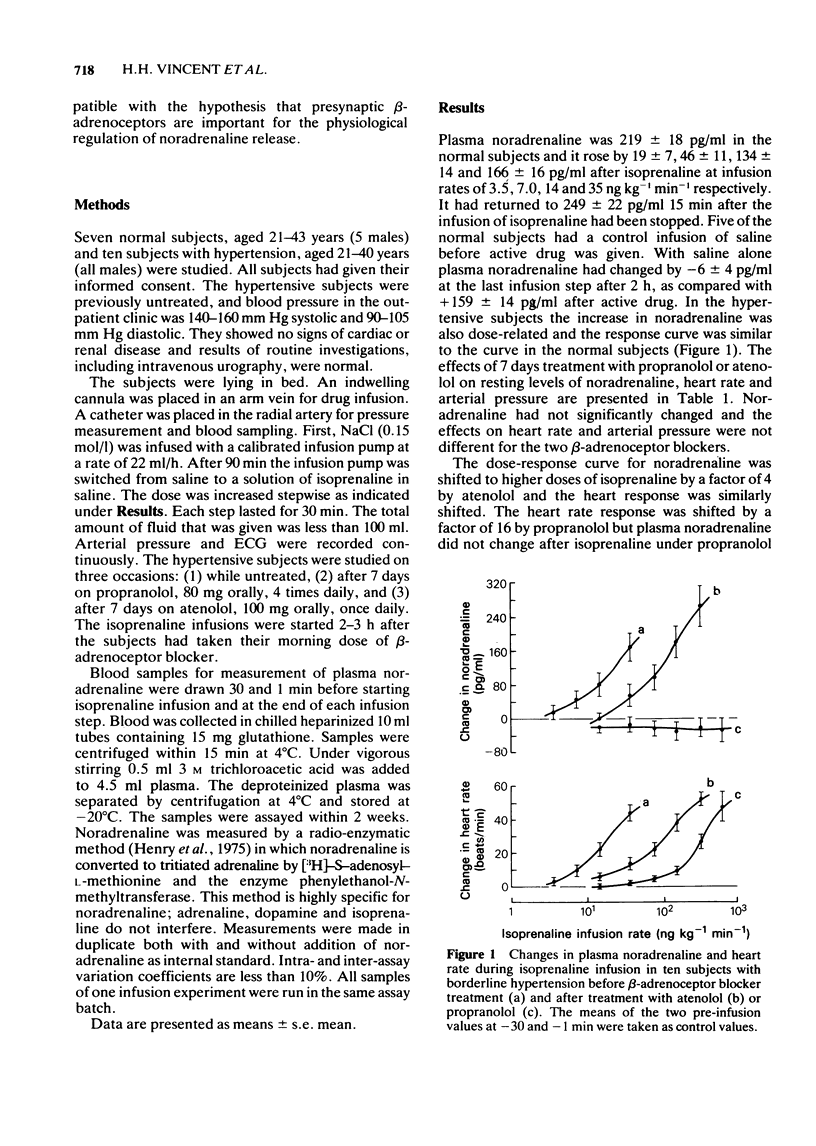
2 In the subjects with borderline hypertension isoprenaline infusions were repeated after 7 days of treatment with (±)propranolol (320 mg/day, divided into 4 doses) and subsequently after 7 days of treatment with (±)atenolol (100 mg/day) 2-3 h after the morning dose of β-adrenoceptor blocker. The dose-response curve for plasma noradrenaline was shifted to higher doses of isoprenaline by a factor of 4 by atenolol and the heart rate response was similarly shifted. The heart rate response was shifted by a factor of 16 by propranolol, but plasma noradrenaline did not change after isoprenaline under propranolol treatment, even when isoprenaline was given at doses high enough to induce increments of heart rate similar to those without β-adrenoceptor blocker treatment.
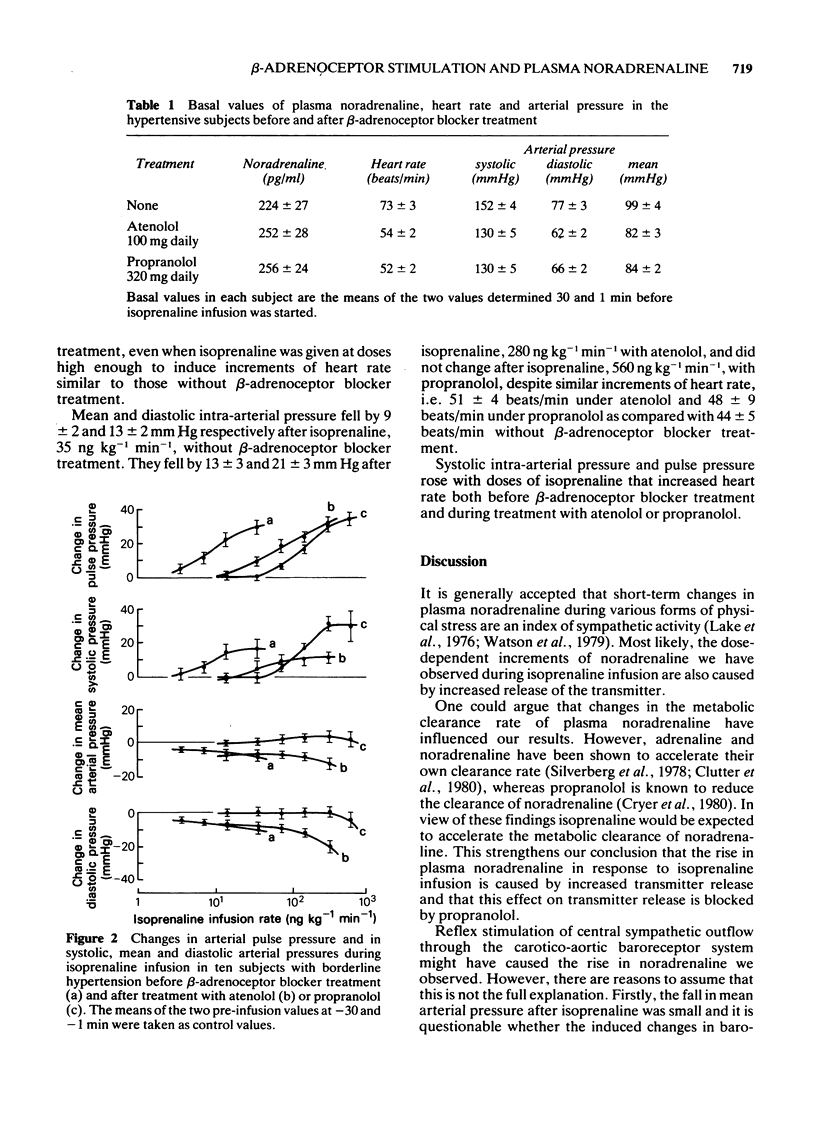
3 In the subjects with borderline hypertension mean and diastolic intra-arterial pressures fell at the highest dose of isoprenaline by 9 ± 2 and 13 ± 2 mm Hg respectively. These effects were antagonized by propranolol and not by atenolol.
4 The observed rise in plasma noradrenaline after isoprenaline might have been caused by baro-reflex-stimulation of central sympathetic outflow. The isoprenaline-induced decrease in mean arterial pressure, however, was small. Moreover pulse pressure rose and this tends to suppress rather than stimulate baroreflex-mediated sympathetic activity. Activation of presynaptic β-adrenoceptors, allegedly of the β2-subtype, is known to facilitate noradrenaline release upon nerve stimulation of isolated tissues. Our results lend support to the hypothesis that such a facilitatory mechanism is also operative in intact man.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clutter W. E., Bier D. M., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Epinephrine plasma metabolic clearance rates and physiologic thresholds for metabolic and hemodynamic actions in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):94–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI109840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Rizza R. A., Haymond M. W., Gerich J. E. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are cleared through beta-adrenergic, but not alpha-adrenergic, mechanisms in man. Metabolism. 1980 Nov;29(11 Suppl 1):1114–1118. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Champlain J., Cousineau D., Van Amerigen M. R., Marc-Aurèle J., Yamaguchi N. The role of the sympathetic system in experimental and human hypertension. Postgrad Med J. 1977;53 (Suppl 3):15–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco-Morselli R., Elghozi J. L., Joly E., Di Giuilio S., Meyer P. Increased plasma adrenaline concentrations in benign essential hypertension. Br Med J. 1977 Nov 12;2(6097):1251–1254. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6097.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry D. P., Starman B. J., Johnson D. G., Williams R. H. A sensitive radioenzymatic assay for norepinephrine in tissues and plasma. Life Sci. 1975 Feb 1;16(3):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. E., Daly M. de B. Comparison of the reflex vasomotor responses to separate and combined stimulation of the carotid sinus and aortic arch baroreceptors by pulsatile and non-pulsatile pressures in the dog. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(2):257–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake C. R., Ziegler M. G., Kopin I. J. Use of plasma norepinephrine for evaluation of sympathetic neuronal function in man. Life Sci. 1976 Jun 1;18(11):1315–1325. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90210-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski H., McCulloch M. W., Rand M. J., Story D. F. Adrenaline activation of prejunctional beta-adrenoceptors in guinea-pig atria. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):435–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski H., Tung L. H., Rand M. J. Adrenaline-induced hypertension in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):179–185. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198101000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancia G., Leonetti G., Picotti G. B., Ferrari A., Galva M. D., Gregorini L., Parati G., Pomidossi G., Ravazzani C., Sala C. Plasma catecholamines and blood pressure responses to the carotid baroreceptor reflex in essential hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Dec;57 (Suppl 5):165s–167s. doi: 10.1042/cs057165s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn K. H., Gierlichs H. W., Planz G., Planz R., Schols M., Stephany W. Studies on the effects of propanolol on plasma catecholamine levels in patients with essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;8(3):143–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1978.tb00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg A. B., Shah S. D., Haymond M. W., Cryer P. E. Norepinephrine: hormone and neurotransmitter in man. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):E252–E256. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.3.E252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stj-5aarne L., Brundin J. Dual adreoceptor-mediated control of noradrenaline secretion from human vasoconstrictor nerves: facilitation by BETA-receptors and inhibitor by alpha-receptors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 May;94(1):139–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Brundin J. Beta2-adrenoceptors facilitating noradrenaline secretion from human vasoconstrictor nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Mar;97(1):88–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. D., Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L., Littler W. A. Changes in plasma norepinephrine, blood pressure and heart rate during physical activity in hypertensive man. Hypertension. 1979 Jul-Aug;1(4):341–346. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.1.4.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi N., de Champlain J., Nadeau R. A. Regulation of norepinephrine release from cardiac sympathetic fibers in the dog by presynaptic alpha- and beta-receptors. Circ Res. 1977 Jul;41(1):108–117. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Champlain J., Farley L., Cousineau D., van Ameringen M. R. Circulating catecholamine levels in human and experimental hypertension. Circ Res. 1976 Feb;38(2):109–114. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.2.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


