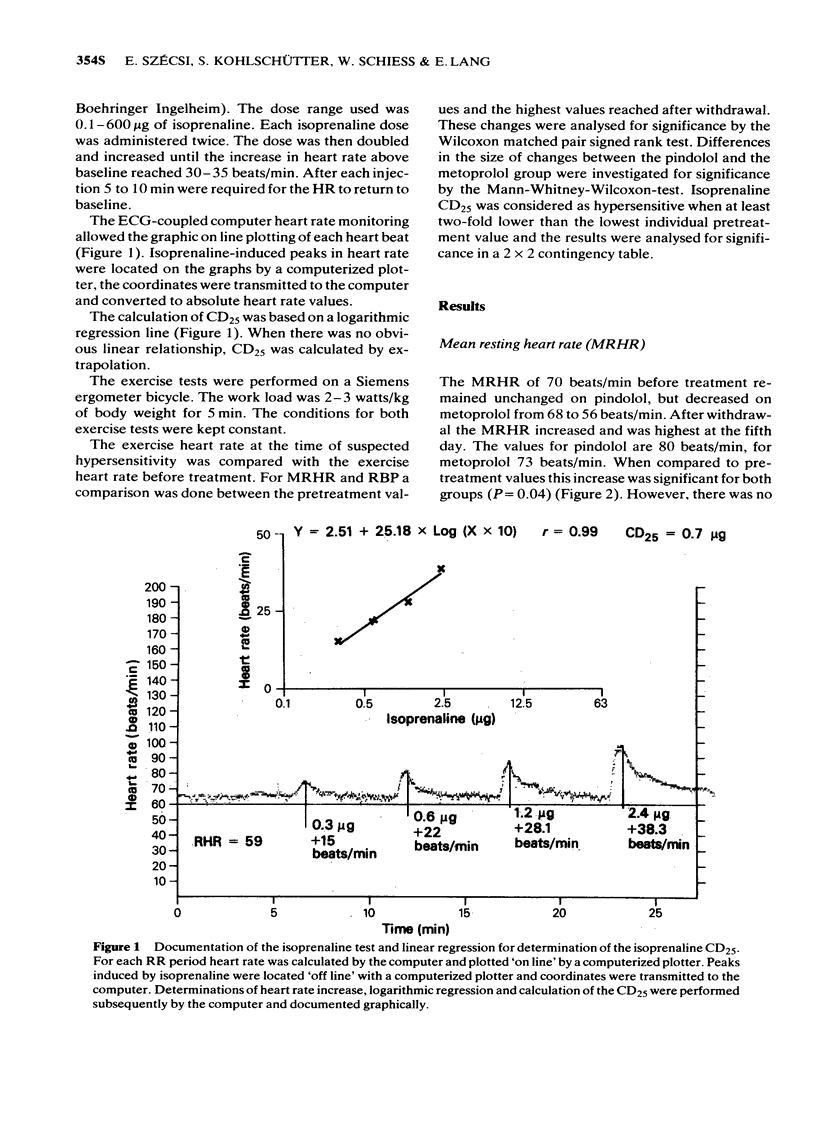
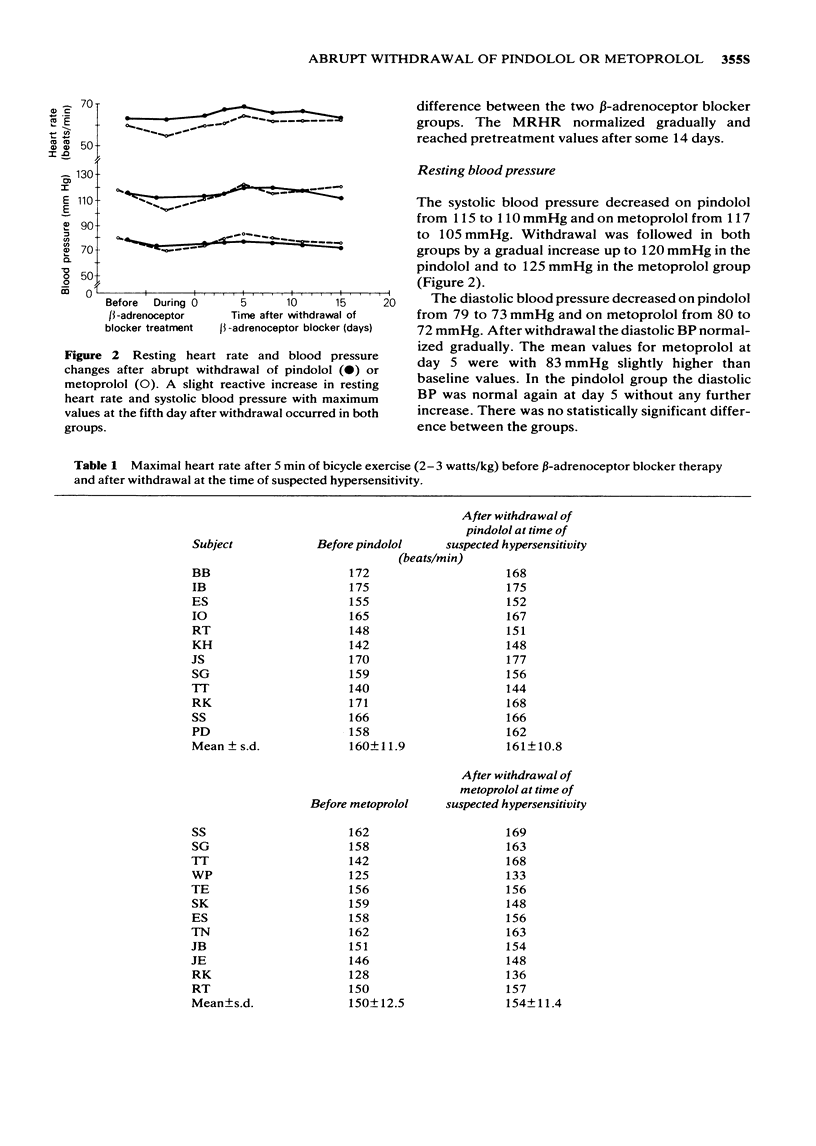
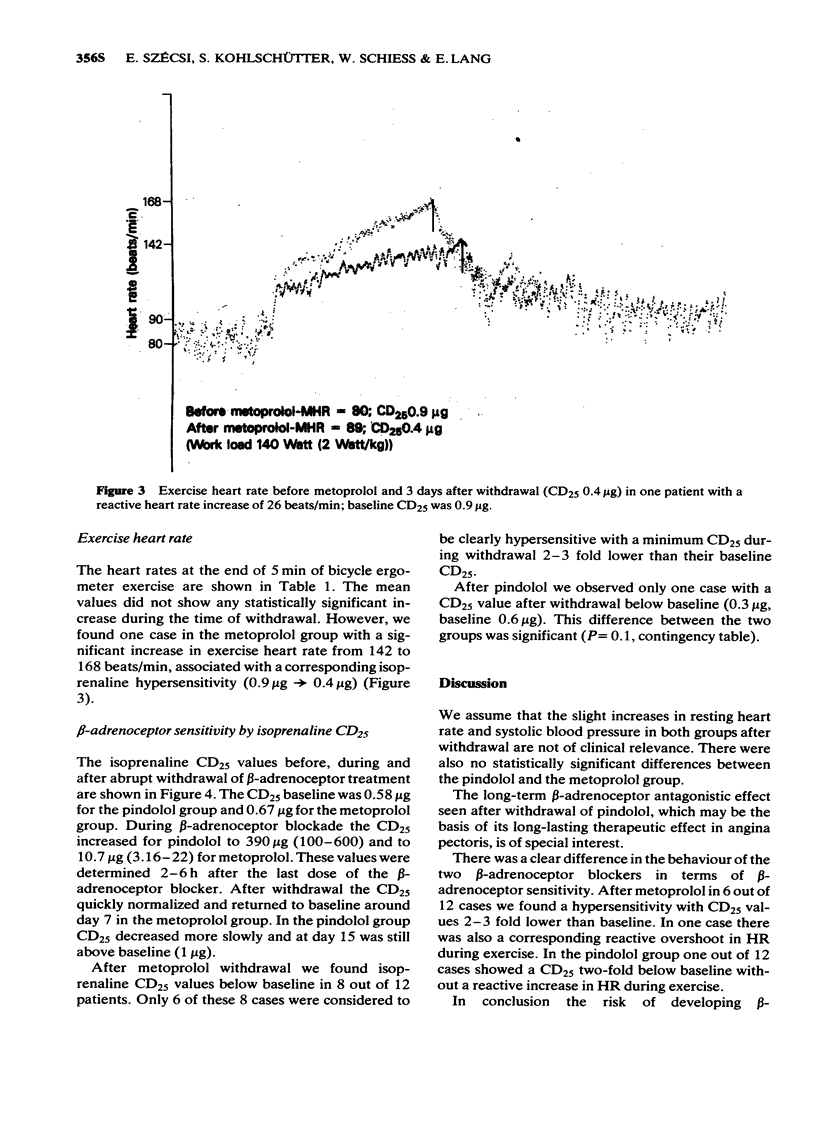
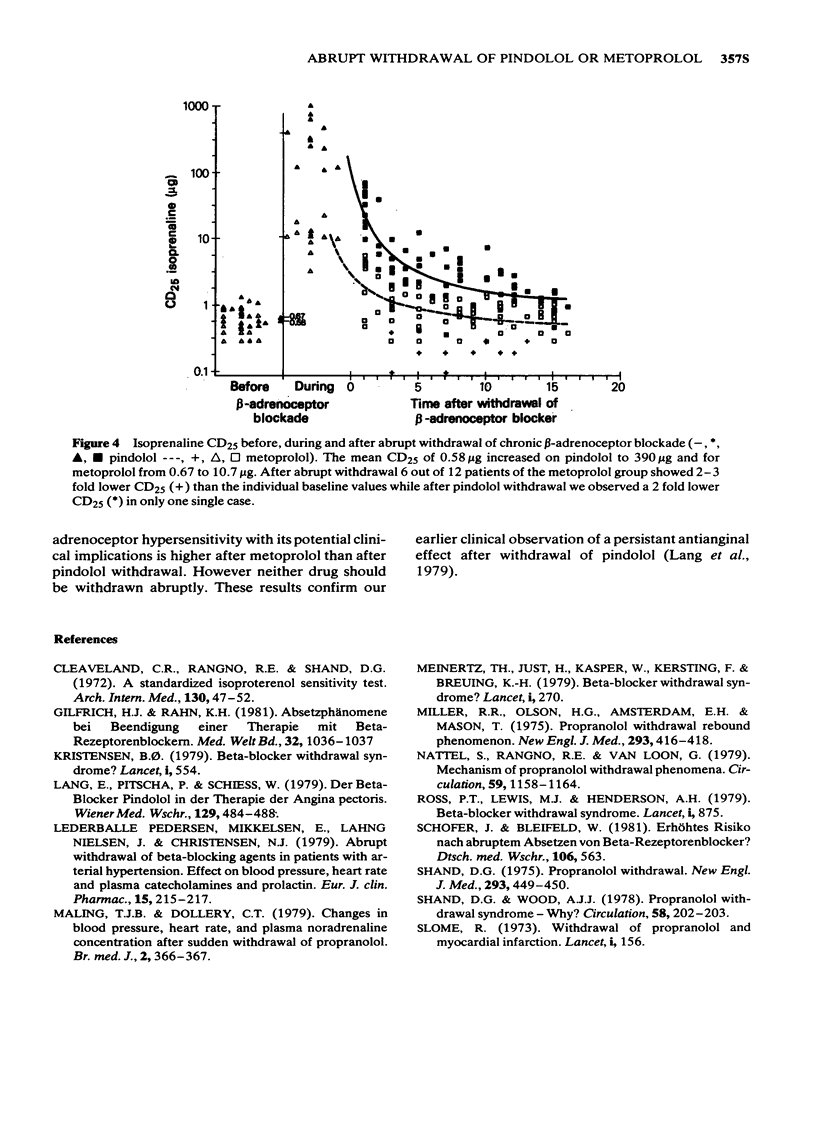
Abstract
1 In an open controlled study a group of 18 healthy volunteers received either pindolol 10 mg three times daily or metoprolol 100 mg three times daily for 4 weeks. Before treatment, and after abrupt withdrawal the resting heart rate, the blood pressure, the exercise heart rate and the isoprenaline CD25 (dose of isoprenaline to increase the heart rate of 25 beats/min) were determined. Heart rates were continuously monitored by an ECG-coupled computer. The CD25 values were calculated by an off line computer procedure from the on line recorded data. 2 After metoprolol we found 6 out of 12 patients with a CD25 below baseline, in one case with a corresponding increase in heart rate during exercise. After pindolol we observed a CD25 below baseline only in one case with no corresponding reaction in the exercise test. In both groups we observed a reactive increase in resting heart rate and systolic blood pressure around day 5 after withdrawal. 3 We conclude that abrupt withdrawal of metoprolol in contrast to pindolol is associated with a higher risk of developing beta-adrenergic receptor hypersensitivity.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleaveland C. R., Rangno R. E., Shand D. G. A standardized isoproterenol sensitivity test. The effects of sinus arrhythmia, atropine, and propranolol. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Jul;130(1):47–52. doi: 10.1001/archinte.130.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfrich H. J., Rahn K. H. Absetzphänomene bei Beendigung einer Therapie mit Beta-Rezeptorenblockern. Med Welt. 1981 Jun 26;32(26):1036–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen B. O. Beta-blocker withdrawal syndrome? Lancet. 1979 Mar 10;1(8115):554–554. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90976-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang E., Fitscha P., Schiess W. Der Beta-Blocker Pindolol in der Therapie der Angina pectors; Bericht über eine multizentrische kointrollierte Studie. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1979 Sep 30;129(17):484–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederballe Pedersen O., Mikkelsen E., Lanng Nielsen J., Christensen N. J. Abrupt withdrawal of beta-blocking agents in patients with arterial hypertension. Effect on blood pressure, heart rate and plasma catecholamines and prolactin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 17;15(3):215–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00563108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maling T. J., Dollery C. T. Changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and plasma noradrenaline concentration after sudden withdrawal of propranolol. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 11;2(6186):366–367. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6186.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinertz T., Just H., Kasper W., Kersting F., Breuing K. H. Beta-blocker withdrawal syndrome? Lancet. 1979 Feb 3;1(8110):270–270. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90793-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. R., Olson H. G., Amsterdam E. A., Mason D. T. Propranolol-withdrawal rebound phenomenon. Exacerbation of coronary events after abrupt cessation of antianginal therapy. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 28;293(9):416–418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508282930902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nattel S., Rangno R. E., Van Loon G. Mechanism of propranolol withdrawal phenomena. Circulation. 1979 Jun;59(6):1158–1164. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.59.6.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. J., Lewis M. J., Henderson A. H. Beta-blocker withdrawal syndrome. Lancet. 1979 Apr 21;1(8121):875–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofer J., Bleifeld W. Erhöhtes Risiko nach abruptem Absetzen von Beta-Rezeptorenblockern? Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1981 May 1;106(18):563–565. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1070355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G. Editorial: Propranolol withdrawal. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 28;293(9):449–450. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508282930910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G., Wood A. J. Propranolol withdrawal syndrome - why? Circulation. 1978 Aug;58(2):202–203. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.58.2.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slome R. Withdrawal of propranolol and myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1973 Jan 20;1(7795):156–156. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90235-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


