Abstract
1 The metabolism of a standard oral dose of levodopa was studied in forty-two patients with Parkinsonism. Plasma levodopa and 3-o-methyldopa concentrations were estimated at intervals for 8 h after ingestion and the concentration of homovanillic acid (HVA) in the lumbar cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was measured at 8 hours. Clinical responses 3 months after the test were compared with these findings.
2 Although therapeutic benefit correlated significantly with calculated estimates of both plasma levodopa concentration and CSF HVA at optimal levodopa dose, individual values were widely scattered. There was no significant correlation between toxic effects and plasma levodopa or CSF HVA; and 3-o-methyldopa concentrations similarly did not show a significant correlation with either toxic or therapeutic effects.
3 Blood and CSF levels of levodopa or the metabolites measured in this study were not significantly altered by concurrent treatment with either anticholinergic drugs or amantadine nor by previous treatment with levodopa.
Full text
PDF
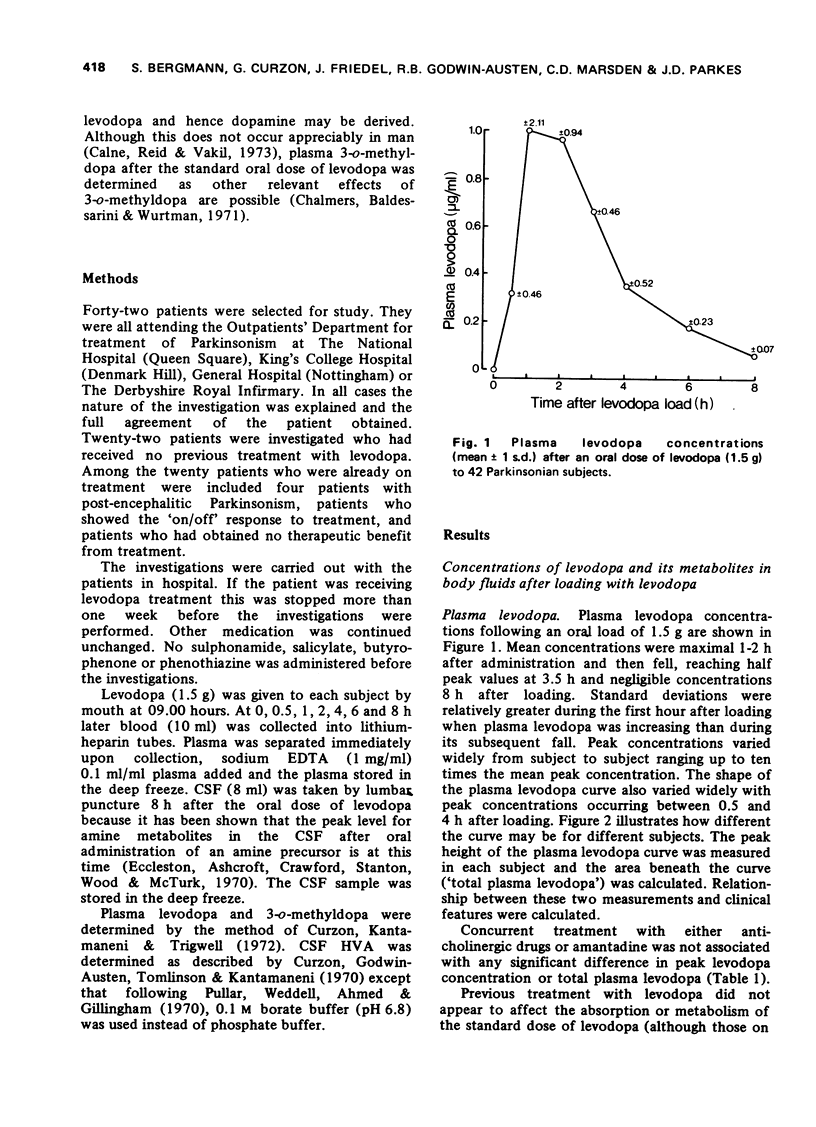
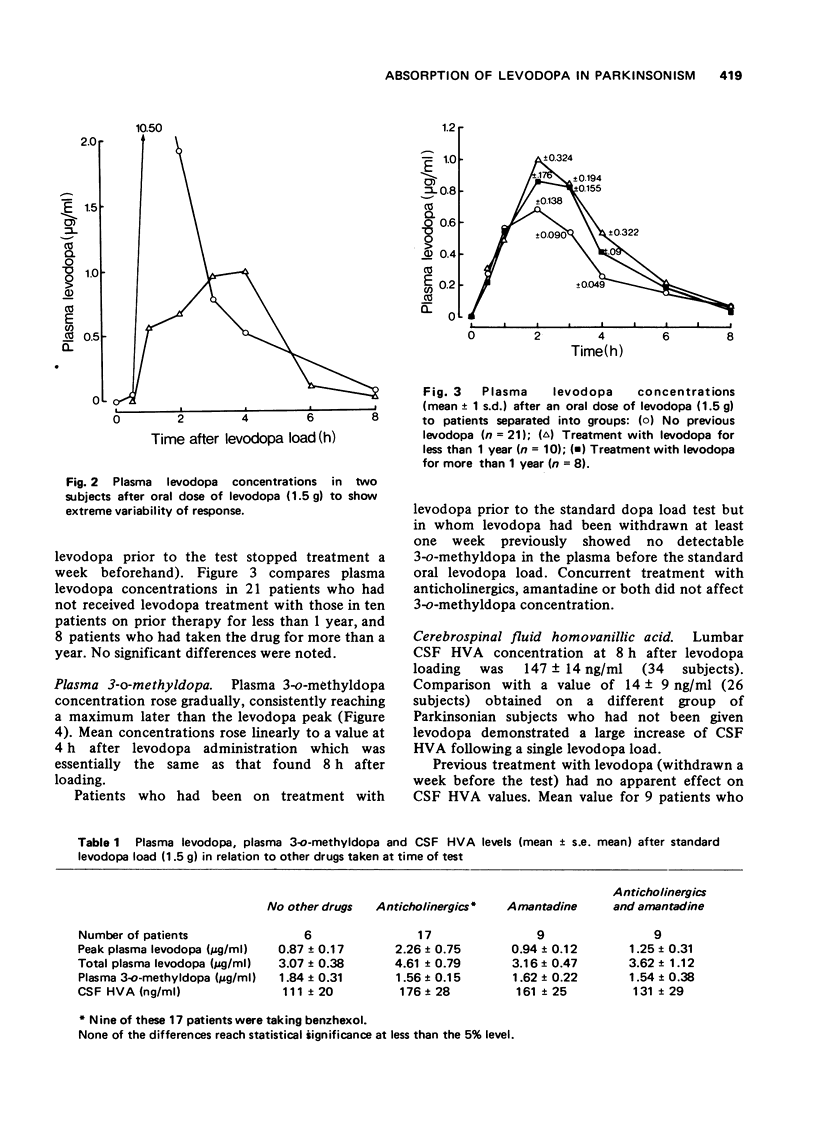
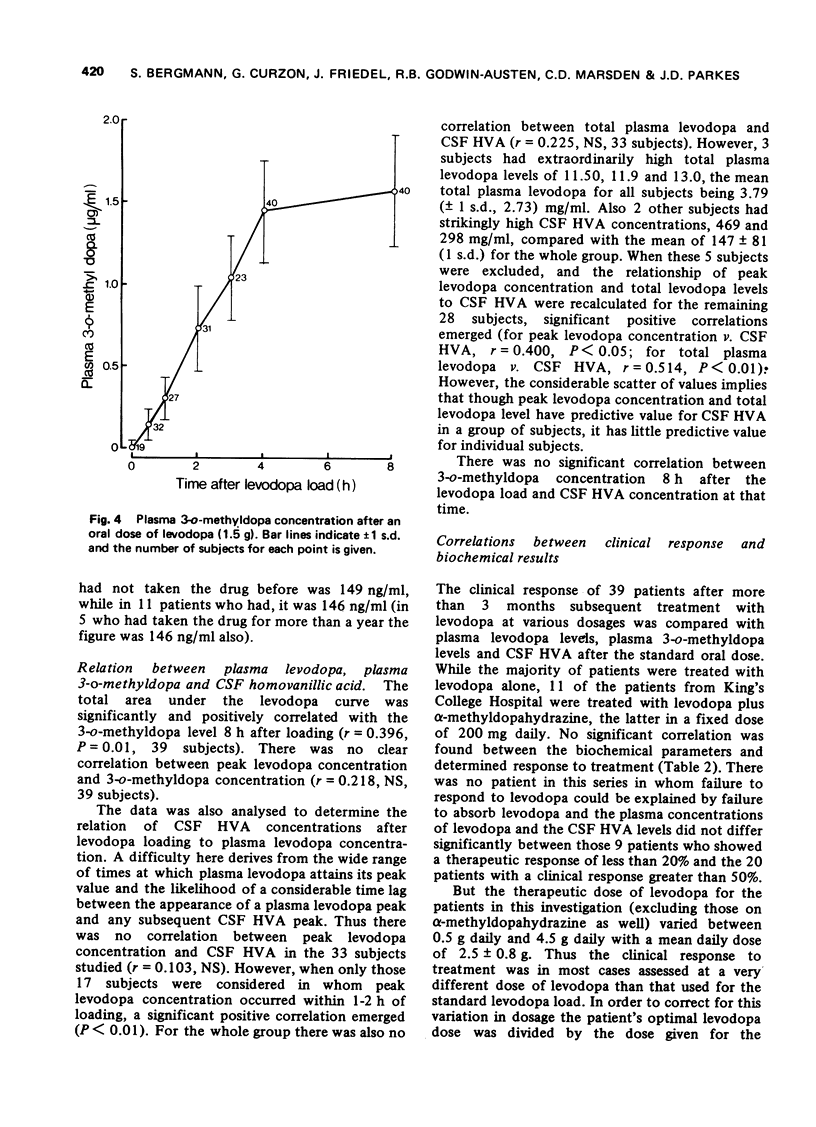
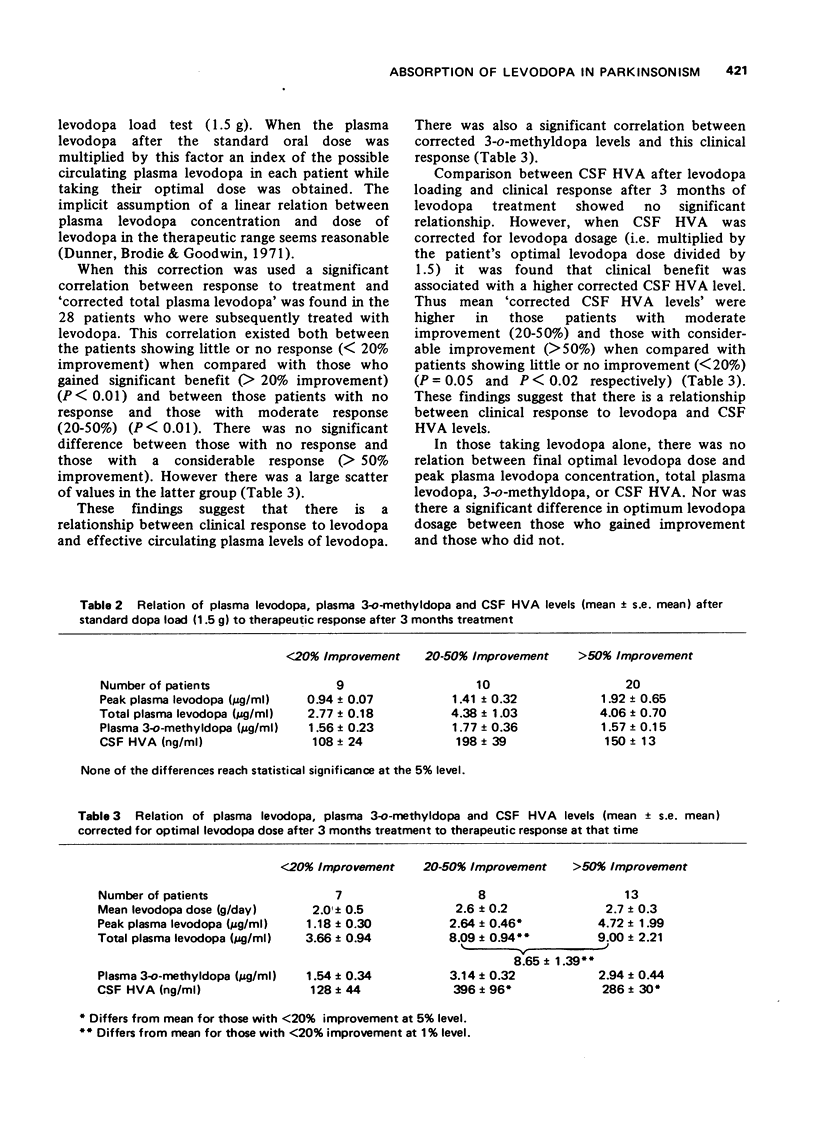


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARBEAU A. The pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease: a new hypothesis. Can Med Assoc J. 1962 Oct 13;87:802–807. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKMAYER W., HORNYKIEWICZ O. [The L-3,4-dioxyphenylalanine (DOPA)-effect in Parkinson-akinesia]. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1961 Nov 10;73:787–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbeau A. Long-term side-effects of levodopa. Lancet. 1971 Feb 20;1(7695):395–395. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne D. B., Reid J. L., Vakil S. D. Parkinsonism treated with 3-O-methyldopa. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 May-Jun;14(3):386–389. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973143386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers J. P., Baldessarini R. J., Wurtman R. J. Effects of L-dopa on norepinephrine metabolism in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):662–666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claveria L. E., Calne D. B., Allen J. G. "On-off" phenomena related to high plasma levodopa. Br Med J. 1973 Jun 16;2(5867):641–643. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5867.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Godwin-Austen R. B., Tomlinson E. B., Kantamaneni B. D. The cerebrospinal fluid homovanillic acid concentration in patients with Parkinsonism treated with L-dopa. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Feb;33(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Kantamaneni B. D., Trigwell J. A method for the determination of dopa and 3-O-methyldopa in the plasma of Parkinsonian patients. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Mar;37:335–341. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunner D. L., Brodie H. K., Goodwin F. K. Plasma DOPA response to levodopa administration in man: effects of a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1971 Mar-Apr;12(2):212–217. doi: 10.1002/cpt1971122part1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston D., Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B. Effect of tryptophan administration on 5HIAA in cerebrospinal fluid in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Apr;33(2):269–272. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornykiewicz O. Dopamine in the basal ganglia. Its role and therapeutic implications (including the clinical use of L-DOPA). Br Med Bull. 1973 May;29(2):172–178. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuruma I., Bartholini G., Pletscher A. L-dopa-induced accumulation of 3-O-metyldopa in brain and heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970 May;10(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90272-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullar I. A., Weddell J. M., Ahmed R., Gillingham F. J. Phenolic acid concentrations in the lumbar cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinsonian patients treated with L-dopa. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Dec;33(6):851–857. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.6.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Calimlim L., Dujovne C. A., Morgan J. P., Lasagna L., Bianchine J. R. L-dopa treatment failure: explanation and correction. Br Med J. 1970 Oct 10;4(5727):93–94. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5727.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


