Abstract
1 The effect of caffeine alkaloid base (300 mg) on whole night sleep was investigated by electrophysiological techniques in six late middle age subjects (mean age 56 years), comparison being made with decaffeinated coffee and with no drink prior to sleep, using each condition five times in a balanced order on non-consecutive nights.
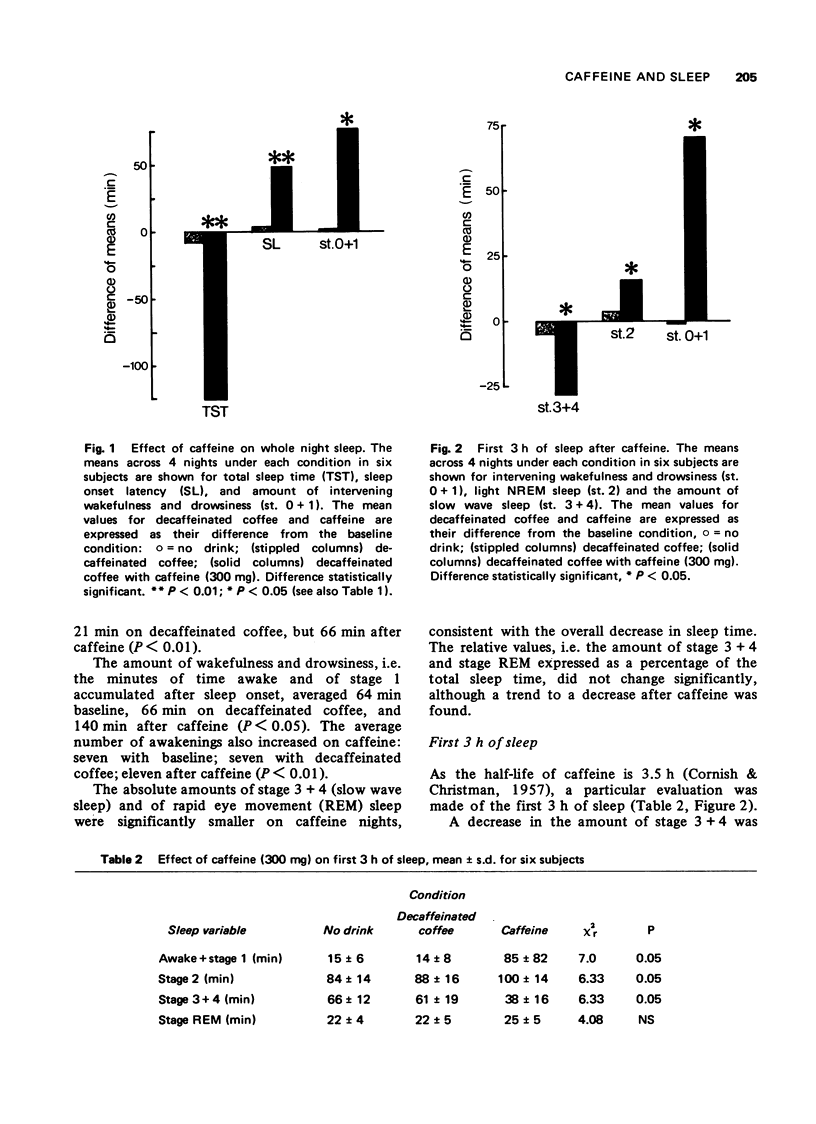
2 After caffeine the mean total sleep time decreased on average by 2 h, the mean sleep latency increased to 66 minutes. The number of awakenings increased and the mean total intervening wakefulness was more than doubled after caffeine.
3 In the first 3 h of sleep a decreased amount of stage 3 + 4 was observed, accompanied by an increased amount of stage 2 and of intervening wakefulness, without a significant change in the amount of rapid eye movement sleep.
4 The change in sleep pattern observed suggests an increased capability for arousal and decreased ability to develop or sustain deeper stages of non-rapid eye movement sleep after caffeine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkowitz B. A., Tarver J. H., Spector S. Release of norepinephrine in the central nervous system by theophylline and caffeine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;10(1):64–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers M. B., Jr, Gerbode F. A. Relationship of monoamine metabolites in human cerebrospinal fluid to age. Nature. 1968 Sep 21;219(5160):1256–1257. doi: 10.1038/2191256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORNISH H. H., CHRISTMAN A. A. A study of the metabolism of theobromine, theophylline, and caffeine in man. J Biol Chem. 1957 Sep;228(1):315–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRESHAM S. C., WEBB W. B., WILLIAMS R. L. Alcohol and caffeine: effect on inferred visual dreaming. Science. 1963 Jun 14;140(3572):1226–1227. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3572.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Kaizer S., Warren R. Psychotropic effects of caffeine in man. II. Alertness, psychomotor coordination, and mood. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Oct;150(1):146–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Kaizer S., Whitby O. Psychotropic effects of caffeine in man. IV. Quantitative and qualitative differences associated with habituation to coffee. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Jul-Aug;10(4):489–497. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969104489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E. On the pharmacology of dreaming sleep. (The D state). J Nerv Ment Dis. 1968 Feb;146(2):165–173. doi: 10.1097/00005053-196802000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald I., Lewis S. A., Dunleavy D. L., Brezinova V., Briggs M. Drugs of dependence though not of abuse: fenfluramine and imipramine. Br Med J. 1971 Jul 10;3(5766):70–73. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5766.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. S., Nies A., Davis J. N., Bunney W. E., Davis J. M., Colburn R. W., Bourne H. R., Shaw D. M., Coppen A. J. Ageing, monoamines, and monoamine-oxidase levels. Lancet. 1972 Feb 5;1(7745):290–291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stradomsky N. Untersuchungen über Schlabewegungen nach coffeinhaltigem und coffeinfreiem Bohnenkaffee. Med Klin. 1970 Jul 17;65(29):1372–1376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck B. Some effects of caffeine and aminophylline on the turnover of catecholamines in the brain. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Nov;23(11):824–830. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb10198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


