Abstract
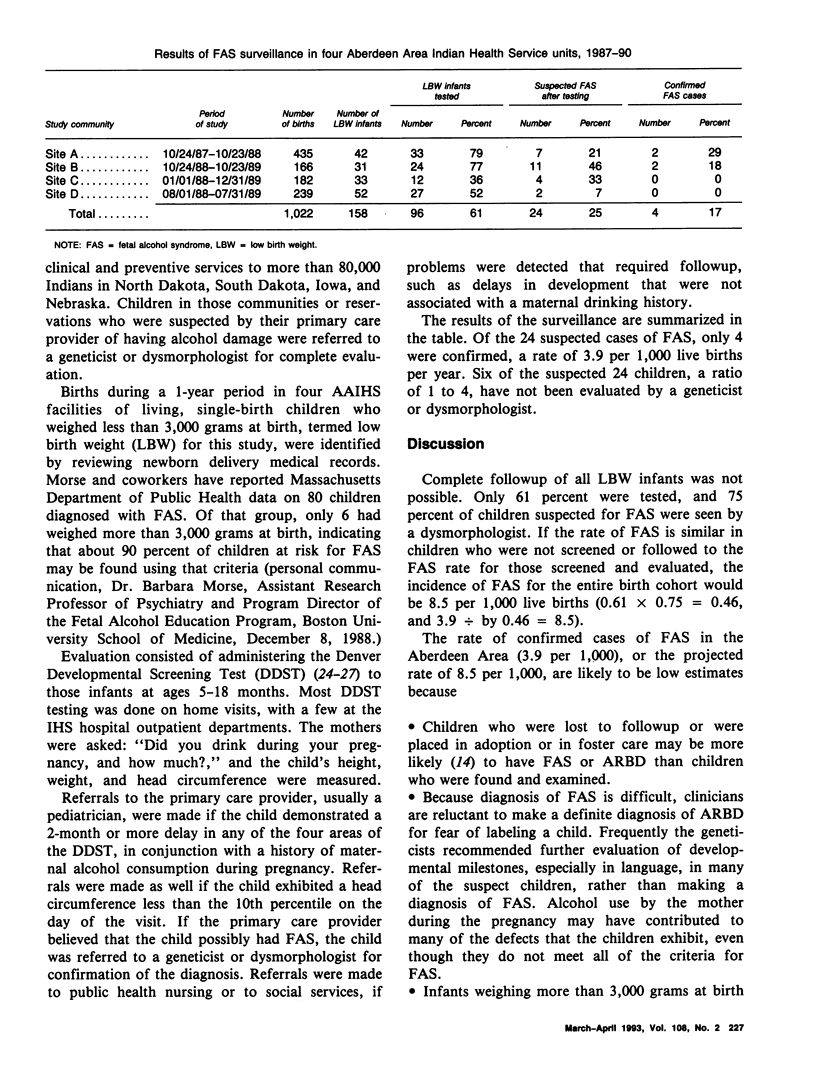
A pilot fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) surveillance was carried out in four American Indian communities in the Northern Plains by the Aberdeen Area Indian Health Service to determine the incidence of FAS and to evaluate the feasibility of establishing continuing surveillance for FAS. Baseline data on the incidence of FAS would be used by the Indian Health Service to develop and evaluate preventive interventions, including treatment programs for pregnant women who drink alcohol. Four of the 1,022 children included in the project were found to have FAS, a rate of 3.9 per 1,000 live births. The rate is believed to underestimate the true rate of FAS because some low birth weight children were not screened, parents or guardians were reluctant to bring children suspected of FAS for evaluation, clinicians were hesitant to diagnose possible alcohol-damaged children for fear of labeling the child, and some children with FAS died before the diagnosis of FAS could be confirmed. If the rate of FAS is similar for the 39 percent of the infants not screened and for the 25 percent of suspected infants who were not evaluated, a rate of 8.5 cases of FAS per 1,000 live births may be postulated. The authors recommend routine screening of prenatal patients for substance abuse and establishing a tracking system for low birth weight infants suspected to have FAS or other alcohol-related developmental disorders, in an effort to establish more accurate FAS rates.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aase J. M. The fetal alcohol syndrome in American Indians: a high risk group. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1981 Summer;3(2):153–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson M., Kyllerman M., Sabel K. G., Sandin B., Olegård R. Children of alcoholic mothers. Developmental, perceptual and behavioural characteristics as compared to matched controls. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 Jan;74(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonthius D. J., Goodlett C. R., West J. R. Blood alcohol concentration and severity of microencephaly in neonatal rats depend on the pattern of alcohol administration. Alcohol. 1988 May-Jun;5(3):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(88)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo R. A., Devoe L. D., Ruedrich D. A., Gardner P. The effects of acute alcohol intoxication on biophysical activities: a case report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Mar;160(3):692–693. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(89)80061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chávez G. F., Cordero J. F., Becerra J. E. Leading major congenital malformations among minority groups in the United States, 1981-1986. MMWR CDC Surveill Summ. 1988 Jul;37(3):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles C. D., Smith I. E., Falek A. Prenatal alcohol exposure and infant behavior: immediate effects and implications for later development. Adv Alcohol Subst Abuse. 1987 Summer;6(4):87–104. doi: 10.1300/J251v06n04_07. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. An evaluation of the use of the Denver Developmental Screening Test. Nurs Res. 1981 Sep-Oct;30(5):290–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenburg W. K., Dodds J. B. The Denver developmental screening test. J Pediatr. 1967 Aug;71(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frezza M., di Padova C., Pozzato G., Terpin M., Baraona E., Lieber C. S. High blood alcohol levels in women. The role of decreased gastric alcohol dehydrogenase activity and first-pass metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 11;322(2):95–99. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001113220205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedler G. Effects of limited paternal exposure to xenobiotic agents on the development of progeny. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1985 Nov-Dec;7(6):739–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. M., Jr, Hanson J. W., Darby B. L., Barr H. M., Streissguth A. P. Independent dysmorphology evaluations at birth and 4 years of age for children exposed to varying amounts of alcohol in utero. Pediatrics. 1988 Jun;81(6):772–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. T., Hussain K. Craniofacial and oral manifestations of fetal alcohol syndrome. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990 Apr;85(4):505–512. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199004000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masis K. B., May P. A. A comprehensive local program for the prevention of fetal alcohol syndrome. Public Health Rep. 1991 Sep-Oct;106(5):484–489. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P. A., Hymbaugh K. J. A pilot project on fetal alcohol syndrome among American Indians. Alcohol Health Res World. 1982;7(2):3–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P. A., Hymbaugh K. J., Aase J. M., Samet J. M. Epidemiology of fetal alcohol syndrome among American Indians of the Southwest. Soc Biol. 1983 Winter;30(4):374–387. doi: 10.1080/19485565.1983.9988551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciarillo W. G., Brown M. M., Robinson N. M., Bennett F. C., Sells C. J. Effectiveness of the Denver Developmental Screening Test with biologically vulnerable infants. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1986 Apr;7(2):77–83. doi: 10.1097/00004703-198604000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W., Jones K. L., Hanson J. W. Perspectives on the cause and frequency of the fetal alcohol syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;273:138–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb52874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol R. J., Clarren S. K. Guidelines for use of terminology describing the impact of prenatal alcohol on the offspring. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1989 Aug;13(4):597–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1989.tb00384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streissguth A. P., Landesman-Dwyer S., Martin J. C., Smith D. W. Teratogenic effects of alcohol in humans and laboratory animals. Science. 1980 Jul 18;209(4454):353–361. doi: 10.1126/science.6992275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streissguth A. P., Sampson P. D., Barr H. M. Neurobehavioral dose-response effects of prenatal alcohol exposure in humans from infancy to adulthood. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;562:145–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb21013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



