Abstract
High rates of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection among jail and prison inmates suggest that HIV prevention efforts should focus on incarcerated populations. Overcrowding, the high prevalence of injection drug use, and other high-risk behaviors among inmates create a prime opportunity for public health officials to affect the course of the HIV epidemic if they can remedy these problems. Yet, along with the opportunity, there are certain obstacles that correctional institutions present to public health efforts. The various jurisdictions have differing approaches to HIV prevention and control. Whether testing should be mandatory or voluntary, whether housing should be integrated or segregated by HIV serostatus, and whether condoms, bleach, or clean needles should be made available to the prisoners, are questions hotly debated by public health and correctional officials. Even accurate assessment of risk-taking within the institutions leads to controversy, as asking questions could imply acceptance of the very behaviors correctional officials are trying to prevent. Education and risk-reduction counseling are the least controversial and most widely employed modes of prevention, but the effectiveness of current prevention efforts in reducing HIV transmission in this high-risk population is largely undetermined.
Full text
PDF
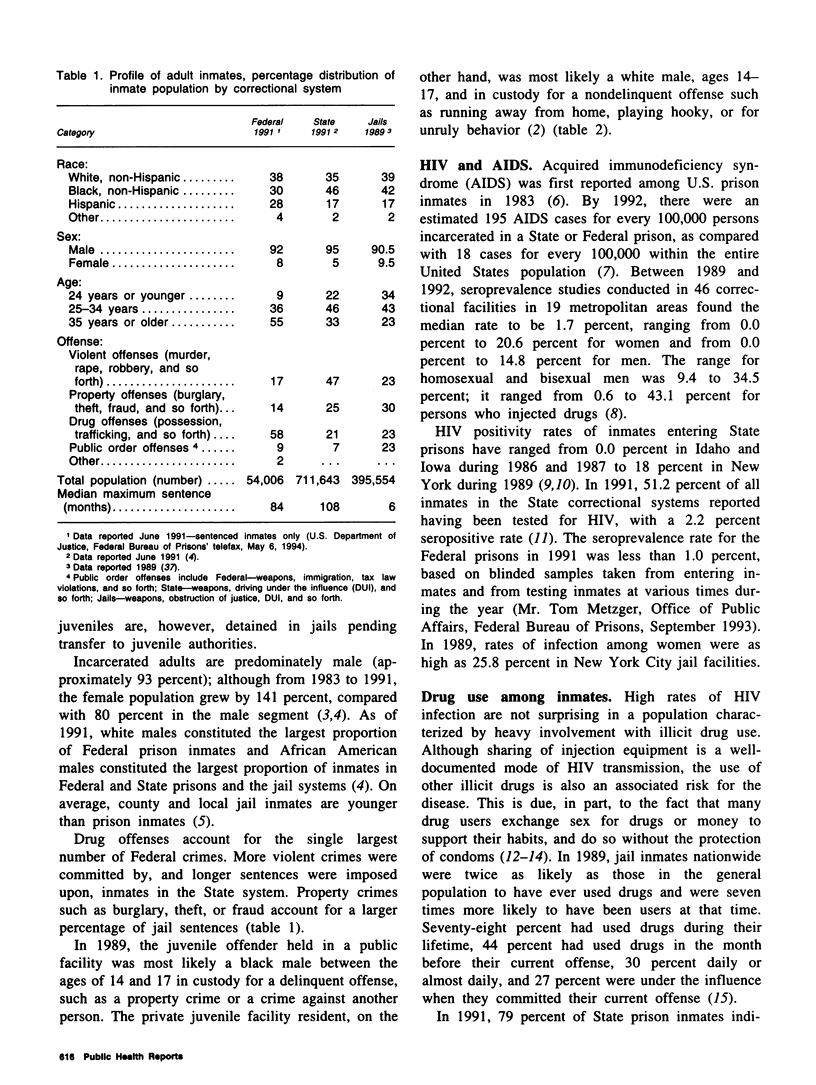
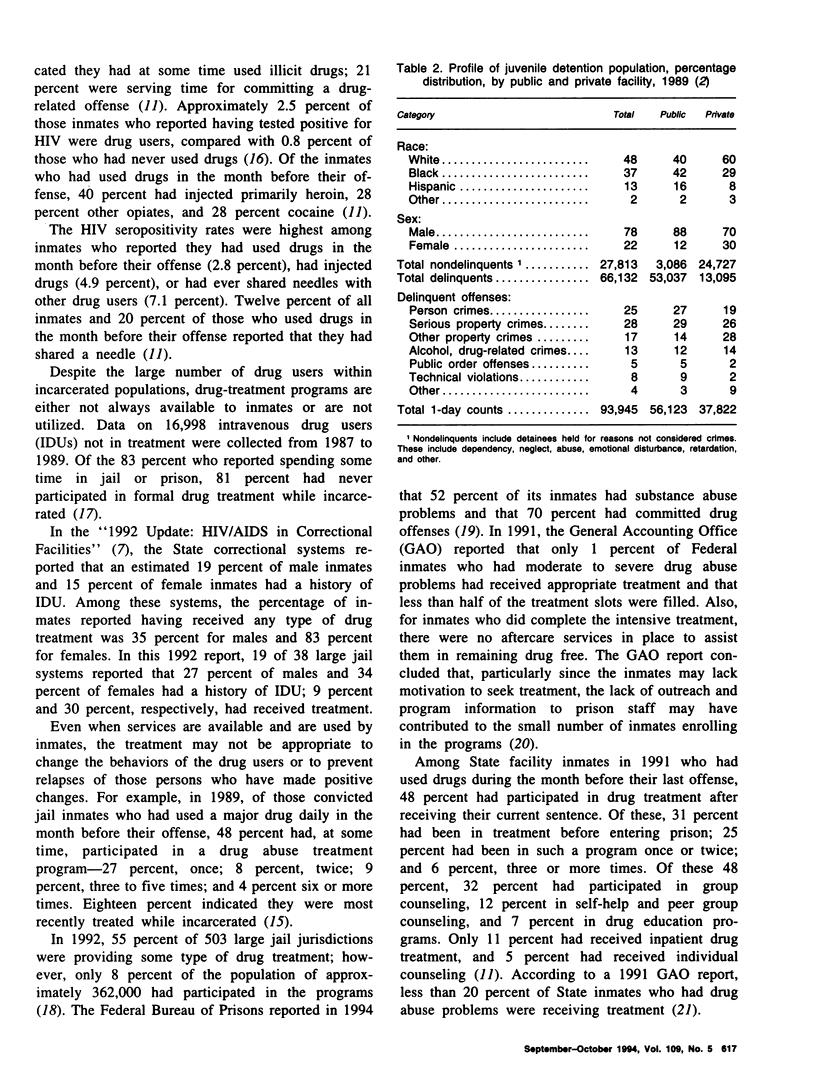








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell T. A., Farrow J. A., Stamm W. E., Critchlow C. W., Holmes K. K. Sexually transmitted diseases in females in a juvenile detention center. Sex Transm Dis. 1985 Jul-Sep;12(3):140–144. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198507000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer T. F., Derrickson J. AIDS in prison: a review of epidemiology and preventive policy. AIDS. 1992 Jul;6(7):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer T. F. HIV in prisons: the pragmatic approach. AIDS. 1991 Jul;5(7):897–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer T. F., Vlahov D., Taylor E., Hall D., Munoz A., Polk B. F. Transmission of HIV-1 within a statewide prison system. AIDS. 1988 Oct;2(5):363–367. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198810000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Hartman C. R., McCormack A. Abused to abuser: antecedents of socially deviant behaviors. Am J Psychiatry. 1987 Nov;144(11):1431–1436. doi: 10.1176/ajp.144.11.1431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Hazelwood R. R., Rokous F. E., Hartman C. R., Burgess A. G. Serial rapists and their victims: reenactment and repetition. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;528:277–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiClemente R. J., Boyer C. B., Morales E. S. Minorities and AIDS: knowledge, attitudes, and misconceptions among black and Latino adolescents. Am J Public Health. 1988 Jan;78(1):55–57. doi: 10.2105/ajph.78.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiClemente R. J., Lanier M. M., Horan P. F., Lodico M. Comparison of AIDS knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors among incarcerated adolescents and a public school sample in San Francisco. Am J Public Health. 1991 May;81(5):628–630. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.5.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubler N. N., Sidel V. W. On research on HIV infection and AIDS in correctional institutions. Milbank Q. 1989;67(2):171–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell M., Strang J. Drugs, HIV, and prisons. BMJ. 1991 Jun 22;302(6791):1477–1478. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6791.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. B., Greifinger R. B. Correctional health care: a public health opportunity. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Jan 15;118(2):139–145. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-118-2-199301150-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass G. E., Hausler W. J., Loeffelholz P. L., Yesalis C. E., 3rd Seroprevalence of HIV antibody among individuals entering the Iowa Prison System. Am J Public Health. 1988 Apr;78(4):447–449. doi: 10.2105/ajph.78.4.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanrahan J. P., Wormser G. P., Reilly A. A., Maguire B. H., Gavis G., Morse D. L. Prolonged incubation period of AIDS in intravenous drug abusers: epidemiological evidence in prison inmates. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):263–266. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellinger F. J. Forecasting the medical care costs of the HIV epidemic: 1991-1994. Inquiry. 1991 Fall;28(3):213–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie N. J., Vergeront J. M., Frisby H. R., Pfister J. R., Golubjatnikov R., Davis J. P. HIV seroprevalence and the acceptance of voluntary HIV testing among newly incarcerated male prison inmates in Wisconsin. Am J Public Health. 1990 Sep;80(9):1129–1131. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.9.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampinen T. M., Brewer A. M., Raba J. M. HIV in prison: a counseling opportunity. JAMA. 1991 Jul 17;266(3):361–361. doi: 10.1001/jama.266.3.361b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfs R. T., Goldberg M., Sharrar R. G. Risk factors for syphilis: cocaine use and prostitution. Am J Public Health. 1990 Jul;80(7):853–857. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.7.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdiserri E. V., Hartl A. J., Chambliss C. A. Practices reported by incarcerated drug abusers to reduce risk of AIDS. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1988 Sep;39(9):966–972. doi: 10.1176/ps.39.9.966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viadro C. I., Earp J. A. AIDS education and incarcerated women: a neglected opportunity. Women Health. 1991;17(2):105–117. doi: 10.1300/J013v17n02_06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisfuse I. B., Greenberg B. L., Back S. D., Makki H. A., Thomas P., Rooney W. C., Rautenberg E. L. HIV-1 infection among New York City inmates. AIDS. 1991 Sep;5(9):1133–1138. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199109000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


