Abstract
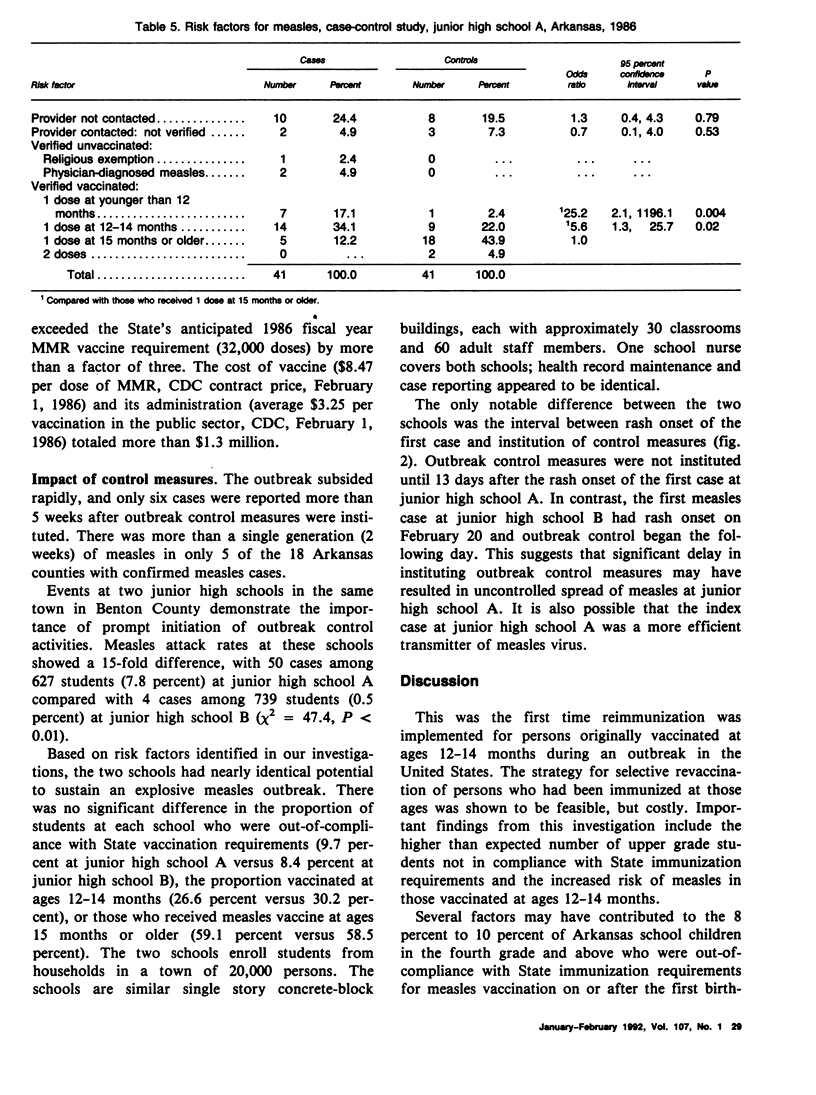
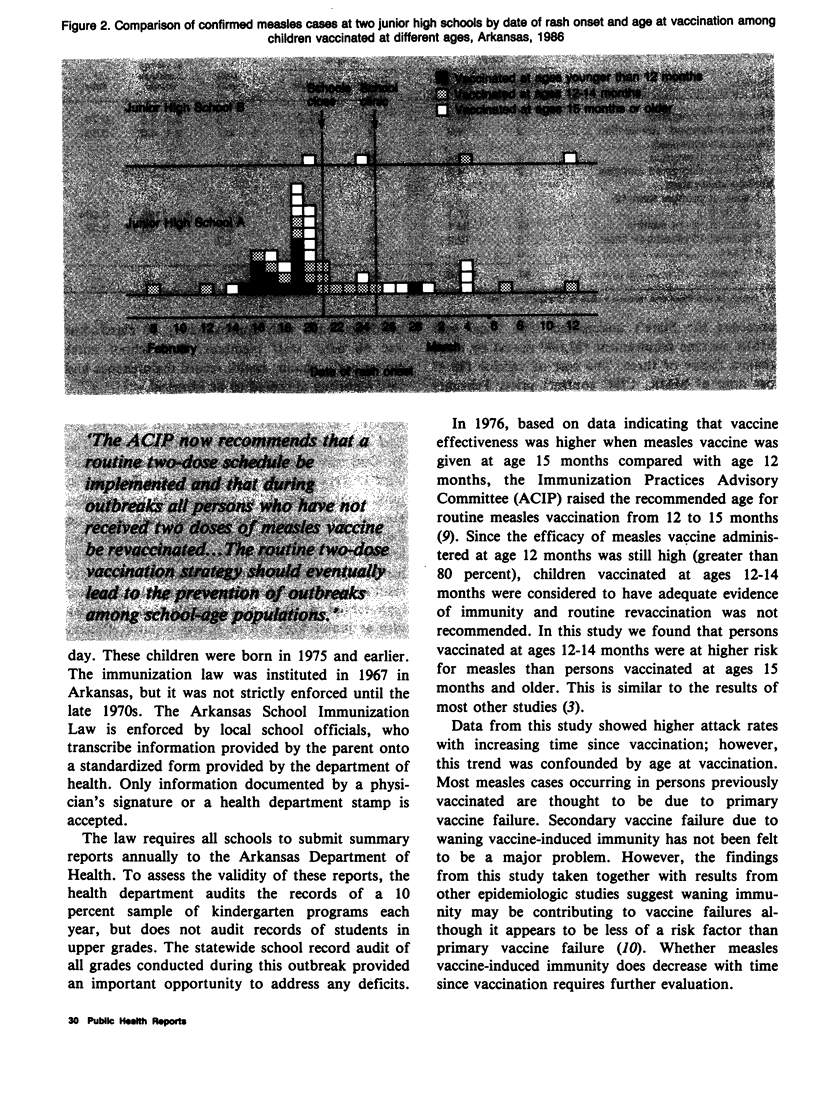
Between February 8 and April 4, 1986, an outbreak of measles occurred in the State of Arkansas. A total of 489 suspected measles cases were reported from 53 counties; 86 schools statewide reported suspected measles cases. There were 284 cases confirmed in 18 counties; 23.6 percent among students in one university and 41.2 percent among students in kindergarten through 12th grade in 32 schools. An epidemiologic investigation was carried out to evaluate risk factors for vaccine failure and to assess the effectiveness of a selective revaccination strategy in the outbreak setting. A cohort study conducted at a junior high school showed that, compared with students vaccinated against measles at ages 15 months or older, those vaccinated at ages 12-14 months had a three-fold increased risk of measles (relative risk 3.2, 95 percent confidence interval 1.5, 6.9). For schools reporting measles, the Arkansas Department of Health and the Department of Education jointly required reimmunization of students vaccinated at ages younger than 15 months and the exclusion of students not vaccinated at ages 15 months or older until they were vaccinated or until 2 weeks after the last rash onset. To implement these recommendations, more than 100,000 doses of combined measles-mumps-rubella vaccine were distributed at a cost greater than $1 million.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Markowitz L. E., Preblud S. R., Fine P. E., Orenstein W. A. Duration of live measles vaccine-induced immunity. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 Feb;9(2):101–110. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199002000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz L. E., Preblud S. R., Orenstein W. A., Rovira E. Z., Adams N. C., Hawkins C. E., Hinman A. R. Patterns of transmission in measles outbreaks in the United States, 1985-1986. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 12;320(2):75–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901123200202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein W. A., Bernier R. H., Dondero T. J., Hinman A. R., Marks J. S., Bart K. J., Sirotkin B. Field evaluation of vaccine efficacy. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(6):1055–1068. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein W. A., Bernier R. H., Hinman A. R. Assessing vaccine efficacy in the field. Further observations. Epidemiol Rev. 1988;10:212–241. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein W. A., Markowitz L., Preblud S. R., Hinman A. R., Tomasi A., Bart K. J. Appropriate age for measles vaccination in the United States. Dev Biol Stand. 1986;65:13–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



