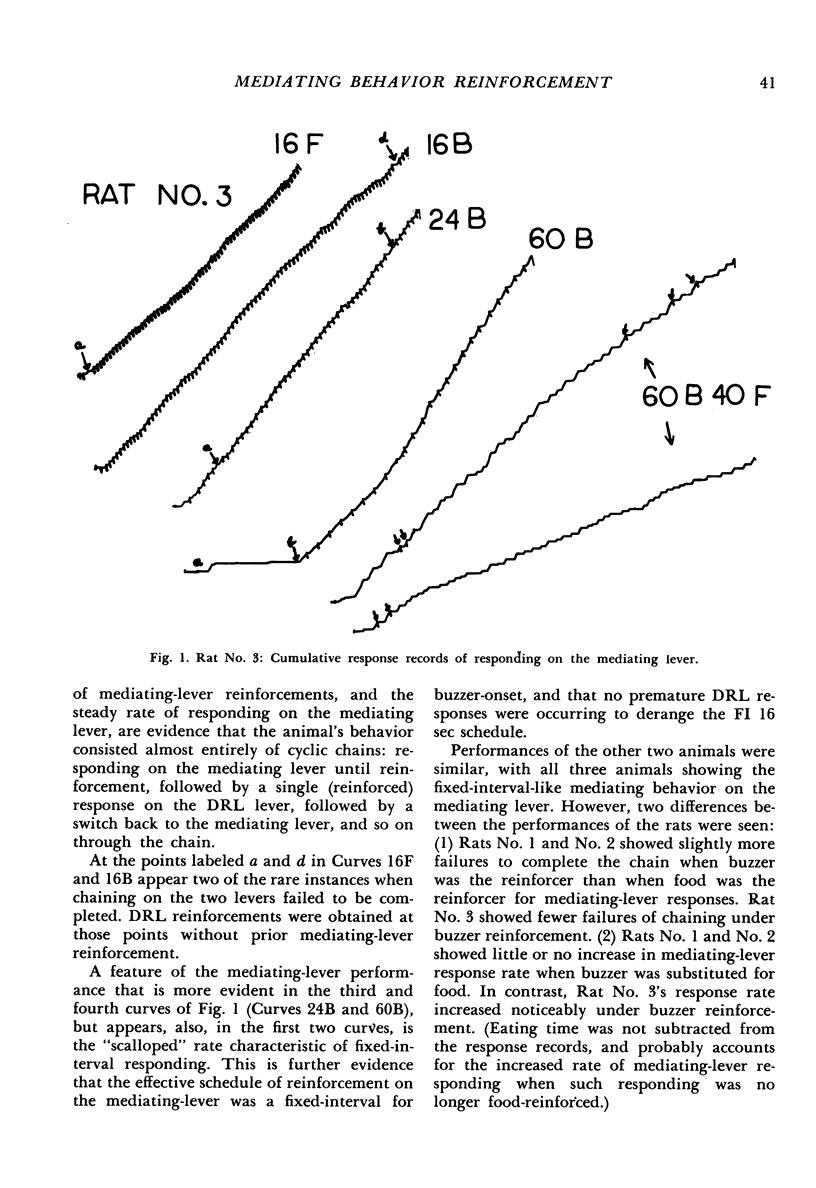
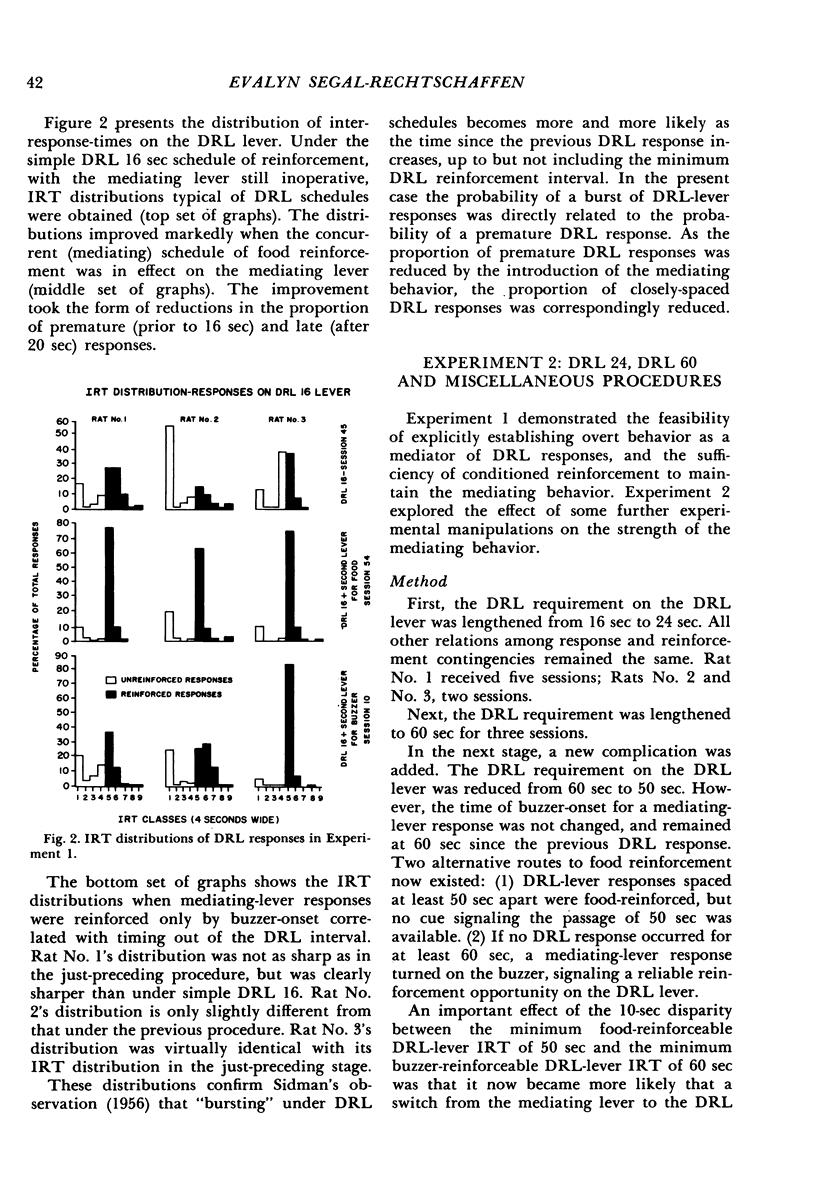
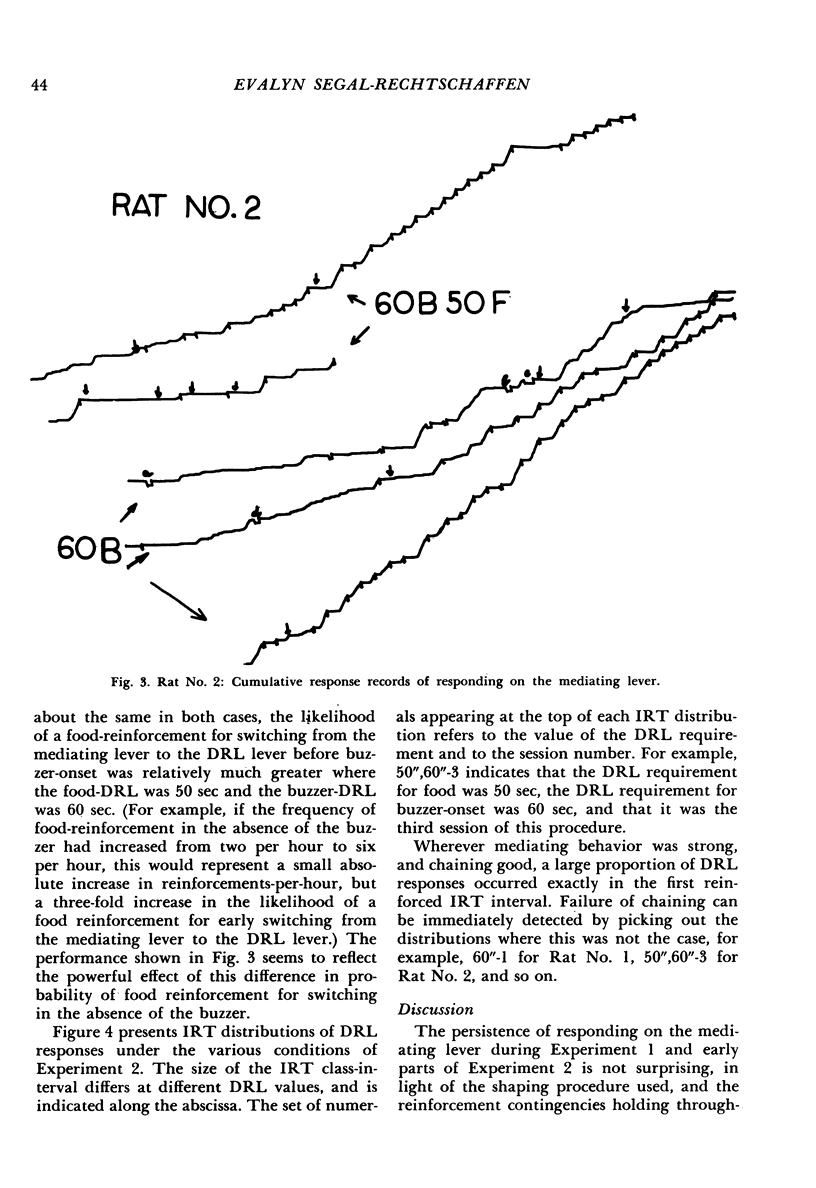
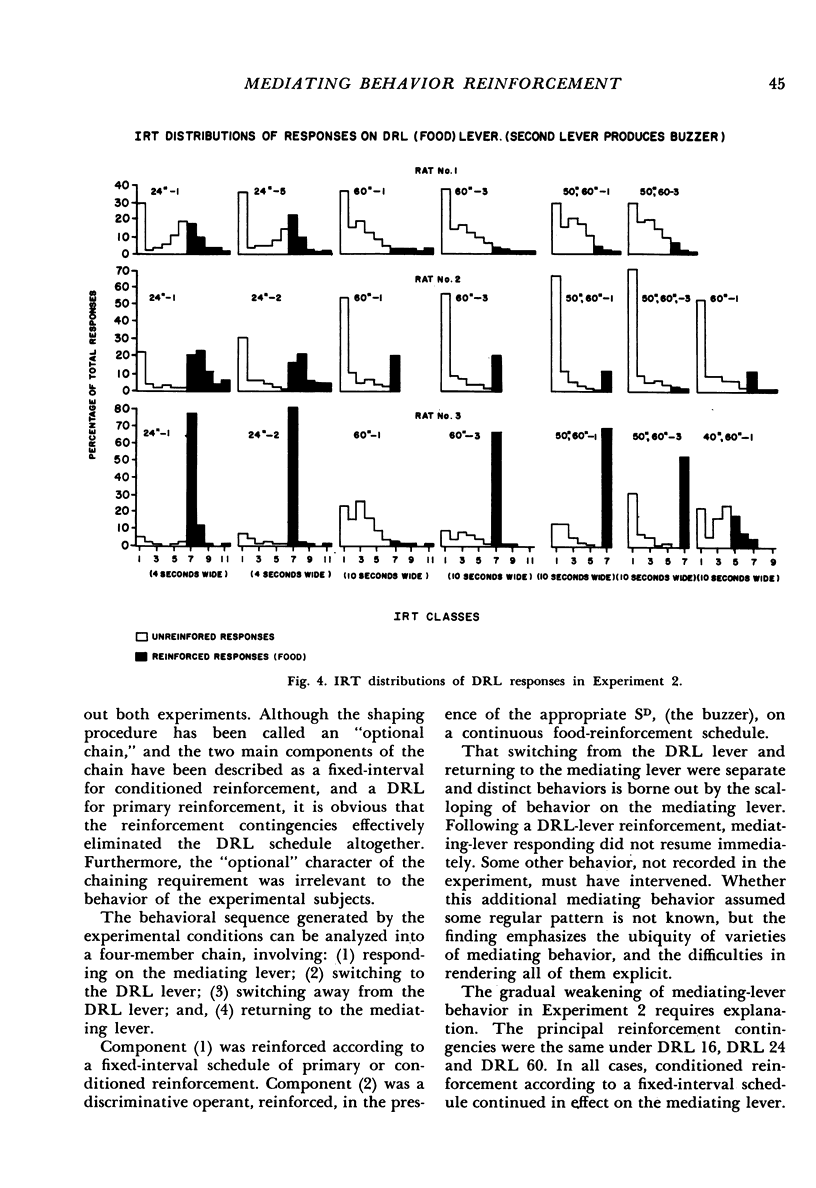
Abstract
This paper describes a procedure for gaining experimental control over mediating behavior on a spaced-responding schedule of food reinforcement. Three rats, food-deprived, were trained on a DRL 16 sec schedule of food reinforcement. Then, a concurrent schedule of food reinforcement was introduced on a second (mediating) lever, such that the first response to occur on the mediating lever, after the DRL interval had timed out, was reinforced with food, as was the next response to occur on the DRL lever. Reinforcement via the mediating lever became a discriminative stimulus for a food-reinforcement opportunity on the DRL lever. Next, food reinforcement for the mediating behavior was replaced by a conditioned reinforcer consisting of onset of a buzzer signaling timing-out of the DRL interval. Under these conditions, chaining of behavior on the two levers was strong, and timing on the DRL lever was more accurate than under ordinary DRL conditions. As the DRL requirement was lengthened from 16 sec to 24 sec to 60 sec, mediating behavior weakened slightly. When the inter-response requirement for food reinforcement on the DRL lever was made shorter than the inter-response requirement for conditioned reinforcement on the mediating lever, the mediating behavior extinguished. Performance in the experiment was analyzed into a four-component chain, and the factors contributing to the maintenance, and later extinction, of mediating behavior are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- SIDMAN M. Time discrimination and behavioral interaction in a free operant situation. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1956 Oct;49(5):469–473. doi: 10.1037/h0041892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


