Abstract
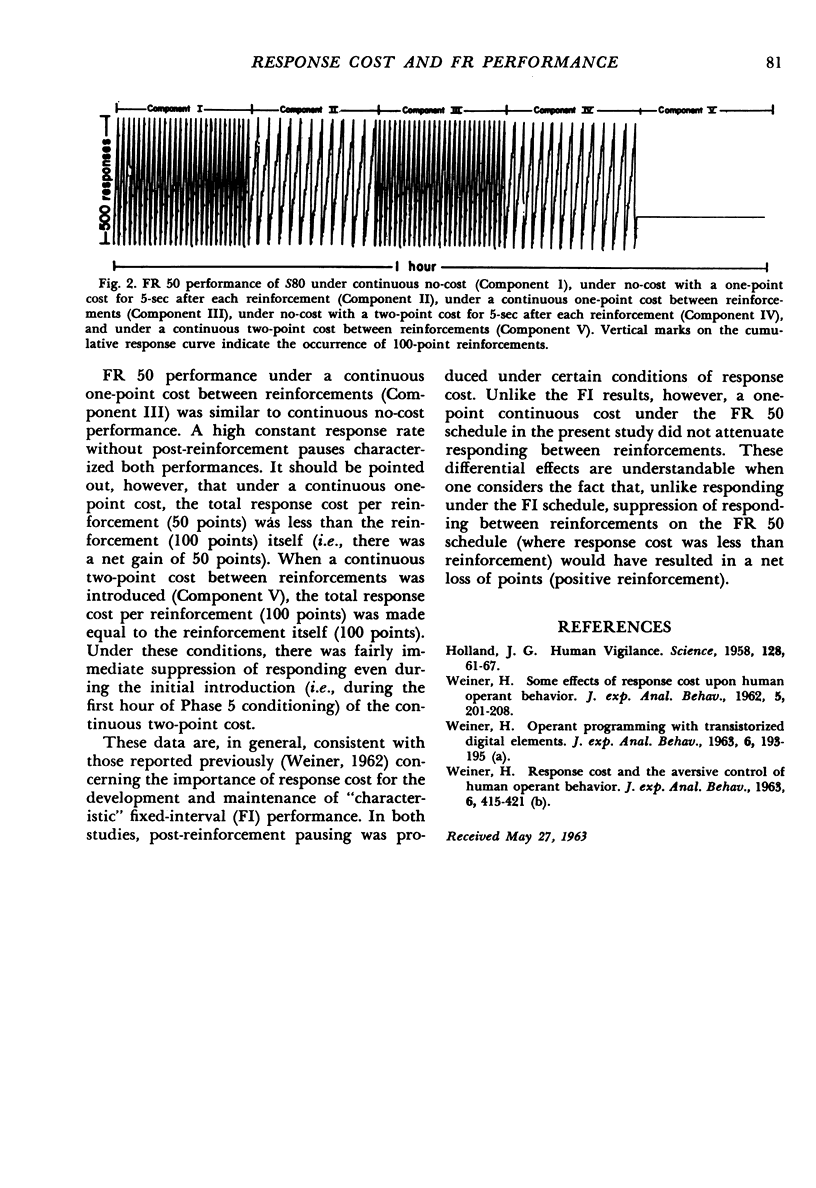
The effects of several conditions of response cost (response-produced point loss) upon FR 50 performance maintained by 100-point reinforcements were investigated. Post-reinforcement pauses did not appear under no-cost (no points deducted per response) conditions. Such pauses were effected, however, by introducing 5-sec periods of one-point and two-point costs after each reinforcement. Continuous response cost did not affect responding as long as the cost was less than the 100-point reinforcements. Rapid cessation of responding occurred when continuous response cost was made equal to reinforcement.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HOLLAND J. G. Human vigilance: the rate of observing an instrument is controlled by the schedule of signal detections. Science. 1958 Jul 11;128(3315):61–67. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3315.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER H. Operant programming with transistorized digital elements. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:193–195. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER H. Response cost and the aversive control of human operant behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:415–421. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER H. Some effects of response cost upon human operant behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:201–208. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


