Abstract
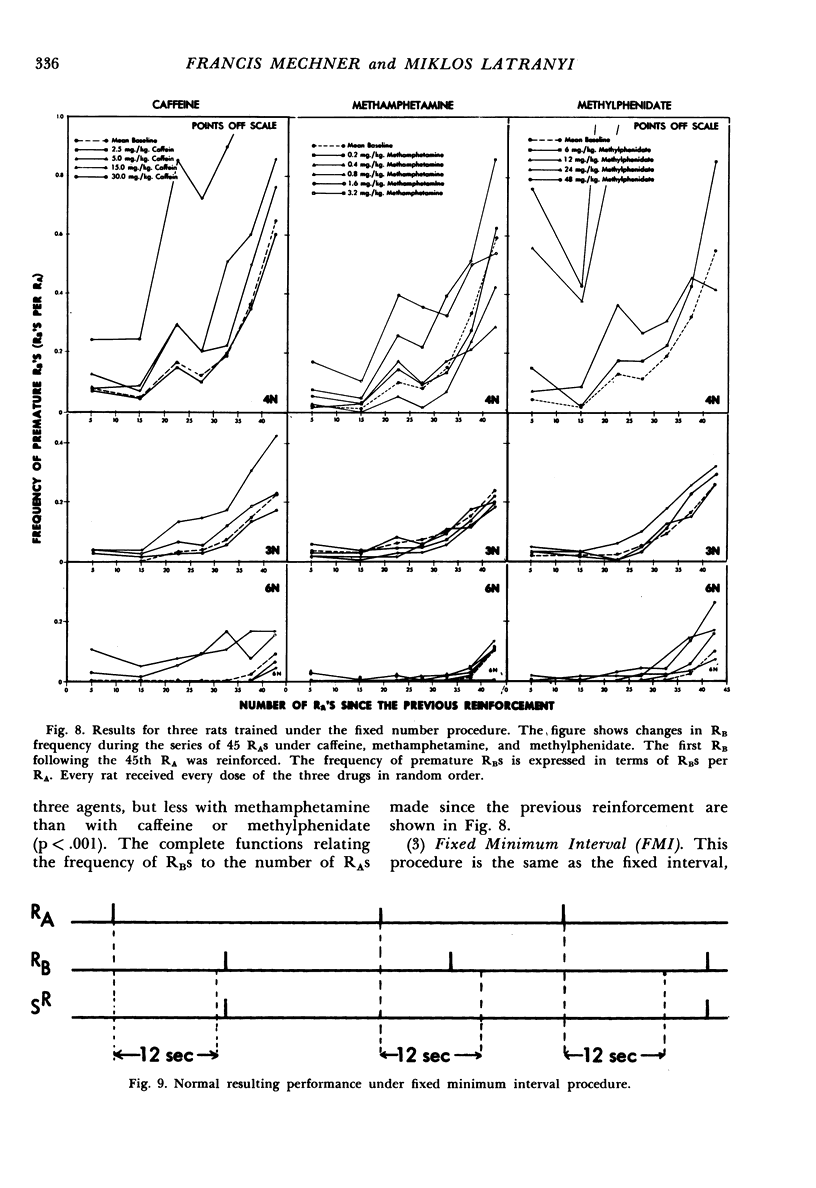
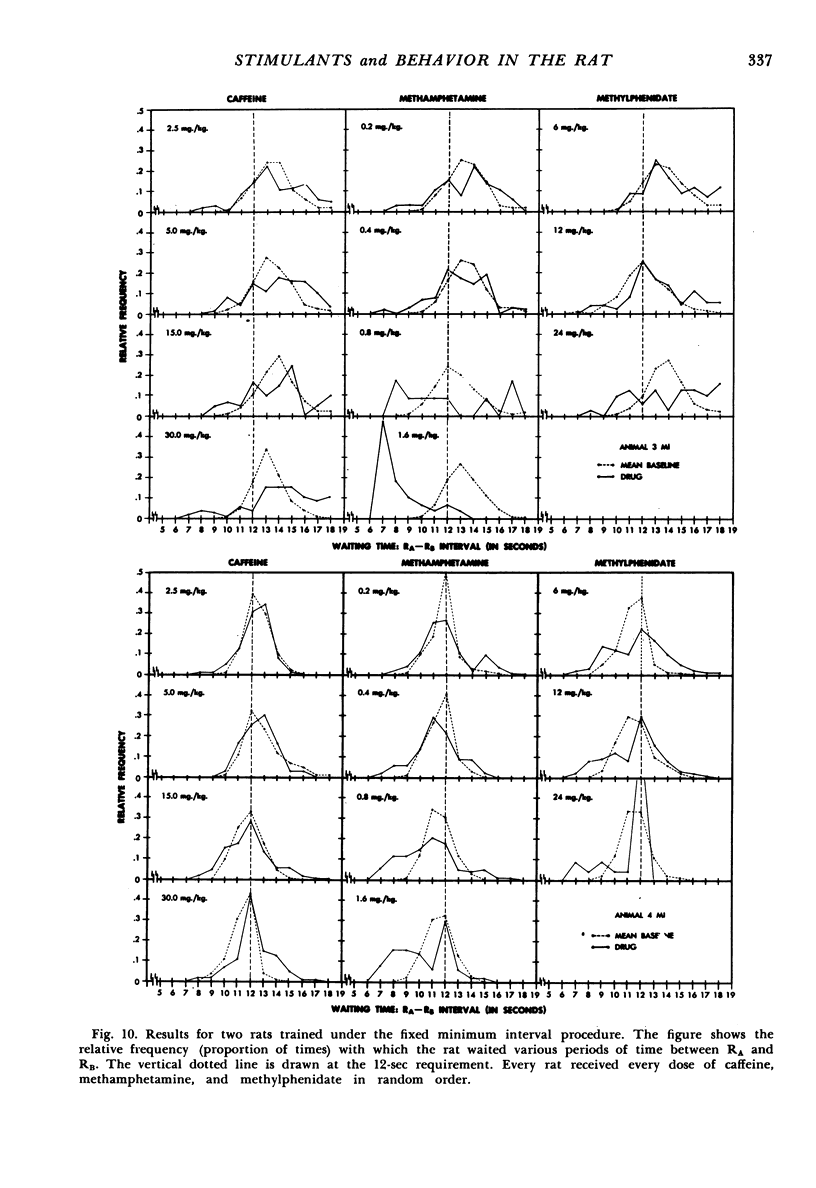
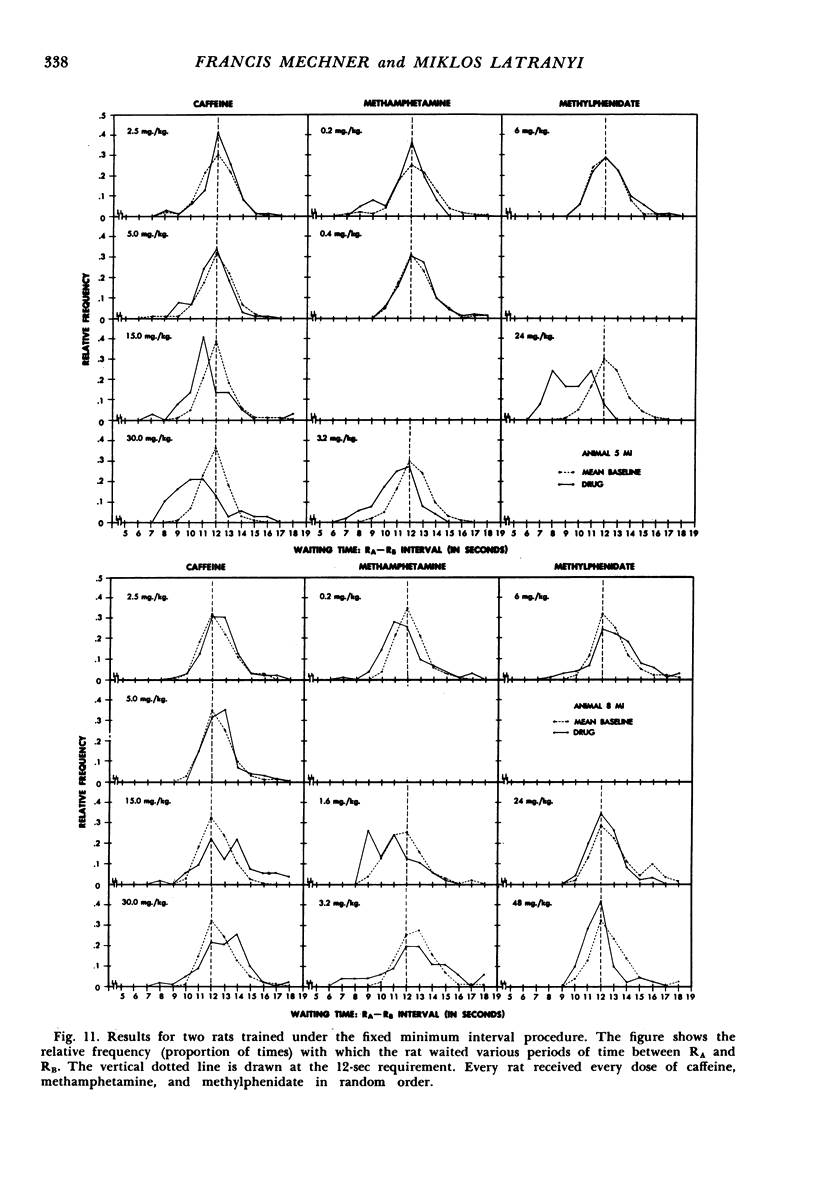
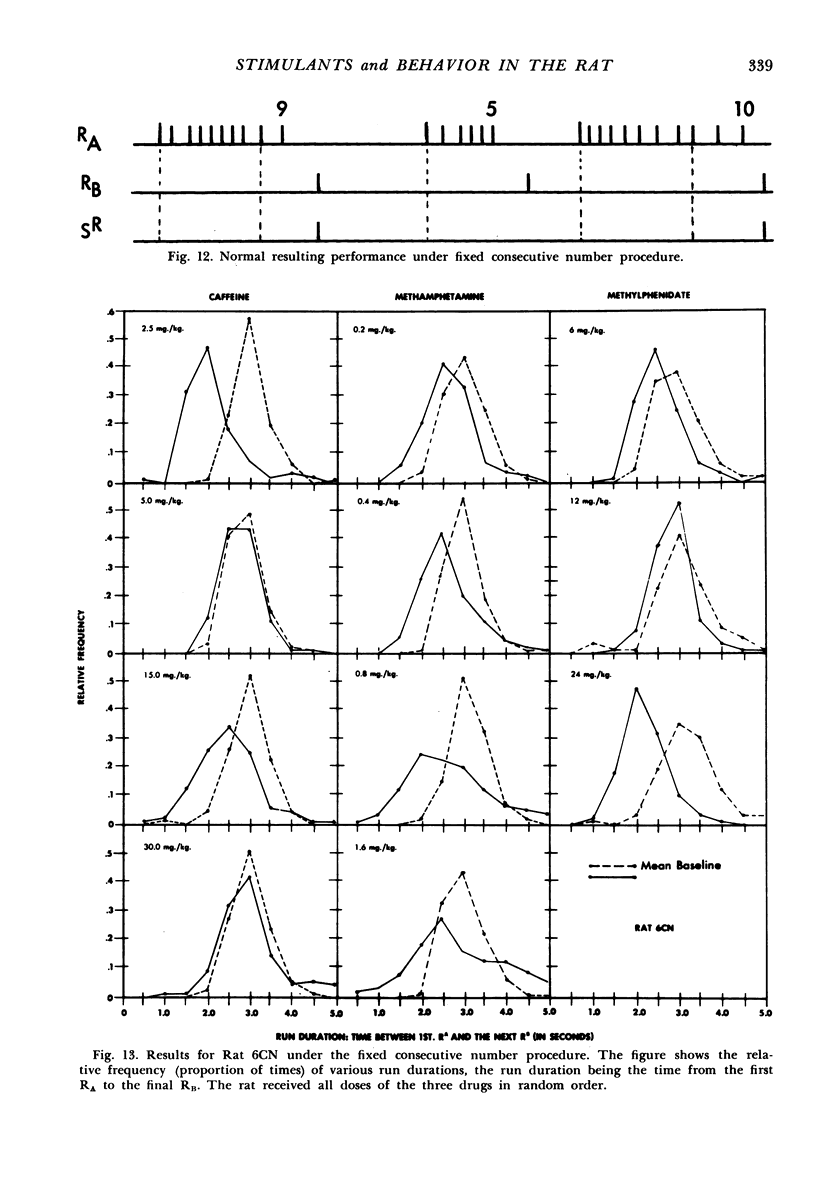
It was possible to distinguish three closely-related psychomotor stimulants, caffeine, methamphetamine, and methylphenidate, by means of two operant behavior procedures, fixed interval and fixed number. Under the fixed interval procedure, the percentage change in the number of RBs per reinforcement was significantly smaller with caffeine than with methamphetamine or methylphenidate (p < .001). Under the fixed number procedure, the percentage change was significantly smaller with methamphetamine than with caffeine or methylphenidate (p < .001). Thus, methylphenidate had a methamphetamine-like effect under fixed interval and a caffeine-like effect under fixed number.
Full text
PDF