Abstract
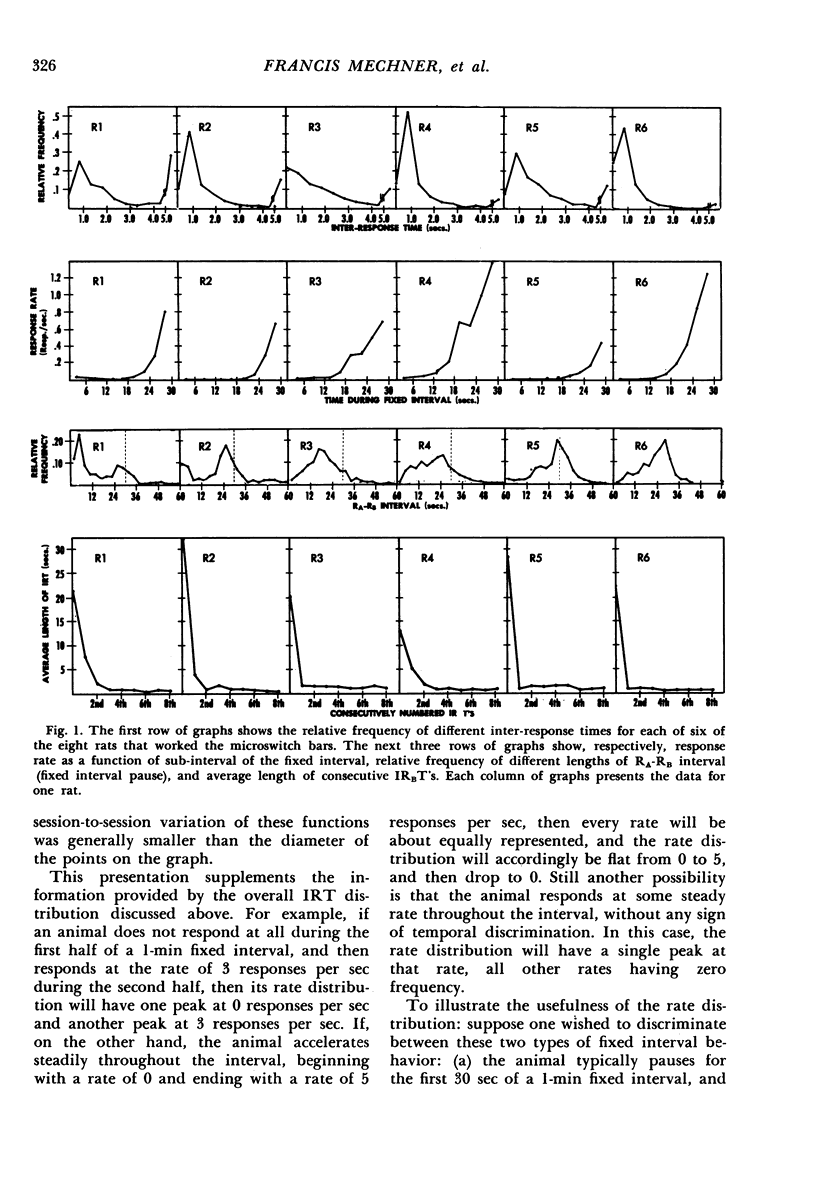
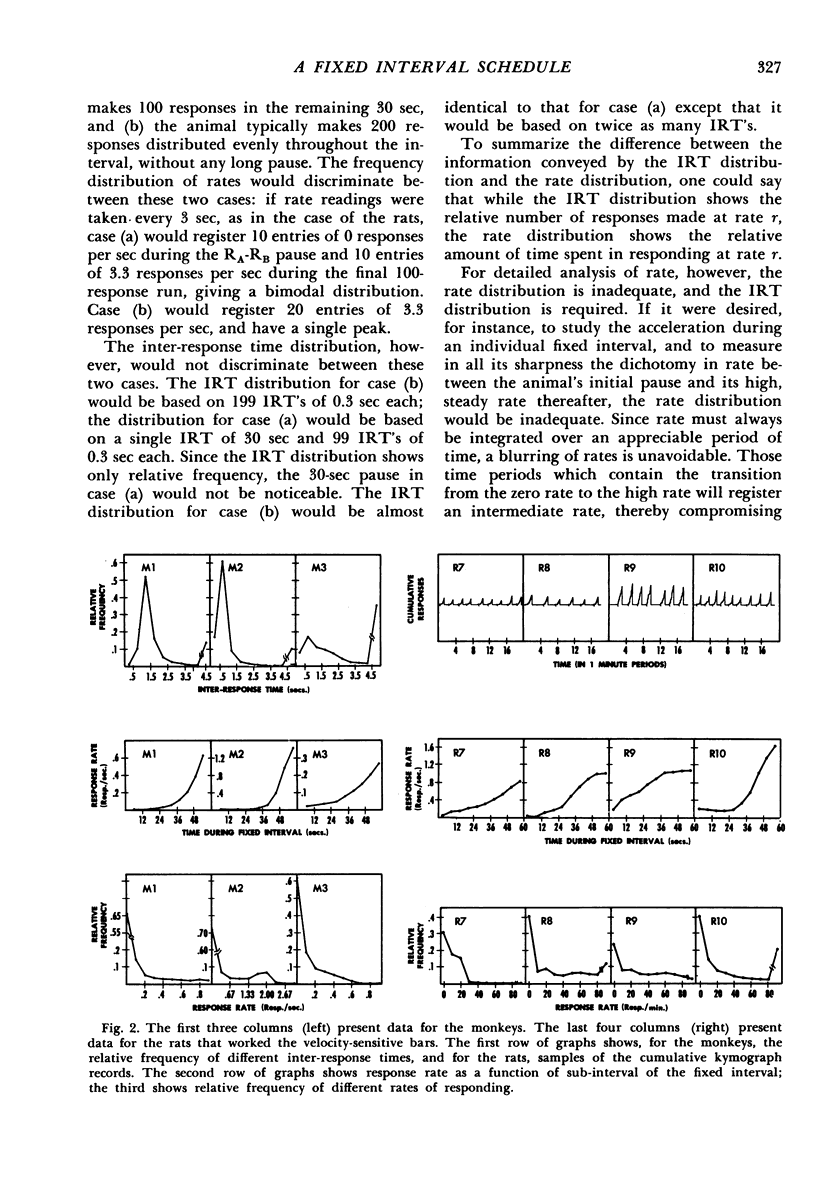
The fixed interval schedule described requires the animal to initiate every time interval by making a response on a bar other than the one on which it is reinforced. This response, RA, demarcates the postreinforcement pause (SR-RA interval) from the fixed interval pause (RA-RB interval) so that these pauses may be measured separately. Twelve rats and three monkeys, working in two-bar Skinner boxes, were trained and stabilized on this schedule. The resulting performances, presented for individual animals, are analyzed in terms of (1) the relative frequencies with which the animal waits various lengths of time between consecutive responses, (2) the relative frequencies with which various rates of responding appear, (3) the change in response rate throughout the fixed interval, (4) the average length of the postreinforcement pause, (5) the relative frequencies with which the animal waits different lengths of time between the RA and the first RB, and (6) the average inter-response time as a function of the rank order in the fixed interval of the inter-response time. The joint interpretation of the several measures taken leads to the following conclusions: 1. The probability of an RB increases throughout the fixed interval. 2. The increase is discontinuous at the first RB, at which point the probability increases sharply. 3. The frequency distributions of RA-RB pauses exhibit three discrete types of behavior with no intermediate cases. 4. The (main) mode of RA-RB interval length usually occurs just below the fixed interval requirement.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Mechner F. A notation system for the description of behavioral procedures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Apr;2(2):133–150. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld W. N., Cumming W. W., Hearst E. ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Aug;42(8):563–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.8.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



