Abstract
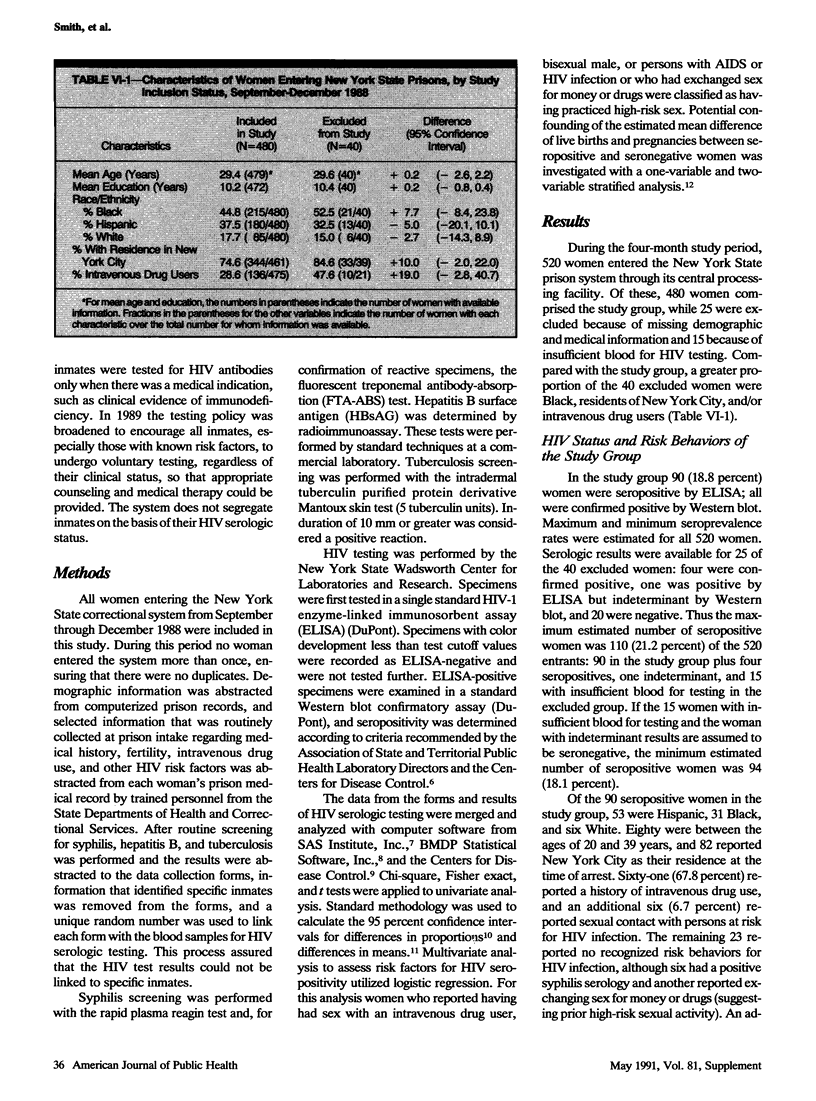
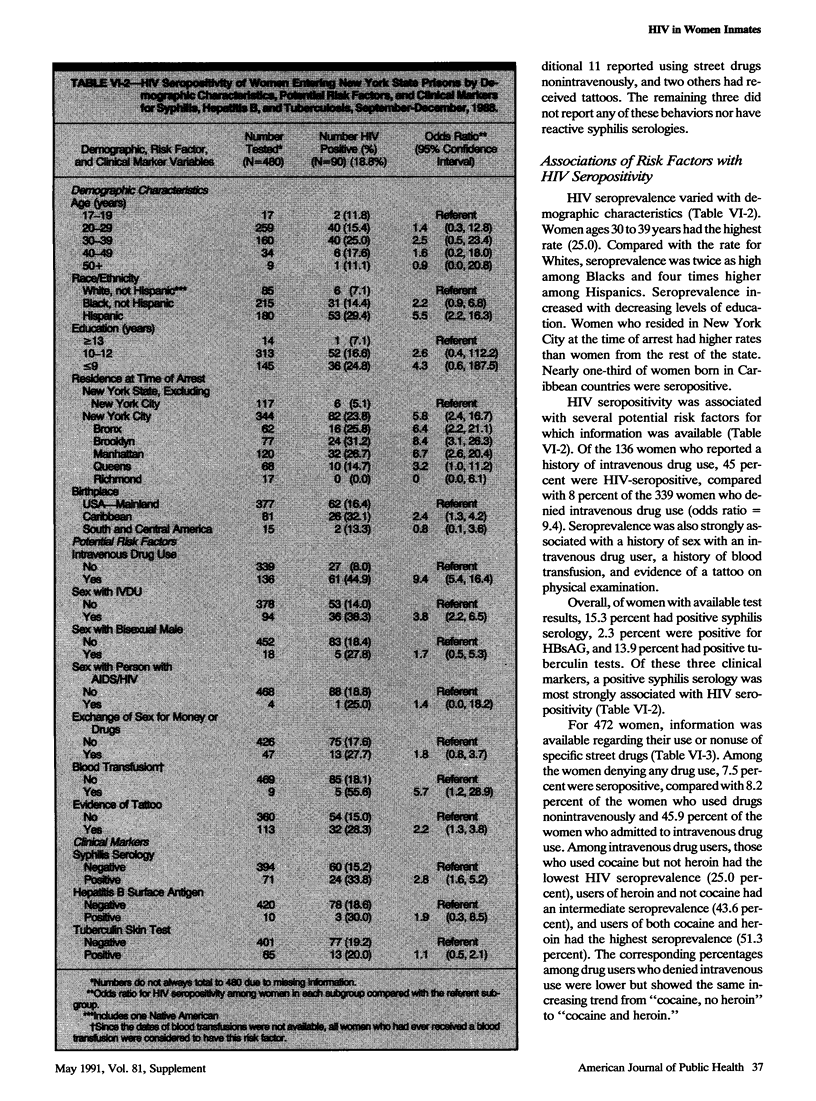
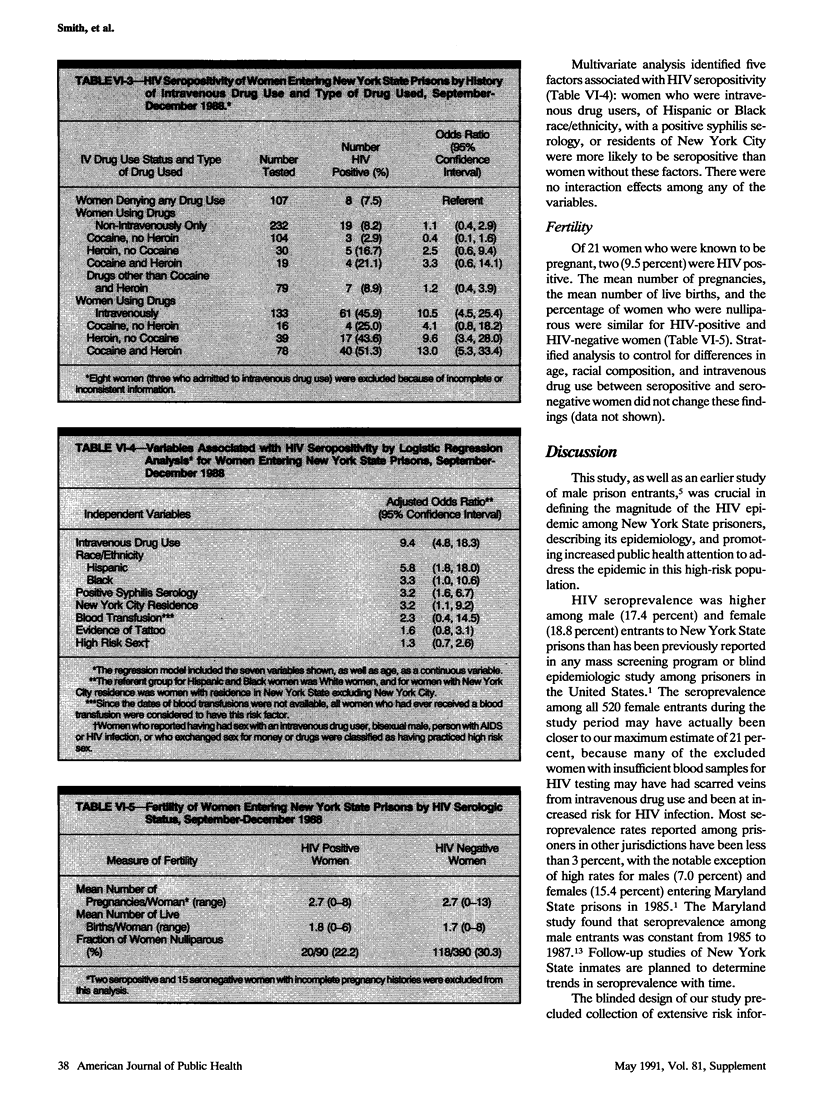
Human immunodeficiency virus infection is the leading medical problem among prison inmates in several states. In 1988 a blinded seroprevalence study was conducted on 480 New York female prison entrants to determine the prevalence of and risk factors for HIV infection in this population. Ninety (18.8 percent) women were HIV-seropositive. Seroprevalence was highest among women ages 30-39 (25.0 percent) and varied by ethnicity (Hispanics, 29.4 percent; Blacks, 14.4 percent; Whites, 7.1 percent) and residence (New York City, 23.8 percent; Upstate, 5.1 percent). Nearly half (44.9 percent) of the 136 acknowledged intravenous drug users and one-third (33.8 percent) of the 71 women with a positive syphilis serology were HIV-seropositive. There was no difference in fertility histories between seropositive and seronegative women, and two of 21 pregnant women were seropositive. This study led to increased clinical and prevention services for this high-risk population.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun M. M., Truman B. I., Maguire B., DiFerdinando G. T., Jr, Wormser G., Broaddus R., Morse D. L. Increasing incidence of tuberculosis in a prison inmate population. Association with HIV infection. JAMA. 1989 Jan 20;261(3):393–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro K. G., Lifson A. R., White C. R., Bush T. J., Chamberland M. E., Lekatsas A. M., Jaffe H. W. Investigations of AIDS patients with no previously identified risk factors. JAMA. 1988 Mar 4;259(9):1338–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson R. E., Bacchetti P., Osmond D., Brodie B., Sande M. A., Moss A. R. Cocaine use and HIV infection in intravenous drug users in San Francisco. JAMA. 1989 Jan 27;261(4):561–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R. HIV infection among persons who inject illicit drugs: problems and prospects. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1988;1(3):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll D. C. Tattooing in prison and HIV infection. Lancet. 1988 Jan 2;1(8575-6):66–67. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt R. M., Lukehart S. A., Plummer F. A., Quinn T. C., Critchlow C. W., Ashley R. L., D'Costa L. J., Ndinya-Achola J. O., Corey L., Ronald A. R. Genital ulceration as a risk factor for human immunodeficiency virus infection. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):47–50. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone F. D., MacCallum L., Brettle R., Inglis J. M., Peutherer J. F. Does infection with HIV affect the outcome of pregnancy? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Feb 13;296(6620):467–467. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6620.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss J. K., Koech D., Plummer F. A., Holmes K. K., Lightfoote M., Piot P., Ronald A. R., Ndinya-Achola J. O., D'Costa L. J., Roberts P. AIDS virus infection in Nairobi prostitutes. Spread of the epidemic to East Africa. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 13;314(7):414–418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602133140704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessner L. Projection of AIDS incidence in women in New York State. Am J Public Health. 1991 May;81 (Suppl):30–34. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.suppl.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum E. E., Hartel D., Selwyn P. A., Klein R. S., Davenny K., Rogers M., Feiner C., Friedland G. Risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus infection in intravenous drug users. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):874–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn P. A., Schoenbaum E. E., Davenny K., Robertson V. J., Feingold A. R., Shulman J. F., Mayers M. M., Klein R. S., Friedland G. H., Rogers M. F. Prospective study of human immunodeficiency virus infection and pregnancy outcomes in intravenous drug users. JAMA. 1989 Mar 3;261(9):1289–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E., Handsfield H. H., Rompalo A. M., Ashley R. L., Roberts P. L., Corey L. The association between genital ulcer disease and acquisition of HIV infection in homosexual men. JAMA. 1988 Sep 9;260(10):1429–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahov D., Brewer F., Muñoz A., Hall D., Taylor E., Polk B. F. Temporal trends of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection among inmates entering a statewide prison system, 1985-1987. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(3):283–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


