Abstract
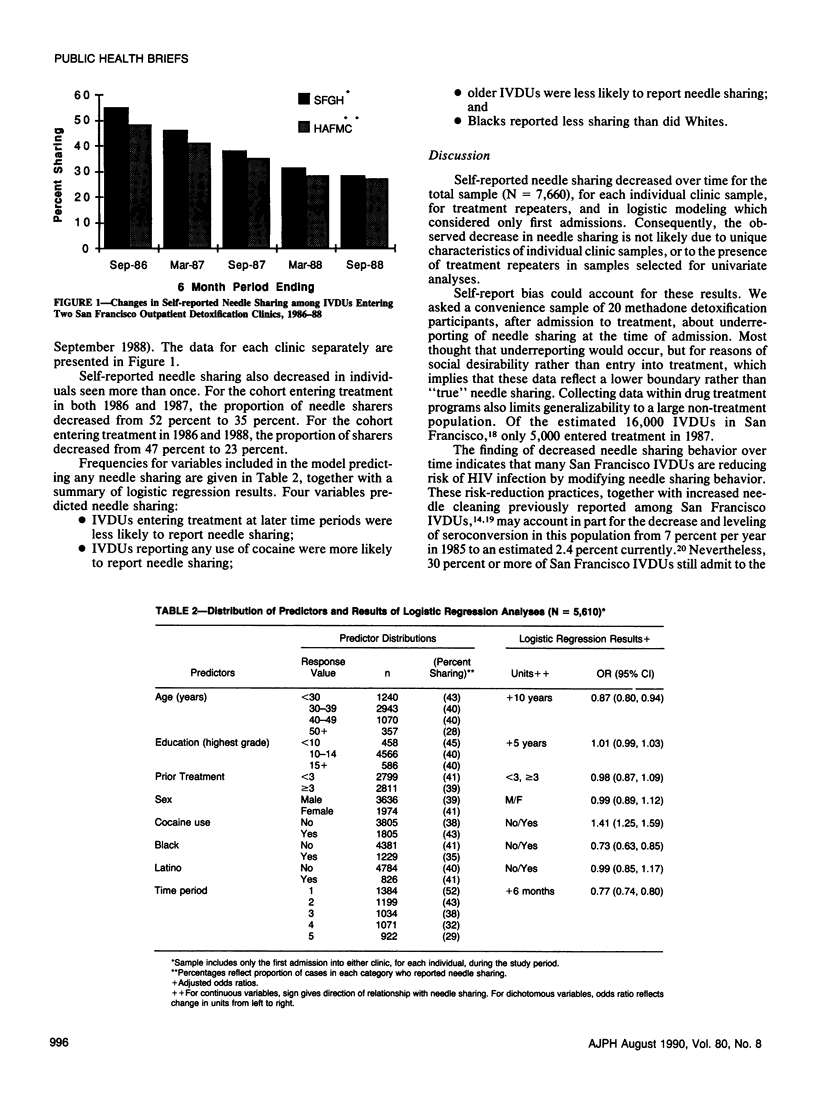
We analyzed data for San Francisco intravenous drug users entering treatment, April 1986-September 1988 (N = 7,660). The proportion of cases reporting any needle sharing in the month preceding treatment decreased from 50 percent in 1986 to 28 percent in 1988. Similar decreases were reported by two longitudinal cohorts (needle sharing by the same individuals) admitted in 1986 and 1987 (n = 303), and in 1986 and 1988 (n = 205). In a multiple logistic regression model four variables predicted needle sharing: earlier time of admission, cocaine use, younger age, and being White rather than Black.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaisson R. E., Osmond D., Moss A. R., Feldman H. W., Bernacki P. HIV, bleach, and needle sharing. Lancet. 1987 Jun 20;1(8547):1430–1430. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90615-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitwood D. D., McCoy C. B., Inciardi J. A., McBride D. C., Comerford M., Trapido E., McCoy H. V., Page J. B., Griffin J., Fletcher M. A. HIV seropositivity of needles from shooting galleries in south Florida. Am J Public Health. 1990 Feb;80(2):150–152. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R., Hopkins W. Risk reduction for the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome among intravenous drug users. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Nov;103(5):755–759. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-5-755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R., Novick D. M., Sotheran J. L., Thomas P., Yancovitz S. R., Mildvan D., Weber J., Kreek M. J., Maslansky R. HIV-1 infection among intravenous drug users in Manhattan, New York City, from 1977 through 1987. JAMA. 1989 Feb 17;261(7):1008–1012. doi: 10.1001/jama.261.7.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R. Shooting galleries and AIDS: infection probabilities and 'tough' policies. Am J Public Health. 1990 Feb;80(2):142–144. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.2.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Hopkins W. "Free" needles for intravenous drug users at risk for AIDS: current developments in New York City. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1476–1476. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. R., Des Jarlais D. C., Sotheran J. L., Garber J., Cohen H., Smith D. AIDS and self-organization among intravenous drug users. Int J Addict. 1987 Mar;22(3):201–219. doi: 10.3109/10826088709027425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guydish J., Temoshok L., Dilley J., Rinaldi J. Evaluation of a hospital based substance abuse intervention and referral service for HIV affected patients. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 1990 Jan;12(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0163-8343(90)90030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer J. A. The prevalence of drug use in San Francisco in 1987. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1988 Apr-Jun;20(2):185–189. doi: 10.1080/02791072.1988.10524493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selwyn P. A., Feiner C., Cox C. P., Lipshutz C., Cohen R. L. Knowledge about AIDS and high-risk behavior among intravenous drug users in New York City. AIDS. 1987 Dec;1(4):247–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen J. L., Guydish J., Costantini M., Batki S. L. Changes in needle sharing and syringe cleaning among San Francisco drug abusers. N Engl J Med. 1989 Mar 23;320(12):807–807. doi: 10.1056/nejm198903233201214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimson G. V., Alldritt L., Dolan K., Donoghoe M. Syringe exchange schemes for drug users in England and Scotland. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Jun 18;296(6638):1717–1719. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6638.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watters J. K. Meaning and context: the social facts of intravenous drug use and HIV transmission in the inner city. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1988 Apr-Jun;20(2):173–177. doi: 10.1080/02791072.1988.10524491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



