Abstract
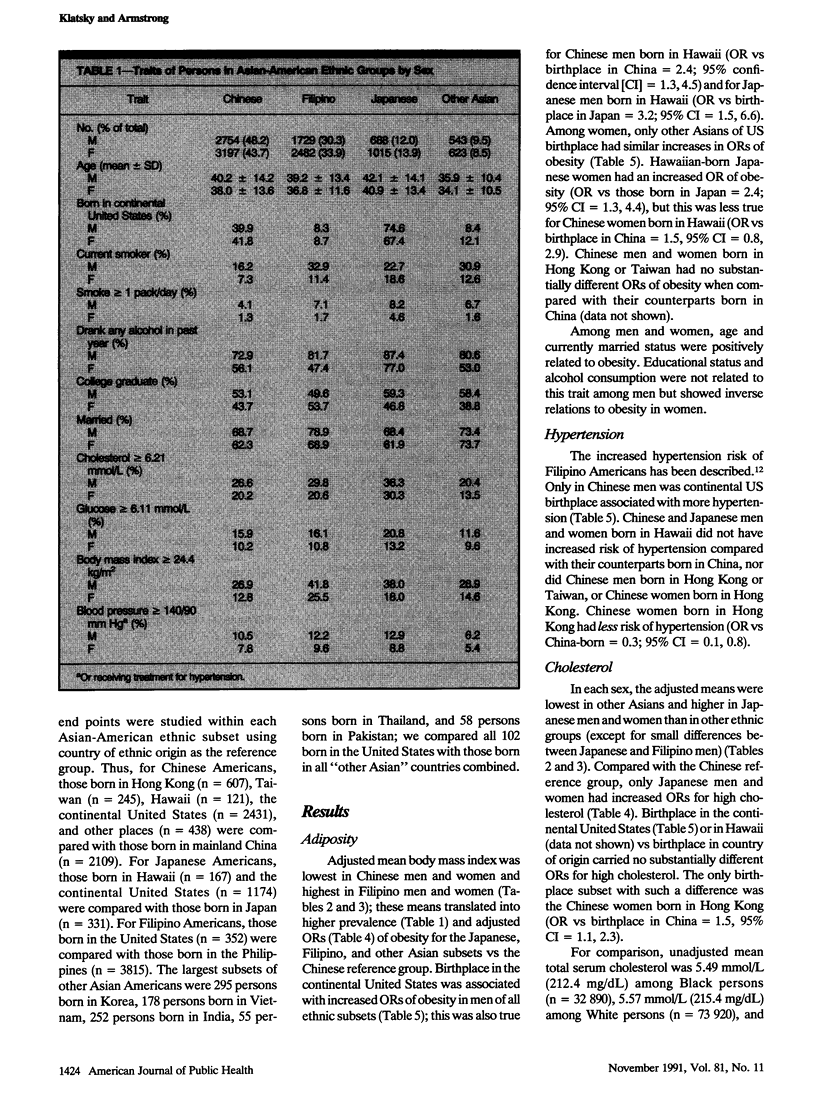
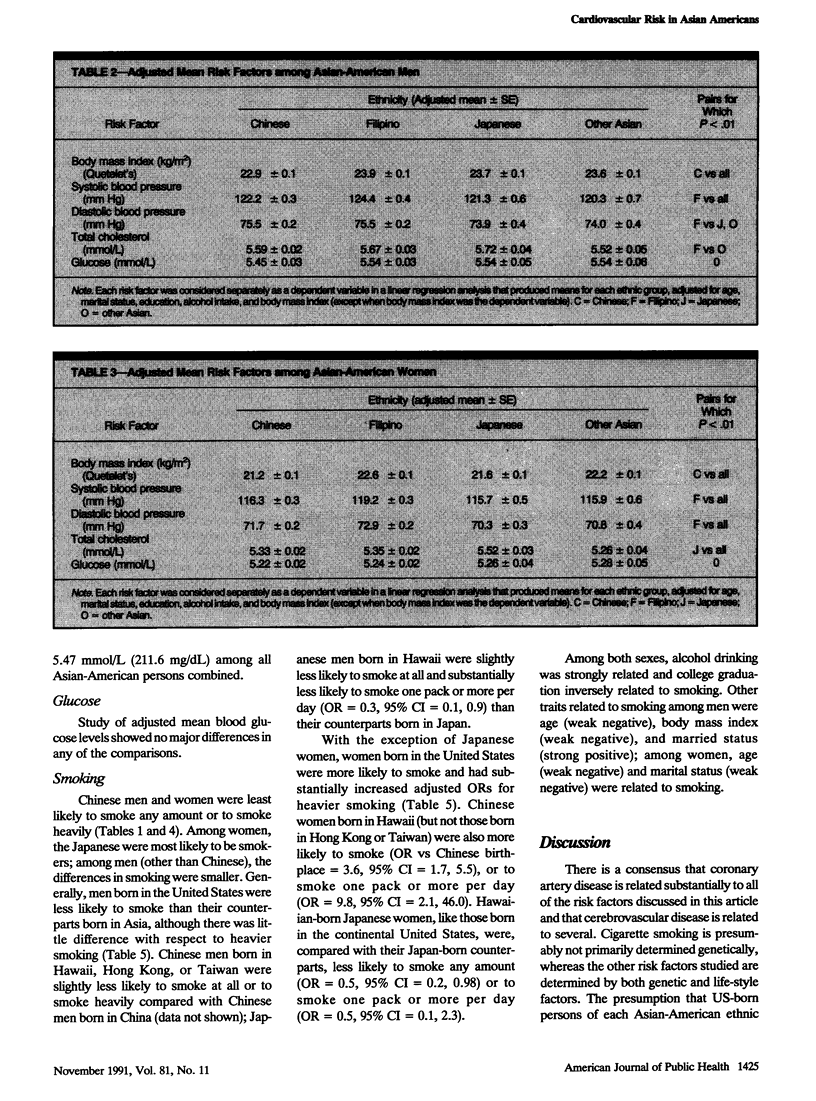
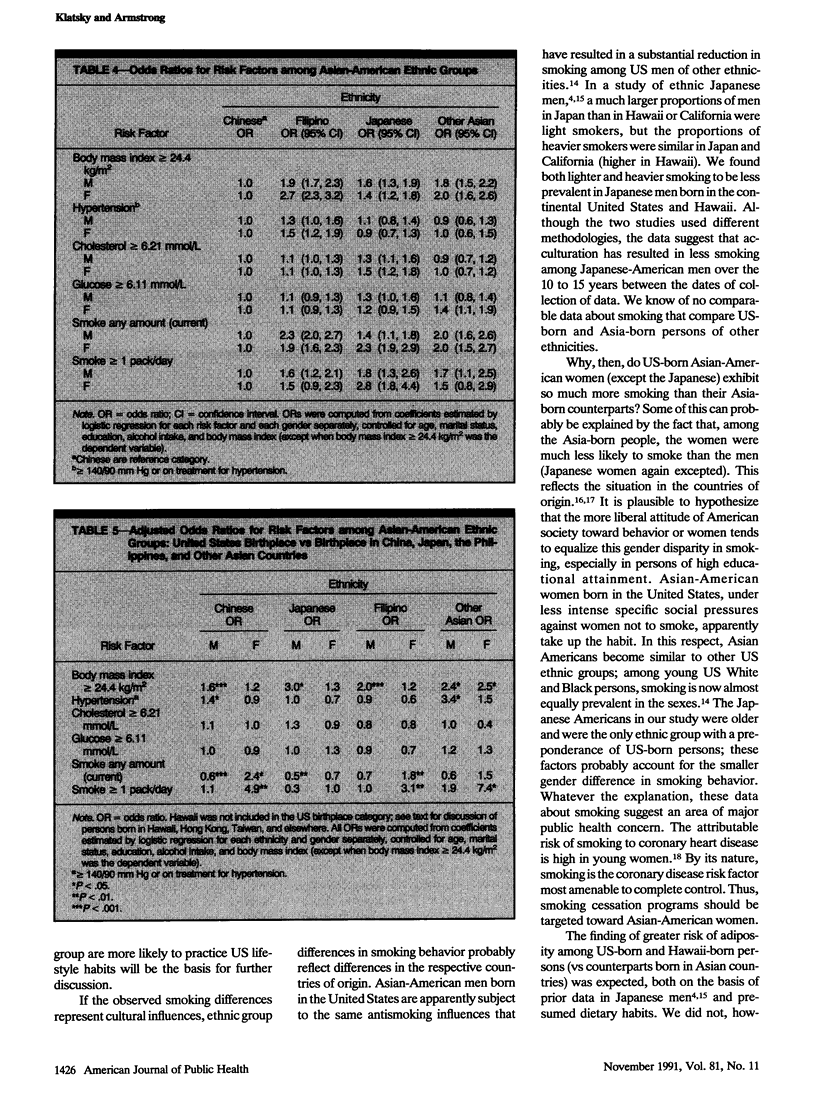
BACKGROUND. Recent substantial immigration has created large population subsets of Asian Americans in the United States. Available data about cardiovascular risk factors in these persons are sparse. METHODS. This study examined data among 13,031 persons self-classified as 5951 Chinese, 4211 Filipinos, 1703 Japanese, and 1166 other Asians. Covariates in regression analyses were age, smoking, alcohol, education, and marital status. RESULTS. Chinese men and women had the lowest adjusted mean body mass index. Filipino men and women had the highest prevalence of hypertension. There were no major differences in blood glucose levels. Total cholesterol levels were highest in Japanese men and women. Comparisons of US-born persons and those born in respective countries of origin showed no major cholesterol or glucose differences; more hypertension only in Chinese and other Asian men; higher body mass index in men, but not in women of most ethnicities; and a lower smoking prevalence in men, but a substantially higher one in women. CONCLUSIONS. These data show important ethnic differences in risk factors among Asian Americans and indicate groups that should be targeted for public health efforts concerned with obesity (Asian-American men), hypertension (Filipino-American men and women), hypercholesteremia (all Asian Americans), and smoking cessation (Asian-American women).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel A., Armstrong M. A., Klatsky A. L. Blood pressure among Asian-Americans living in northern California. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Jul 15;64(3):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90468-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chew W. L., Mah P. K., Tan Y. T., Cheong C. K. A comparison of the levels of total serum cholesterol (1974-1984) and its relations to ischaemic heart disease in Singapore and the United States of America. Singapore Med J. 1988 Feb;29(1):6–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi E. S., McGandy R. B., Dallal G. E., Russell R. M., Jacob R. A., Schaefer E. J., Sadowski J. A. The prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors among elderly Chinese Americans. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Feb;150(2):413–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON T. Mortality experience among the Japanese in the United States, Hawaii, and Japan. Public Health Rep. 1957 Jun;72(6):543–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes K., Yeo P. P., Lun K. C., Sothy S. P., Thai A. C., Wang K. W., Cheah J. S. Ischaemic heart disease and its risk factors in Singapore in comparison with other countries. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 1989 May;18(3):245–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan A., Harris B. R., Winkelstein W., Jr, Johnson K. G., Kato H., Syme S. L., Rhoads G. G., Gay M. L., Nichaman M. Z., Hamilton H. B. Epidemiologic studies of coronary heart disease and stroke in Japanese men living in Japan, Hawaii and California: demographic, physical, dietary and biochemical characteristics. J Chronic Dis. 1974 Sep;27(7-8):345–364. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(74)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesteloot H., Huang D. X., Yang X. S., Claes J., Rosseneu M., Geboers J., Joossens J. V. Serum lipids in the People's Republic of China. Comparison of Western and Eastern populations. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 Sep-Oct;5(5):427–433. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.5.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatsky A. L., Siegelaub A. B., Landy C., Friedman G. D. Racial patterns of alcoholic beverage use. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1983 Fall;7(4):372–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1983.tb05486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koong S. L., Malison M. D., Nakashima A. K. A prevalence survey of behavioural risk factors in Taipei City, Taiwan. Int J Epidemiol. 1990 Mar;19(1):154–159. doi: 10.1093/ije/19.1.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Fu J. S. Population characteristics and health care needs of Asian Pacific Americans. Public Health Rep. 1988 Jan-Feb;103(1):18–27. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichaman M. Z., Hamilton H. B., Kagan A., Grier T., Sacks T., Syme S. L. Epidemiologic studies of coronary heart disease and stroke in Japanese men living in Japan, Hawaii and California: distribution of biochemical risk factors. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Dec;102(6):491–501. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson T. L., Kato H., Gordon T., Kagan A., Rhoads G. G., Land C. E., Worth R. M., Belsky J. L., Dock D. S., Miyanishi M. Epidemiologic studies of coronary heart disease and stroke in Japanese men living in Japan, Hawaii and California. Coronary heart disease risk factors in Japan and Hawaii. Am J Cardiol. 1977 Feb;39(2):244–249. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(77)80198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson T. L., Kato H., Rhoads G. G., Kagan A., Marmot M., Syme S. L., Gordon T., Worth R. M., Belsky J. L., Dock D. S. Epidemiologic studies of coronary heart disease and stroke in Japanese men living in Japan, Hawaii and California. Incidence of myocardial infarction and death from coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 1977 Feb;39(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(77)80197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Miller D. R., Kaufman D. W., Helmrich S. P., Van de Carr S., Stolley P. D., Shapiro S. Myocardial infarction in women under 50 years of age. JAMA. 1983 Nov 25;250(20):2801–2806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh S. M., Shen M., Fuh M. M., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Plasma lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in Chinese males with coronary artery disease, with and without hypertension. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Sep;67(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90264-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavig G. R., Igra A., Leonard A. R. Hypertension among Asians and Pacific islanders in California. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 May;119(5):677–691. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szatrowski T. P., Peterson A. V., Jr, Shimizu Y., Prentice R. L., Mason M. W., Fukunaga Y., Kato H. Serum cholesterol, other risk factors, and cardiovascular disease in a Japanese cohort. J Chronic Dis. 1984;37(7):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(84)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung C. L., Chen W. C., Liang S. P., Pan S. R., Xue W. A reappraisal of the changing proportion of the various types of heart diseases in Shanghai and its relationship to serum cholesterol levels. Chin Med J (Engl) 1984 Mar;97(3):171–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelstein W., Jr, Kagan A., Kato H., Sacks S. T. Epidemiologic studies of coronary heart disease and stroke in Japanese men living in Japan, Hawaii and California: blood pressure distributions. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Dec;102(6):502–513. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. K. Epidemiology and community control of hypertension, stroke and coronary heart disease in China. Chin Med J (Engl) 1979 Oct;92(10):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano K., MacLean C. J., Reed D. M., Shimizu Y., Sasaki H., Kodama K., Kato H., Kagan A. A comparison of the 12-year mortality and predictive factors of coronary heart disease among Japanese men in Japan and Hawaii. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Mar;127(3):476–487. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao C. H., Wu Z. S., Hong Z. G., Xu X. M., Zhang M., Wu Y. Y., Yu S. E., Wu Y. K. Risk factors of cardiovascular diseases in Beijing. Chin Med J (Engl) 1988 Dec;101(12):901–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


