Abstract
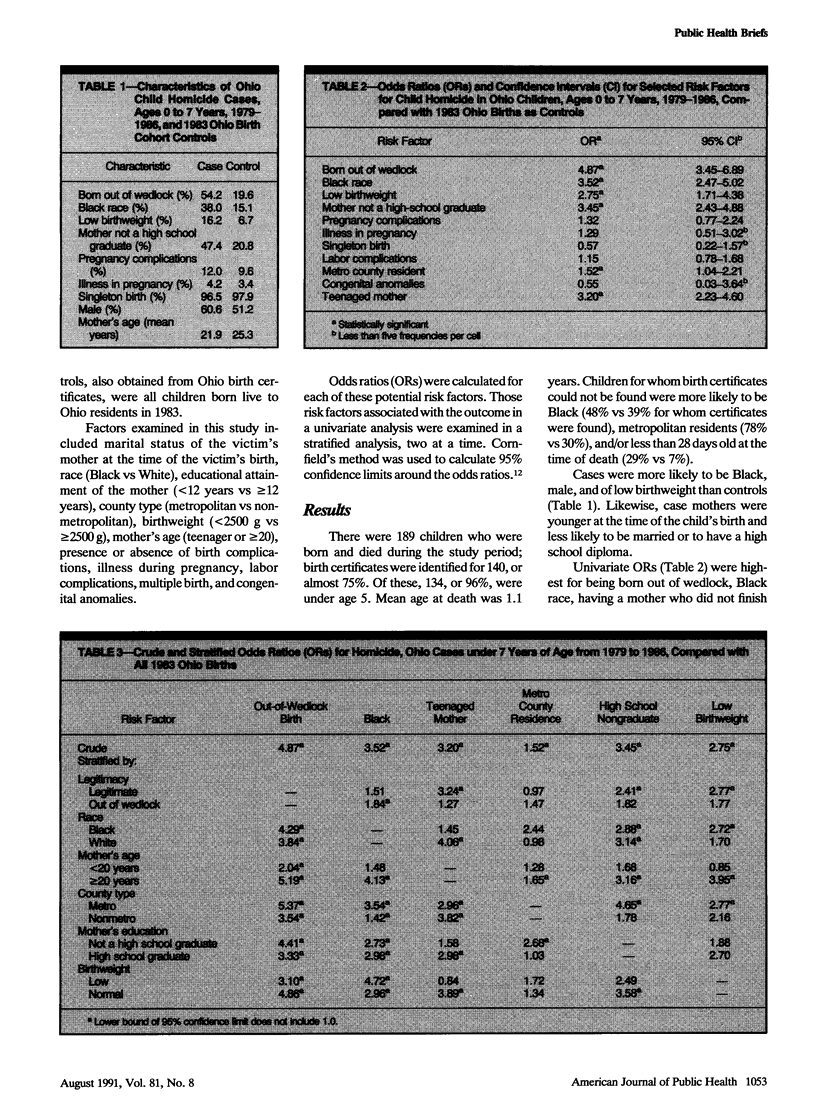
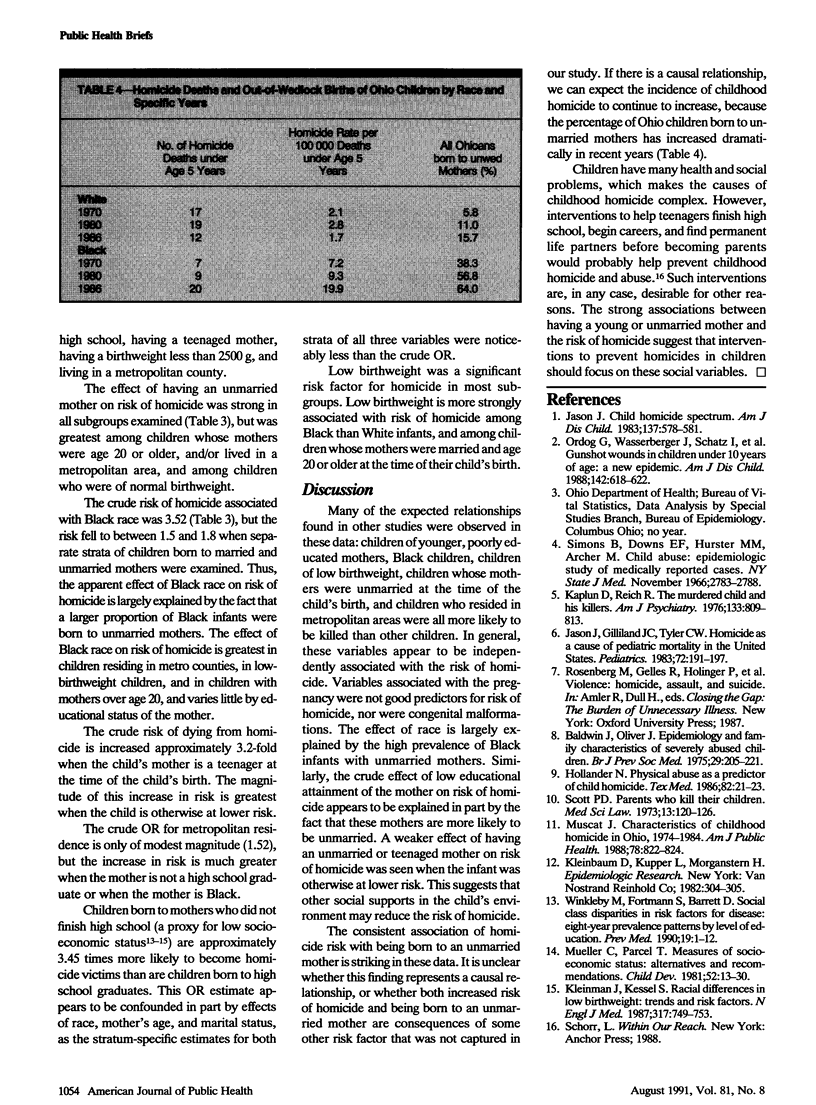
Death certificate of children less than 8 years of age who were killed between 1979 and 1986 were linked to their Ohio birth certificates and compared with those of Ohio children born in 1983 (controls). Having an unmarried mother increased risk of homicide almost fivefold (odds ratio 4.87). Having a teenage mother, a mother who had not graduated from high-school, and being of Black race or low birthweight each increased the risk by approximately threefold. Increases in the proportion of children born to unmarried mothers may contribute to increases in childhood homicide rates.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. A., Oliver J. E. Epidemiology and family characteristics of severely-abused children. Br J Prev Soc Med. 1975 Dec;29(4):205–221. doi: 10.1136/jech.29.4.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jason J. Child homicide spectrum. Am J Dis Child. 1983 Jun;137(6):578–581. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140320054012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jason J., Gilliland J. C., Tyler C. W., Jr Homicide as a cause of pediatric mortality in the United States. Pediatrics. 1983 Aug;72(2):191–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplun D., Reich R. The murdered child and his killers. Am J Psychiatry. 1976 Jul;133(7):809–813. doi: 10.1176/ajp.133.7.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman J. C., Kessel S. S. Racial differences in low birth weight. Trends and risk factors. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 17;317(12):749–753. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709173171207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat J. E. Characteristics of childhood homicide in Ohio, 1974-84. Am J Public Health. 1988 Jul;78(7):822–824. doi: 10.2105/ajph.78.7.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordog G. J., Wasserberger J., Schatz I., Owens-Collins D., English K., Balasubramanian S., Schlater T. Gunshot wounds in children under 10 years of age. A new epidemic. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Jun;142(6):618–622. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1988.02150060052028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. D. Parents who kill their children. Med Sci Law. 1973 Apr;13(2):120–126. doi: 10.1177/002580247301300210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons B., Downs E. F., Hurster M. M., Archer M. Child abuse: epidemiologic study of medically reported cases. N Y State J Med. 1966 Nov 1;66(21):2783–2788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkleby M. A., Fortmann S. P., Barrett D. C. Social class disparities in risk factors for disease: eight-year prevalence patterns by level of education. Prev Med. 1990 Jan;19(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0091-7435(90)90001-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


