Abstract
Heterologous highly specific antimacrophage serum (AMS) was obtained by immunizing rabbits with macrophage membranes, and subsequently absorbing the antiserum on lymphocytes (in the presence of EDTA). This AMS was highly specific against macrophages as demonstrated by cytotoxicity assays and immunofluorescent staining.
Incubation of macrophages with AMS abrogated their phagocytic activity. This inhibition of phagocytic activity could be reversed by incubating AMS-treated macrophages either in normal serum or in trypsin.
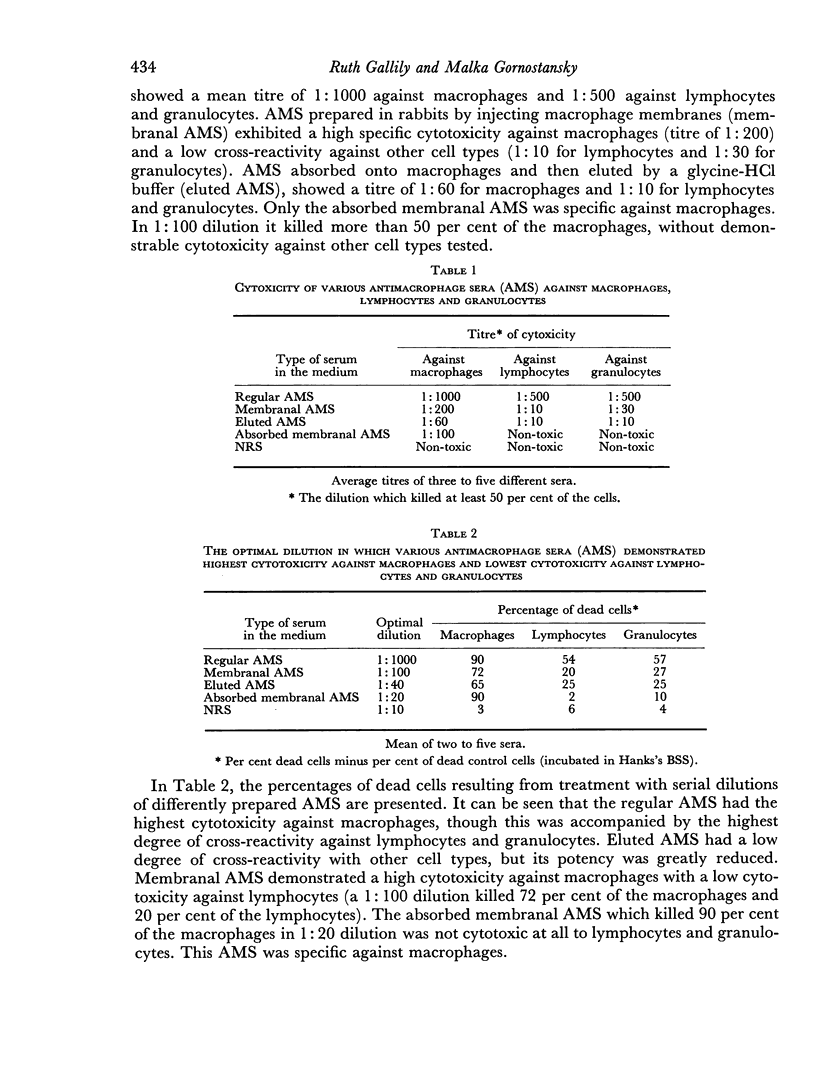
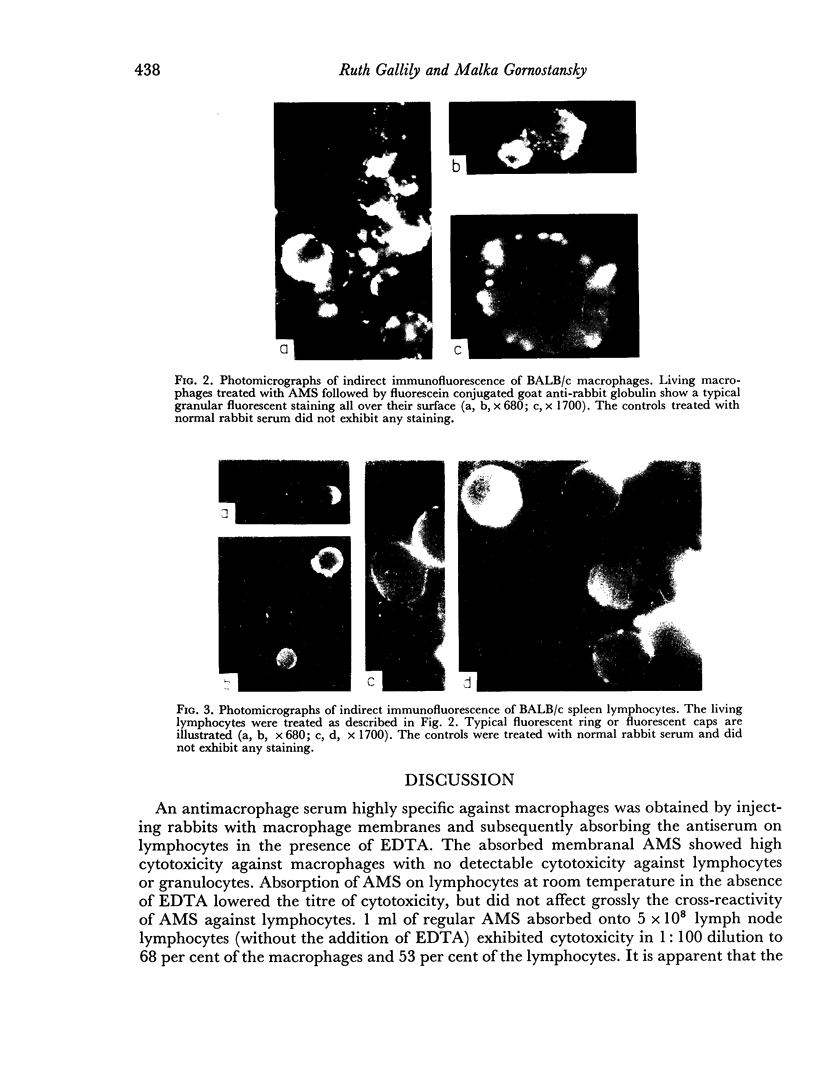
The differences in distribution and location of antigenic determinants on the surfaces of macrophages and lymphocytes was demonstrated by fluorescent staining. Distinct surface antigens, absent on lymphocytes were detected on AMS-treated macrophages.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argyris B. F., Plotkin D. H. Effect of antimacrophage serum on antibody production and phagocytosis in mice. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):372–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyse E. A., Hubbard L., Stockert E., Lamm M. E. Improved complementation in the cytotoxic test. Transplantation. 1970 Nov;10(5):446–449. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197011000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despont J. P., Cruchaud A. In vivo and in vitro effects of anti-macrophage serum. Nature. 1969 Aug 23;223(5208):838–839. doi: 10.1038/223838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyminski J. W., Argyris B. F. Prolongation of allograft survival with antimacrophage serum. Transplantation. 1969 Nov;8(5):595–601. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196911000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallily R., Feldman M. The role of macrophages in the induction of antibody in x-irradiated animals. Immunology. 1967 Feb;12(2):197–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallily R. In vitro and in vivo studies of the properties and effects of antimacrophage sers (AMS). Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Sep;9(3):381–391. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS T. N., OGBURN C. A., HARRIS S., FARBER M. B. PREPARATION BY ELUTION FROM SPECIFIC AGGREGATES OF THE ISOANTIBODY CAUSING REJECTION OF TRANSFERRED RABBIT LYMPH NODE CELLS. Transplantation. 1963 Jul;1:261–269. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196301030-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Gary G. W., Jr, Murphy F. A. In vitro and in vivo properties of antimacrophage sera. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):656–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewi G., Temple A., Nind A. P., Axelrad M. A study of the effects of anti-macrophage sera. Immunology. 1969 Jan;16(1):99–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS H. J., ANDREWS R. V. Some protective solutions for tissue, cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1959 Mar;16(3):678–682. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(59)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panijel J., Cayeux P. Immunosuppressive effects of macrophage antiserum. Immunology. 1968 Jun;14(6):769–780. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulitzeanu D., Slavin M., Karaman H., Goldman W. Antigenic components of rat connective tissue. II. Fluorescent antibody studies with antisera to connective tissue antigens. Br J Exp Pathol. 1967 Apr;48(2):159–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Properties and some uses of anti-macrophage antibodies. Nature. 1968 Apr 6;218(5136):36–38. doi: 10.1038/218036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]