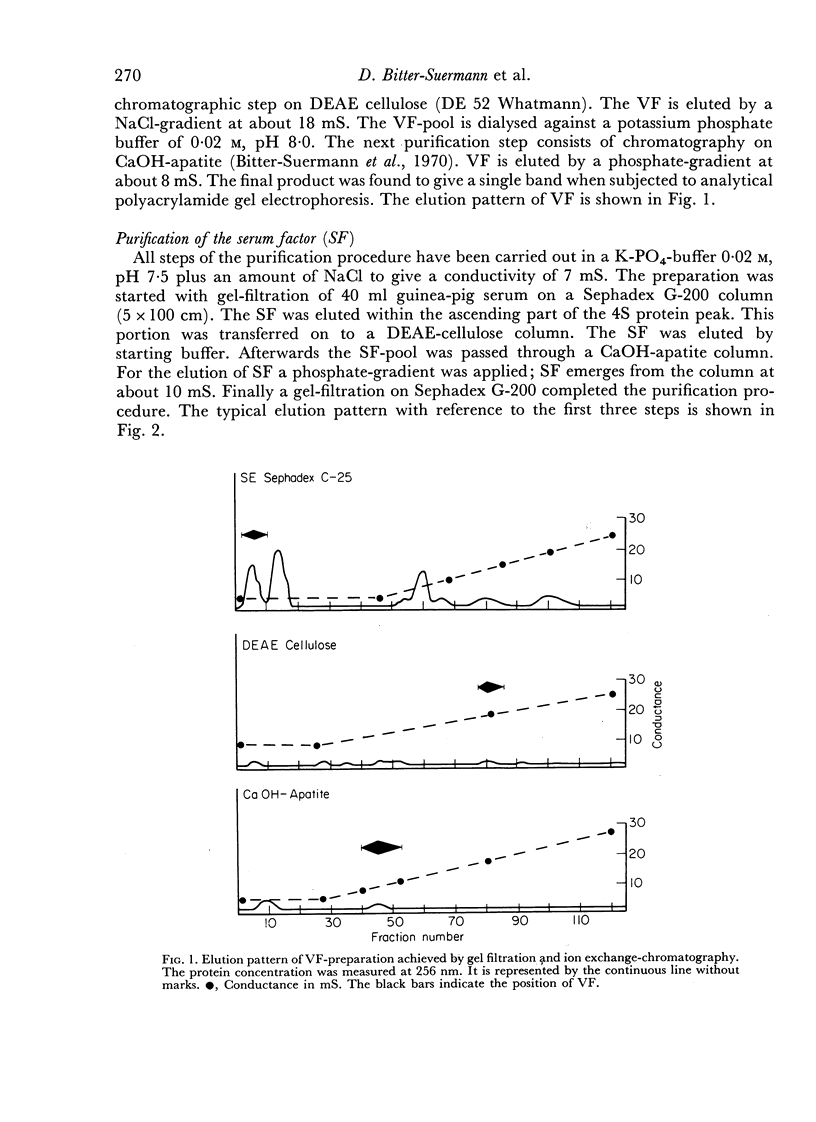
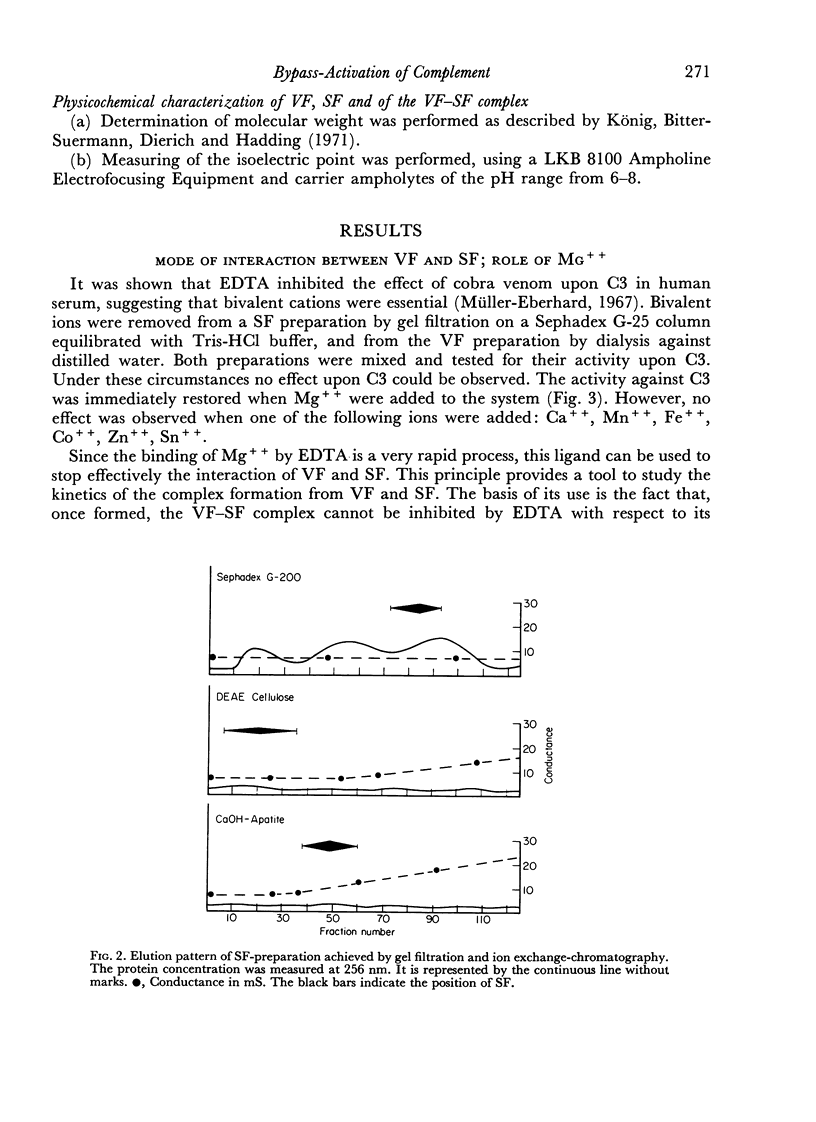
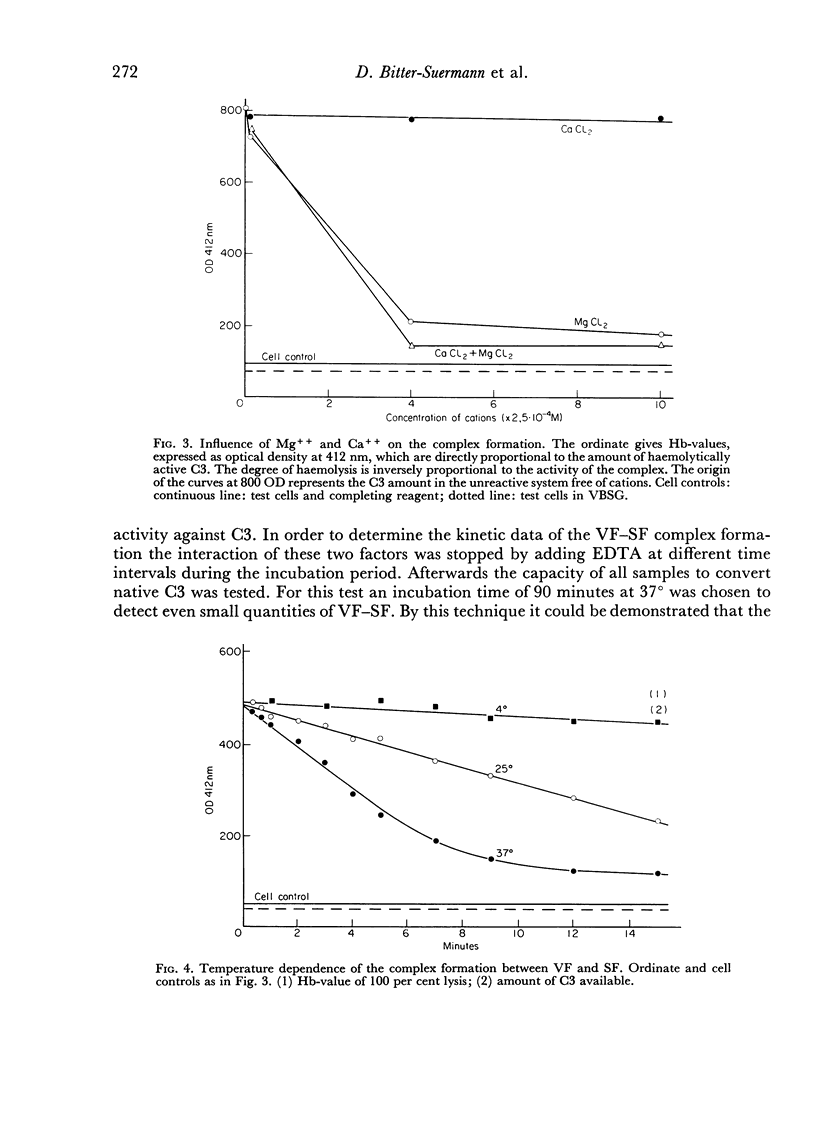
Abstract
Antibody independent activation of the complement system starting with C3 can be achieved by means of a purified factor from cobra venom (VF), which interacts with a purified serum factor (SF). The latter is a normal constituent of guinea-pig and human serum (C3-proactivator).
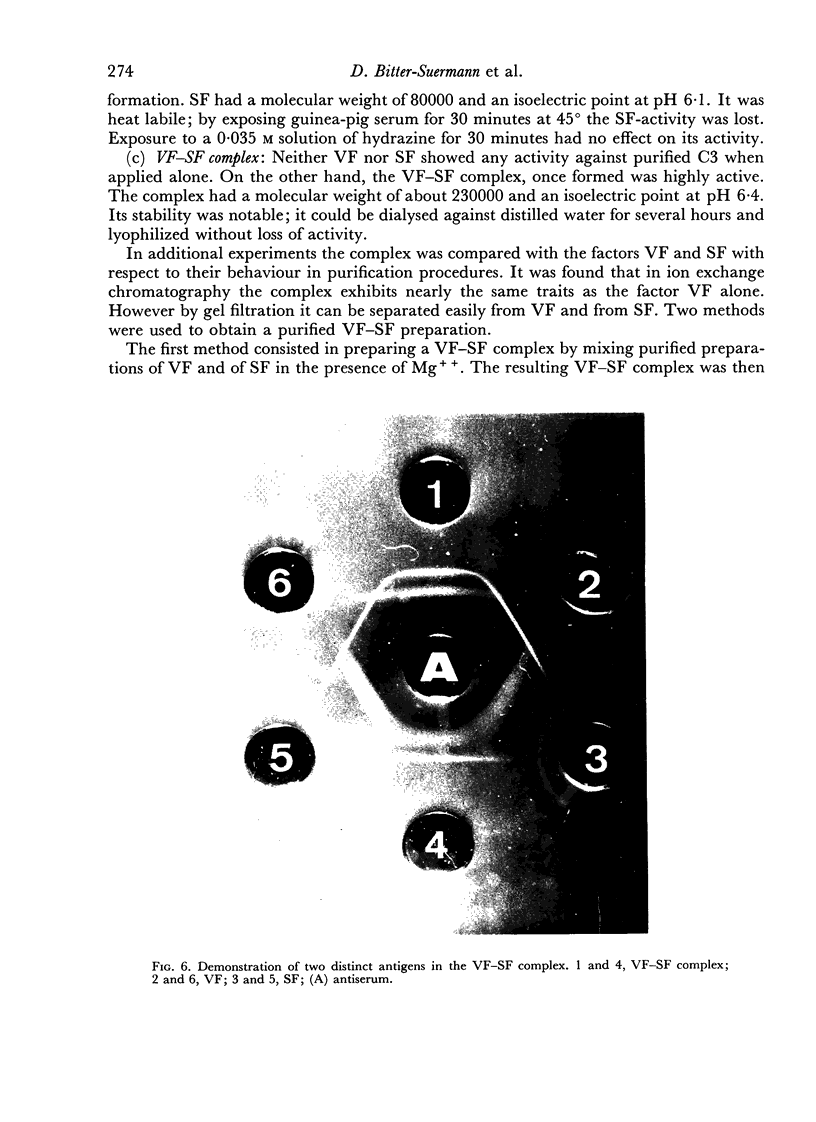
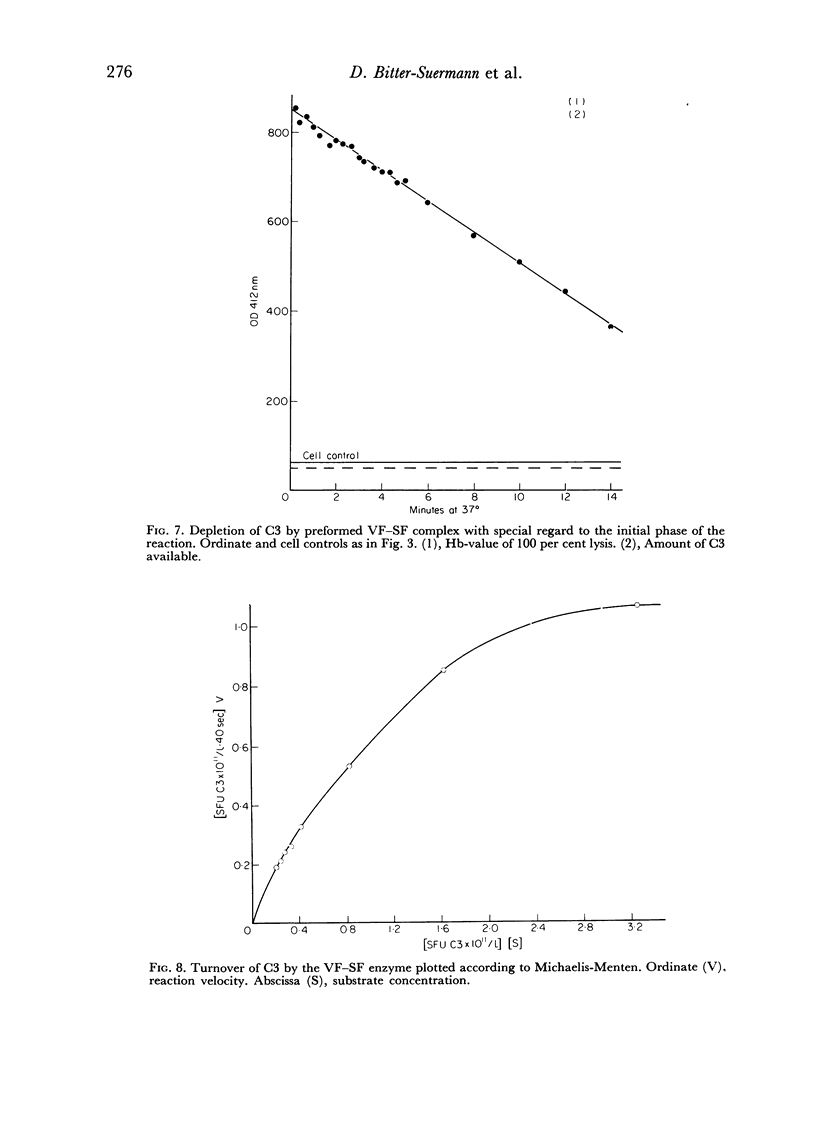
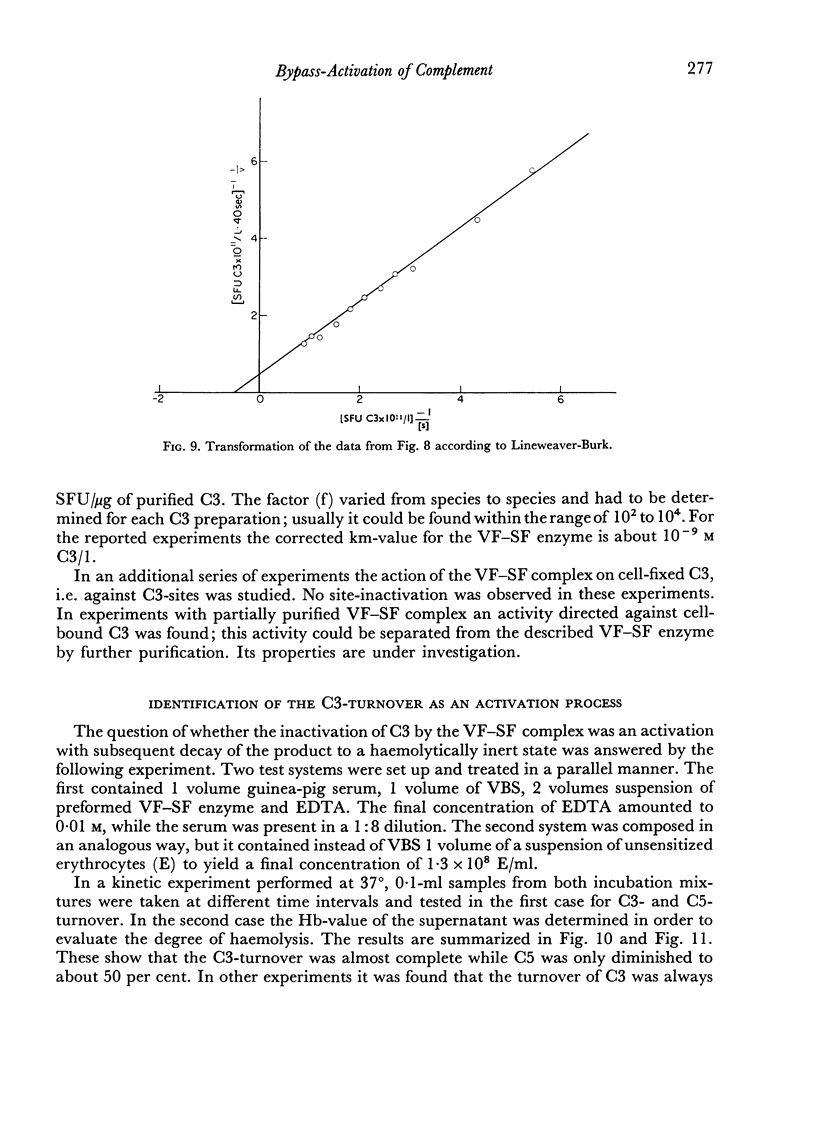
The interaction between VF and SF is Mg+ + dependent and leads to the formation of a complex. Immunological analysis reveals that both VF- and SF-antigens are contained in the complex. The VF—SF complex activates enzymatically isolated C3, which in the presence of the subsequent components yields all effects of the normal complement sequence.
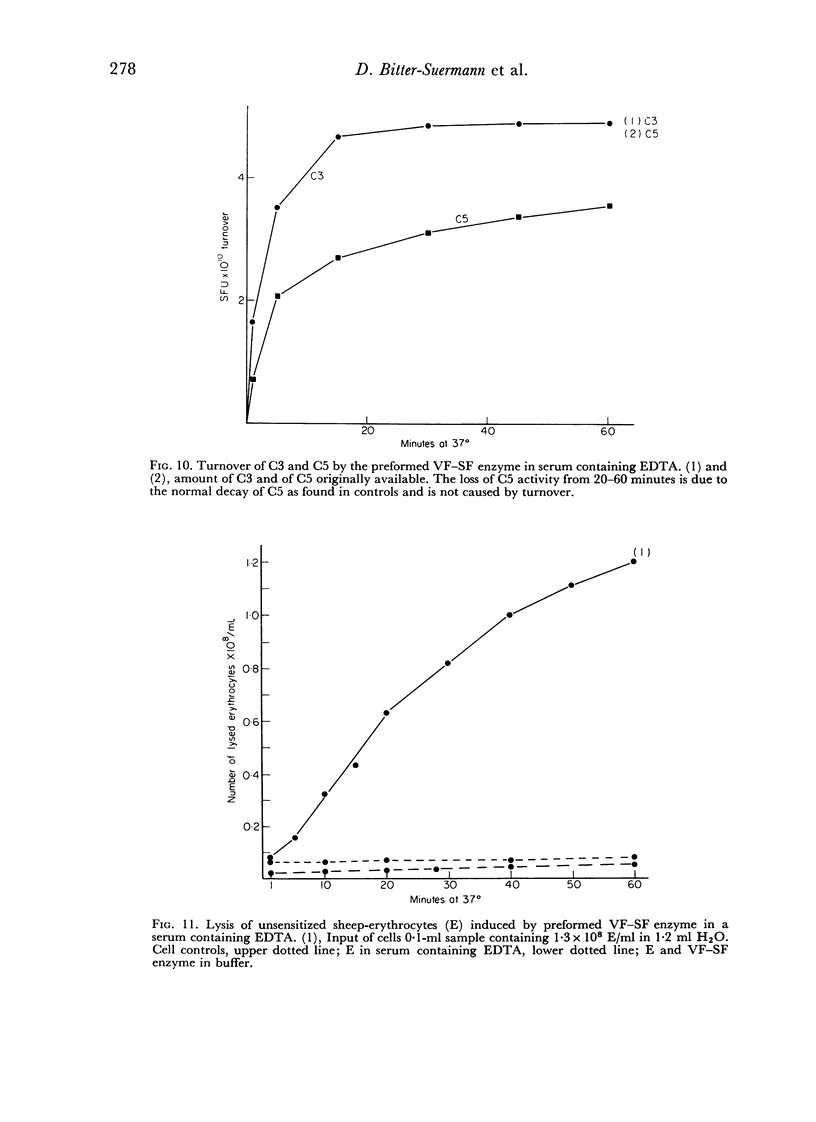
Purified C5 is not affected by the complex. Its activation is mediated by activated C3.
The VF—SF system represents a model for direct activation of C3 to C9 independent of antibody, C1, C4 and C2. An analogous pathway of alternate complement activation might be used by other substances, e.g. endotoxin, guinea-pig γ1-immune aggregates and zymosan. The corresponding serum factors are under investigation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORSOS T., RAPP H. J. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF THE FIRST COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT AND ITS ASSAY ON A MOLECULAR BASIS. J Immunol. 1963 Dec;91:851–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballow M., Cochrane C. G. Two anticomplementary factors in cobra venom: hemolysis of guinea pig erythrocytes by one of them. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):944–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter-Suermann D., Hadding U., Melchert F., Wellensiek H. J. Independent and consecutive action of the complement components C5, C6 and C7 in immune hemolysis. I. Preparation of EAC1-5 with purified guinea pig C3 and C5. Immunochemistry. 1970 Dec;7(12):955–965. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Aikin B. S. Depletion of plasma complement in vivo by a protein of cobra venom: its effect on various immunologic reactions. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):55–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Ultracentrifugation of the first component of complement: effects of ionic strength. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):808–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierich M. P., Bitter-Suermann D., König W., Hadding U. Formation and function of a complement-activating enzyme generated from factors of guinea pig serum and cobra venom. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Aug;1(4):309–311. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P. G., Wellensiek H. J. Multiple nature of the third component of guinea-pig complement. I. Separation and characterization of three factors a, b, and c, essential for haemolysis. Immunology. 1965 Jun;8(6):590–603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König W., Bitter-Suermann D., Dierich M., Hadding U. Physicochemical characterization of the fifth (C5), sixth (C6), seventh (C7), eighth (C8) and ninth (C9) component of guinea pig complement. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Nov;1(5):372–376. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thompson R. A. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. II. The characterization of activated reactor as C56 and the participation of C8 and C9. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):643–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering R. J., Wolfson M. R., Good R. A., Gewurz H. Passive hemolysis by serum and cobra venom factor: a new mechanism inducing membrane damage by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):521–527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringelmann R., Opferkuch W., Röllinghoff M., Loos M. Komplementmessungen mit Hilfe des Mikrolitersystems. Z Med Mikrobiol Immunol. 1969;154(4):329–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Lachmann P. J. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. I. The characterization of the indicator factor and its identification as C7. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):629–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. A., Rowe D. S. Reactive haemolysis--a distinctive form of red cell lysis. Immunology. 1968 May;14(5):745–762. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellensiek H. J., Klein P. G. Multiple nature of the third component of guinea-pig complement. II. Separation and description of two additional factors beta and d; preparation and characterization of four intermediate products. Immunology. 1965 Jun;8(6):604–617. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]