Abstract
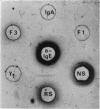
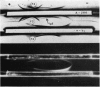
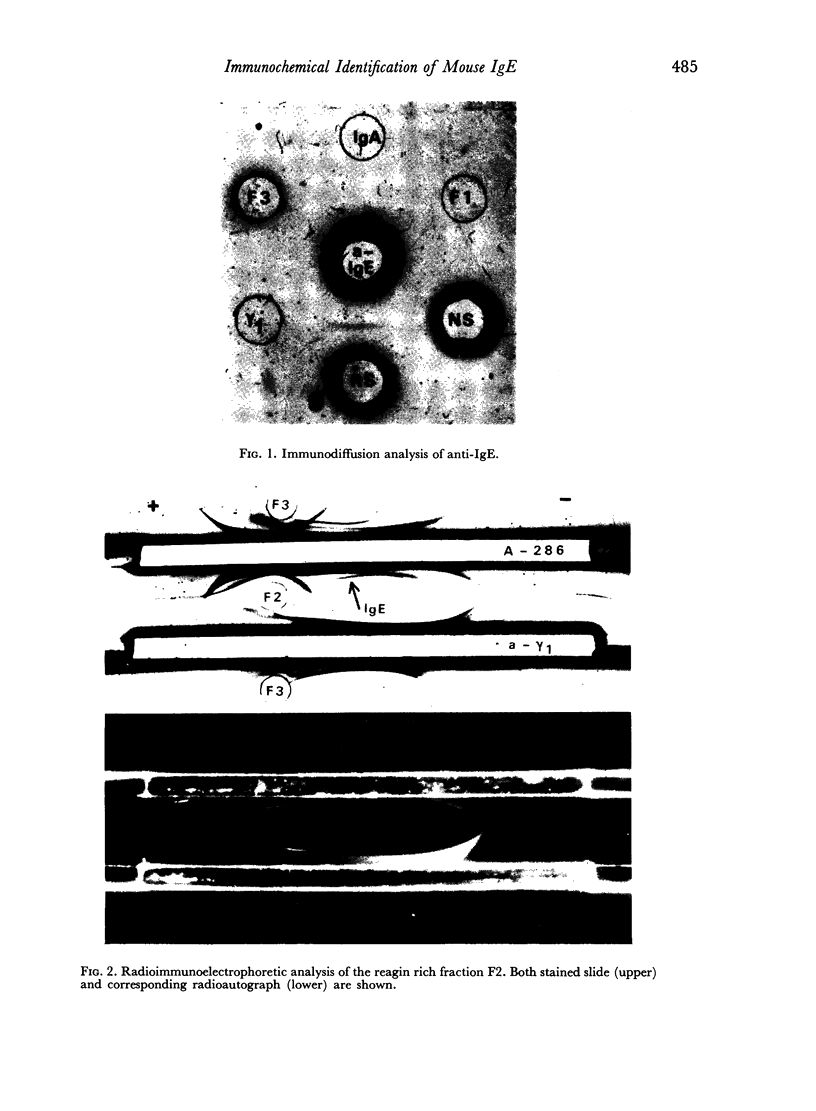
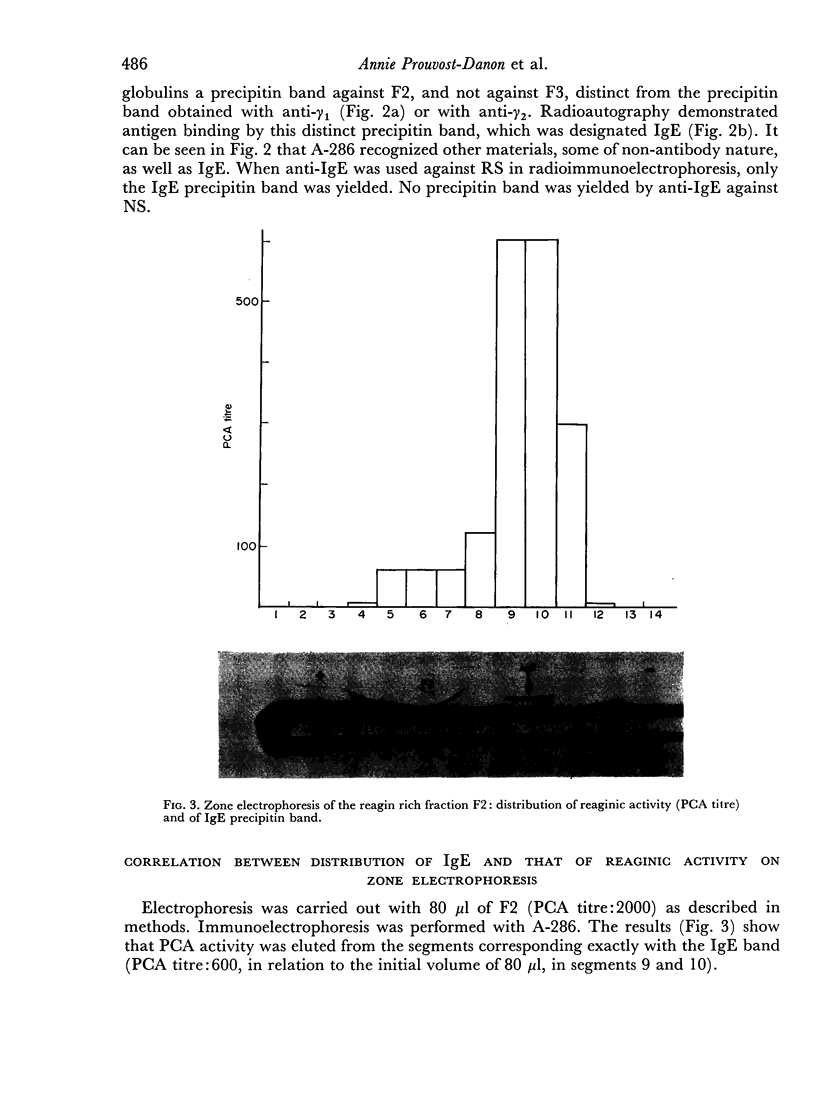
Immunochemical identification of a distinct immunoglobulin class associated with mouse reaginic antibody and designated IgE has been performed. An antiserum against mouse reaginic antibody was prepared in rats by immunization with homologous peritoneal mast cells sensitized with mouse reaginic antibody. This antiserum, after adequate absorption, recognized only one component existing in mouse serum or fractions of serum containing reaginic antibody. This component was not any of the already known γ1, γ2, IgA or IgM immunoglobulins; its immunoglobulin nature was indicated by its antigen-binding capacity in radioimmunodiffusion analysis. Fractionation experiments (zone electrophoresis, gel filtration on Sephadex G-200) showed that there was a strict association between reaginic anaphylactic activity and IgE immunoglobulin. Molecular weight of IgE was found to be about 200,000. In biological tests, anti-IgE neutralized anaphylactic activity attributed to reaginic antibody, but not that attributed to γ1-antibody. Anti-IgE degranulates normal and sensitized mouse peritoneal mast cells, and rat peritoneal mast cells after they have been sensitized by mouse reaginic antibody.
Full text
PDF



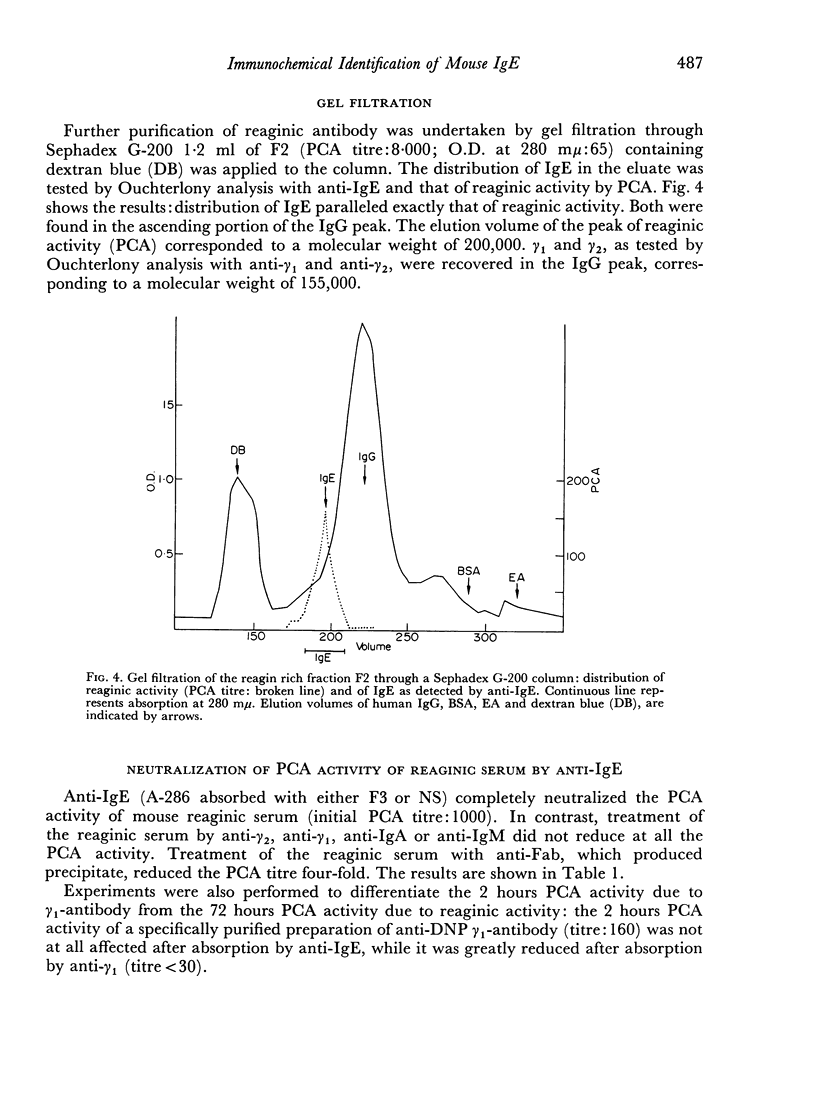
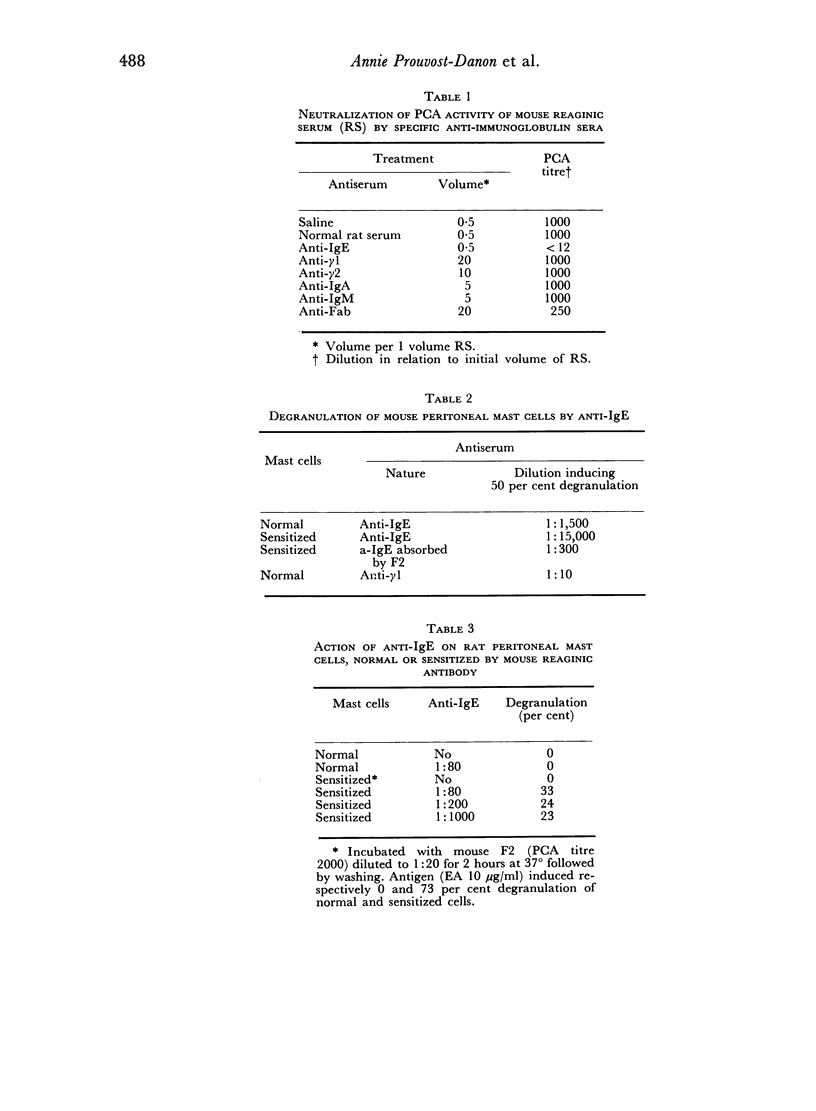



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth W. F., Fahey J. L. Heterologous and homologous skin-sensitizing activity of mouse 7S gamma 1- and 7S gamma 2-globulins. Nature. 1965 May 15;206(985):730–731. doi: 10.1038/206730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. D., Fredholm B., Haegermark O. Studies on the time course of histamine release and morphological changes induced by histamine liberators in rat peritoneal mast cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Dec;71(4):270–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., WUNDERLICH J., MISHELL R. THE IMMUNOGLOBULINS OF MICE. I. FOUR MAJOR CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS: 7S GAMMA-2-, 7S GAMMA-1-, GAMMA-1A (BETA-2A)-, AND 18S GAMMA-1M-GLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:223–242. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., WUNDERLICH J., MISHELL R. THE IMMUNOGLOBULINS OF MICE. II. TWO SUBCLASSES OF MOUSE 7S GAMMA-2-GLOBULINS: GAMMA-2A- AND GAMMA-2B-GLOBULINS. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:243–251. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARAH F. S., KERN M., EISEN H. N. The preparation and some properties of purified antibody specific for the 2,4-dinitrophenyl group. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1195–1210. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer D. K., Kickhöfen B., Schmid T. Detection of homocytotropic antibody associated with a unique immunoglobulin class in the bovine species. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Aug;1(4):249–257. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Hornbrook M. M. A unique rabbit immunoglobulin having homocytotropic antibody activity. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jun;7(6):515–528. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Hornbrook M. M. Physico-chemical properties of human reaginic antibody. IV. Presence of a unique immunoglobulin as a carrier of reaginic activity. J Immunol. 1966 Jul;97(1):75–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Hornbrook M. M. Physicochemical properties of reaginic antibody. V. Correlation of reaginic activity wth gamma-E-globulin antibody. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):840–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Johansson S. G., Bennich H. Histamine release from human leukocytes by anti-gamma E antibodies. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):884–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Tomioka H., Ishizaka K. Degranulation of human basophil leukocytes by anti-gamma E antibody. J Immunol. 1971 Mar;106(3):705–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones V. E., Edwards A. J. Preparation of an antiserum specific for rat reagin (rat E?). Immunology. 1971 Aug;21(2):383–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. B., Vaz N. M. Effect of combinations of inbred strain, antigen, and antigen dose on immune responsiveness and reagin production in the mouse. A potential mouse model for immune aspects of human atopic allergy. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(2-3):156–171. doi: 10.1159/000230343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota I., Peixoto J. M. A skin-sensitizing and thermolabile antibody in the mouse. Life Sci. 1966 Sep;5(18):1723–1728. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90108-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota I., Sadun E. H., Bradshaw R. M., Gore R. W. The immunological response of mice infected with Trichinella spiralis. Biological and physico-chemical distinction of two homocytotropic antibodies. Immunology. 1969 Jan;16(1):71–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSENZWEIG R. S., MERRYMAN C., BENACERRAF B. ELECTROPHORETIC SEPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF MOUSE ANTIHAPTEN ANTIBODIES INVOLVED IN PASSIVE CUTANEOUS ANAPHYLAXIS AND PASSIVE HEMOLYSIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:315–328. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins E. H., Sado T., Makinodan T. Recruitment and proliferation of immunocompetent cells during the log phase of the primary antibody response. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):668–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouvost-Danon A., Binaghi R. In vitro sensitization of mouse peritoneal mast cells with reaginic antibody. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):66–67. doi: 10.1038/228066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouvost-Danon A., Binaghi R. Reaginic antibody in adult and young mice. Production and biological properties. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;38(6):648–656. doi: 10.1159/000230320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouvost-Danon A., Lima M. S., Javierre M. Q. Active anaphylactic reaction in mouse peritoneal mast cells in vitro. Life Sci. 1966 Feb;5(4):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouvost-Danon A., Peixoto J. M., Javierre M. Q. Antigen-indued histamine release from peritoneal mast cells of mice producing reagin-like antibody. Immunology. 1968 Aug;15(2):271–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouvost-Danon A., Peixoto J. M., Javierre M. Q. Immune injury of mouse peritoneal mast cells by antibodies to mouse serum and mouse gamma-globulin. Immunology. 1970 May;18(5):749–758. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouvost-Danon A., Peixoto J. M., Queiroz Javierre M. Reagin-like antibody mediated passive anaphylactic reaction in mouse peritoneal mast cells in vitro. Life Sci. 1967 Sep 1;6(17):1793–1801. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90207-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revoltella R., Ovary Z. Reaginic antibody production in different mouse strains. Immunology. 1969 Jul;17(1):45–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Orange R. P., Austen K. F. Immunochemical and biologic properties of rat IgE. I. Immunochemical identification of rat IgE. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1082–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAGI Y., MAIER P., PRESSMAN D. Immunoelectrophoretic identification of guinea pig anti-insulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1962 Nov;89:736–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]