Abstract
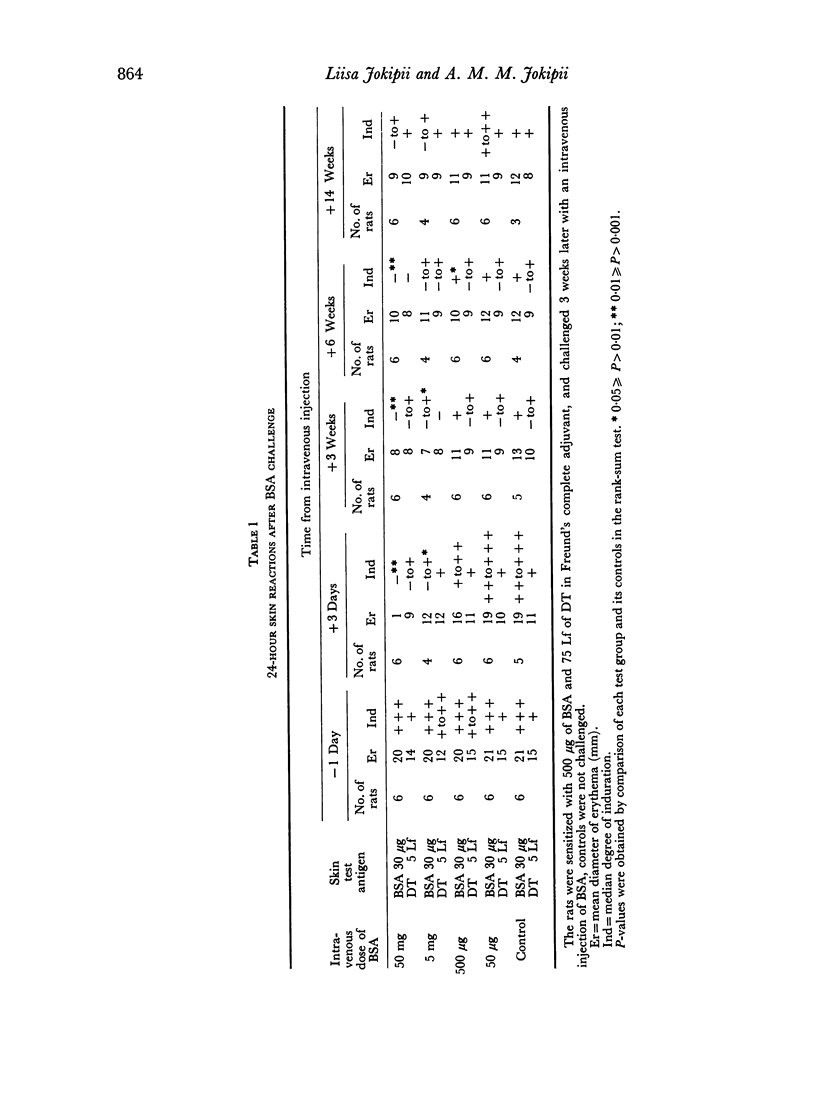
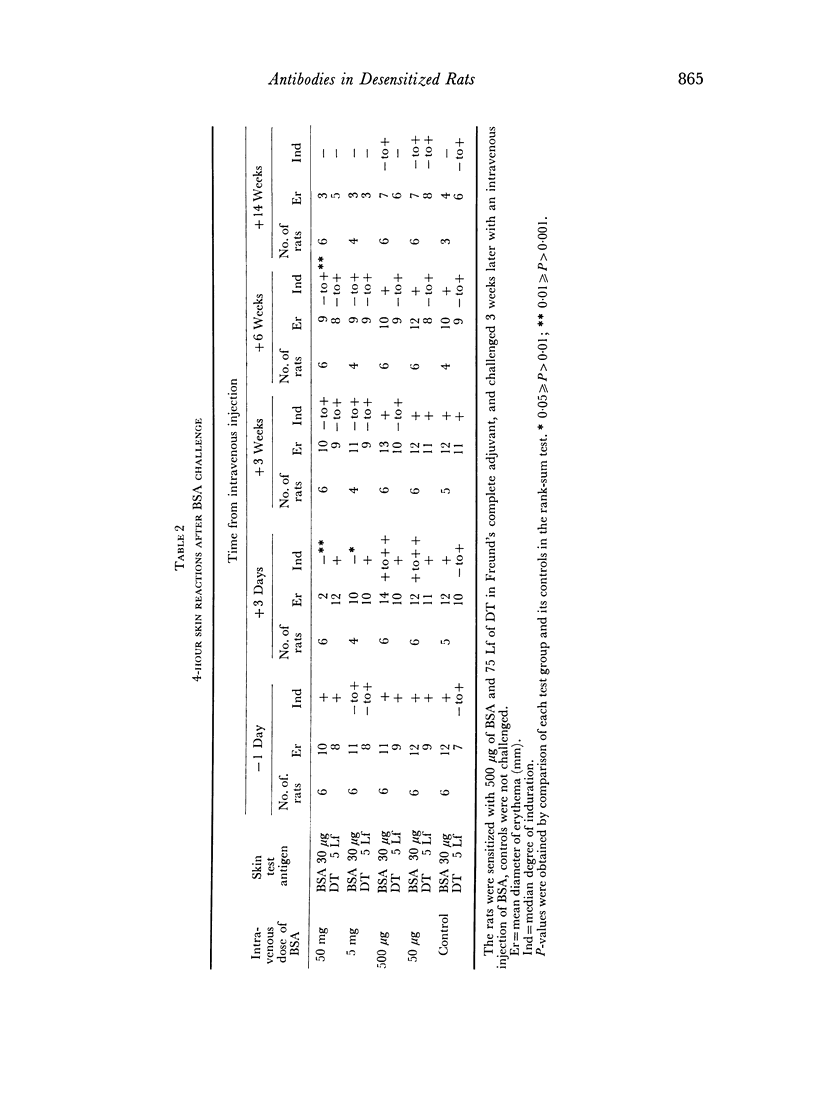
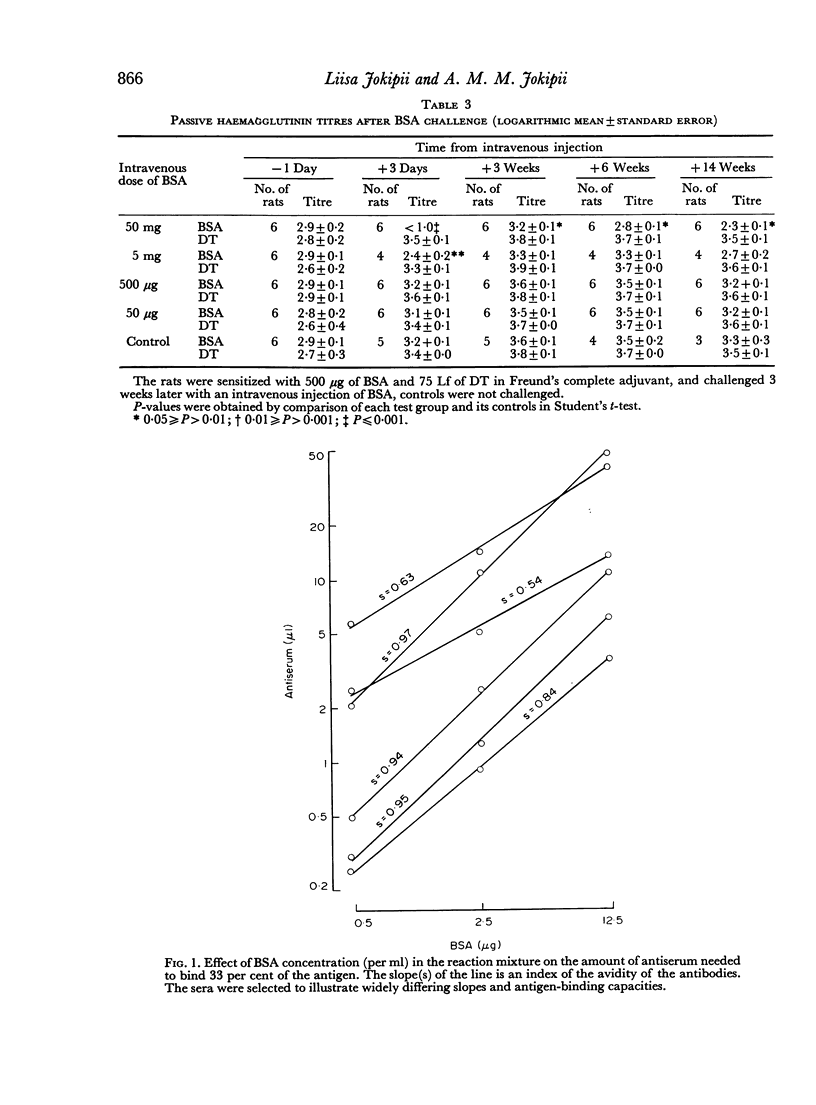
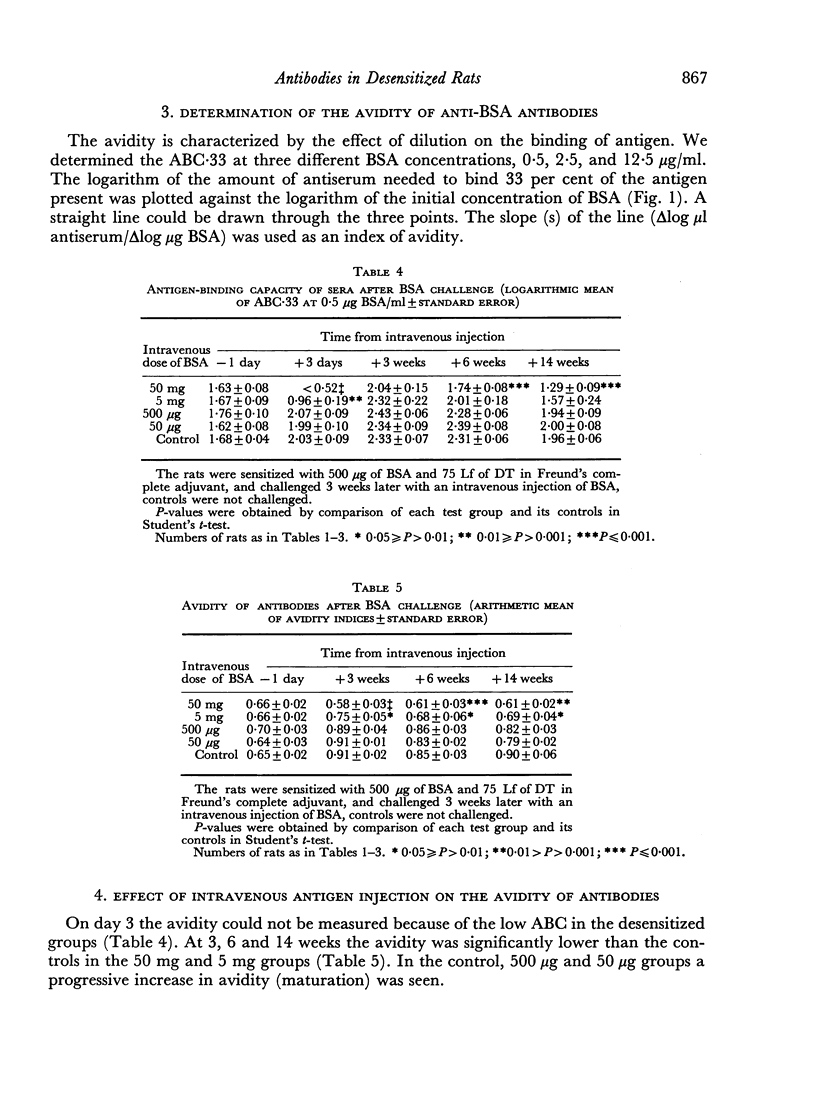
Rats with delayed hypersensitivity to bovine serum albumin (BSA) and diphtheria toxoid were specifically desensitized by an intravenous injection of BSA. The degree of desensitization was positively related to the dose of antigen. The 4-hour skin reactions to BSA were weaker, and the passive haemagglutinin titres, antigen-binding capacity and average avidity of the antibodies were lower in the desensitized rats than in controls. The suppression of delayed hypersensitivity was apparently not caused by increased circulating antibody activity, but by a cellular defect or a humoral blocking factor.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B. Studies on the regulation of avidity at the level of the single antibody-forming cell. The effect of antigen dose and time after immunization. J Exp Med. 1970 Jul 1;132(1):77–88. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson B., Wigzell H. Studies on antibody avidity at the cellular level. Effects of immunological paralysis and administered antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Nov;1(5):384–390. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L. Antigen-mediated depression of delayed hypersensitivity. Br Med Bull. 1967 Jan;23(1):24–29. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrad M. A. Suppression of delayed hypersensitivity by antigen and antibody. Is a common precursor cell responsible for both delayed hypersensitivity and antibody formation? Immunology. 1968 Aug;15(2):159–171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada F., Schmidt D., Strom R. Determination of avidity of anti-albumin antibodies in the mouse. Influence of the number of cells transferred on the quality of the secondary adoptive response. Immunology. 1969 Aug;17(2):189–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N., Chaperon E. A., Triplett R. F. Thymus-marrow cell combinations. Synergism in antibody production. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Aug-Sep;122(4):1167–1171. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRESSER D. W. Elimination of 131-I-labelled protein antigens from the circulation of the mouse. Immunology. 1960 Oct;3:289–295. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J. R., de Weck A. L., Geleick H. Studies on the induction of immunological tolerance by antigen in guinea-pigs already sensitized to dinitrochlorobenzene. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Jan;8(1):131–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S. Studies on the mechanism of suppression of the immune response by antibody. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;40(3):372–381. doi: 10.1159/000230420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez L., Bloom B. R., Blume M. R., Oettgen H. F. On the number and nature of antigen-sensitive lymphocytes in the blood of delayed-hypersensitive human donors. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):740–751. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokipii L. Disappearance of the delayed hypersensitivity reaction after intravenous antigen injection in the rat and guinea pig. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1970;48(4):226–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaliss N. Dynamics of immunologic enhancement. Transplant Proc. 1970 Mar;2(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreth H. W., Williamson A. R. Cell surveillance model for lymphocyte cooperation. Nature. 1971 Dec 24;234(5330):454–456. doi: 10.1038/234454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnas J. L., Fitch F. W. Immunologic competence of thymectomized rats to several soluble and particulate antigens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;30(3):217–230. doi: 10.1159/000229807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polák L., Turk J. L. Studies on the effect of systemic administration of sensitizers in guinea-pigs with contact sensitivity to inorganic metal compounds. 3. The effect of immunosuppressive agents on enhancing the unresponsiveness of already sensitized animals and an investigation of the action of the epicutaneous test within twenty-four hours. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Apr;4(4):423–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roitt I. M., Greaves M. F., Torrigiani G., Brostoff J., Playfair J. H. The cellular basis of immunological responses. A synthesis of some current views. Lancet. 1969 Aug 16;2(7616):367–371. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92712-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. The influence of amount and avidity of persisting primary antibodies on the secondary response to human serum albumin in rabbits. Immunology. 1971 Sep;21(3):475–481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAVITSKY A. B. Micromethods for the study of proteins and antibodies. I. Procedure and general applications of hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition reactions with tannic acid and protein-treated red blood cells. J Immunol. 1954 May;72(5):360–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein A. M., Borek F. Desensitization studies of delayed hypersensitivity, with special reference to the possible role of high-affinity antibodies. J Immunol. 1966 Jun;96(6):953–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda S., Schlamowitz M. Studies of 125I trace labeling of immunoglobulin G by chloramine-T. Immunochemistry. 1970 Nov;7(11):885–898. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek Z. Suppression of delayed hypersensitivity in rabbits by means of immune sera. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1969;17(6):751–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


