Full text
PDF

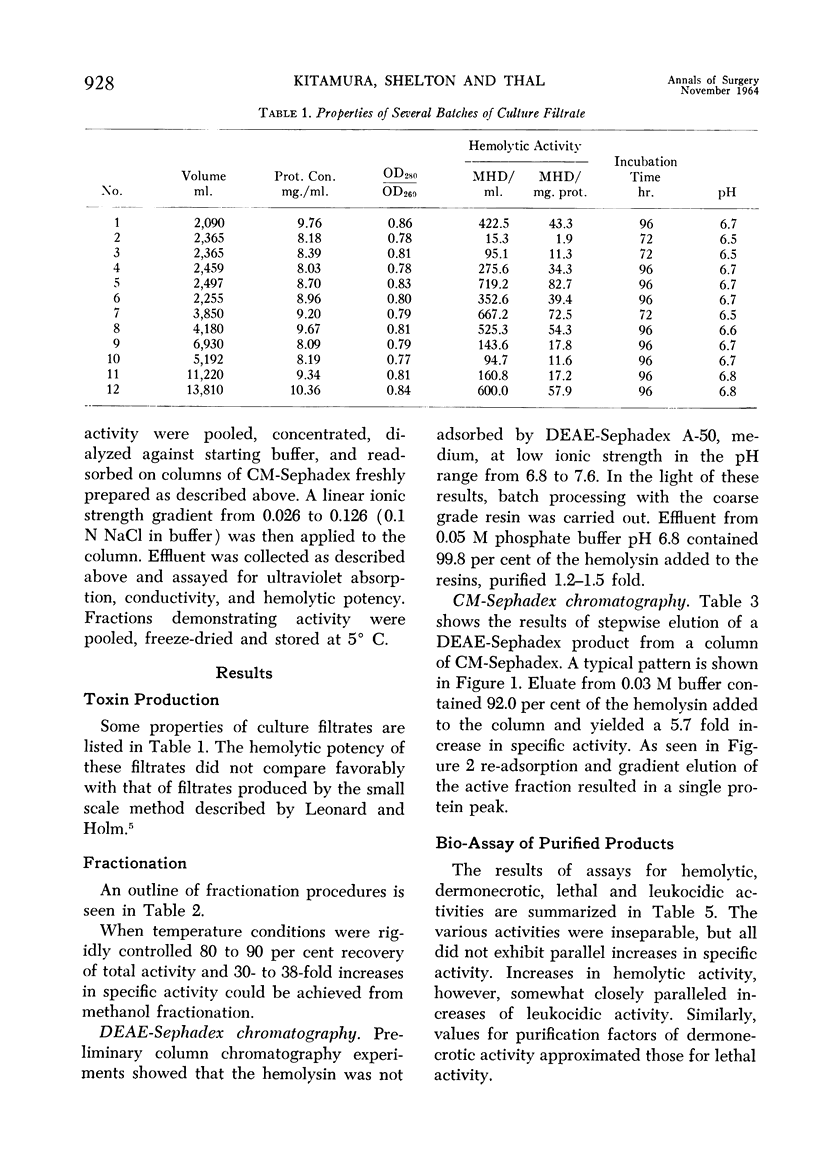

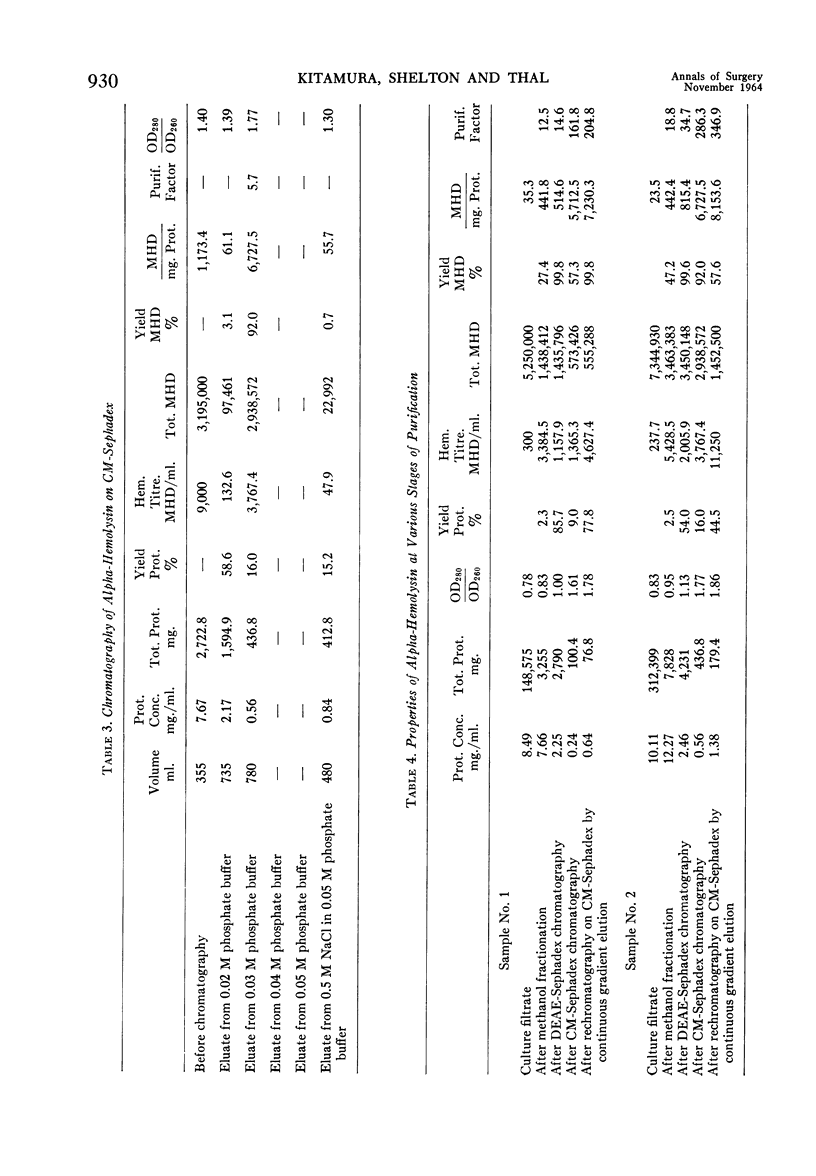
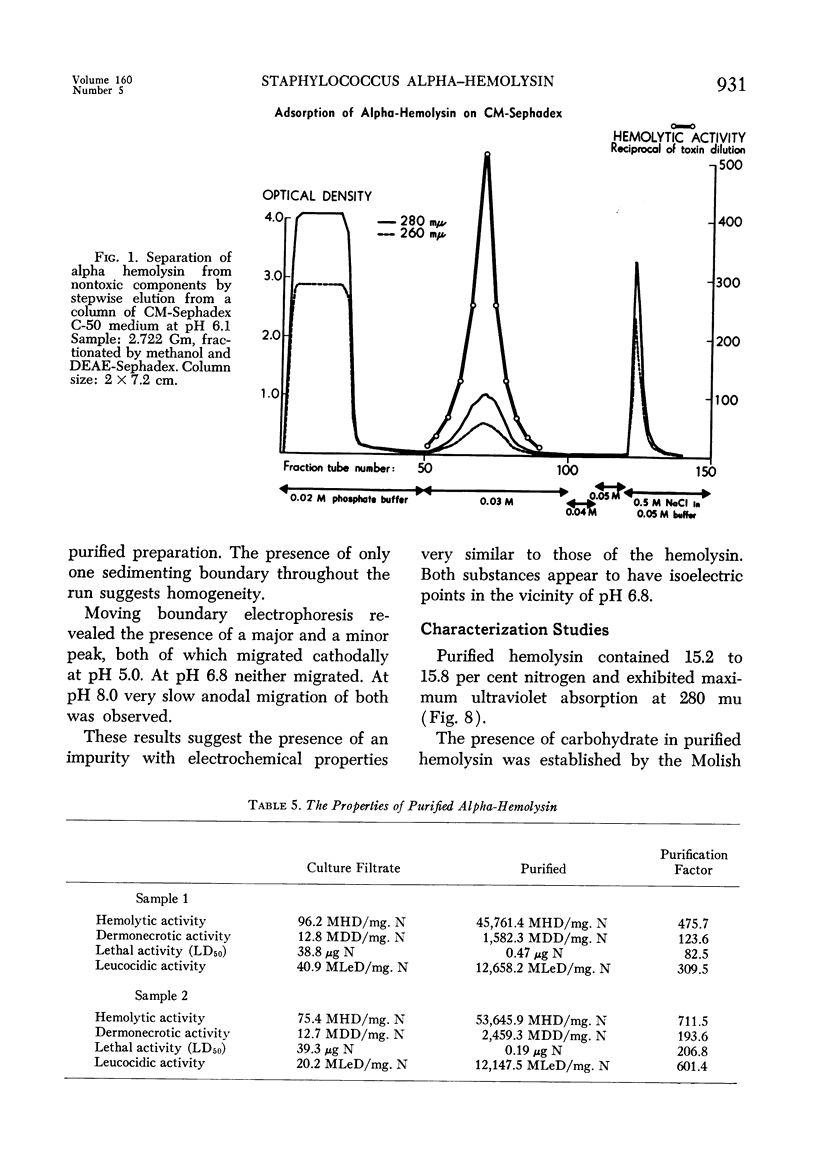
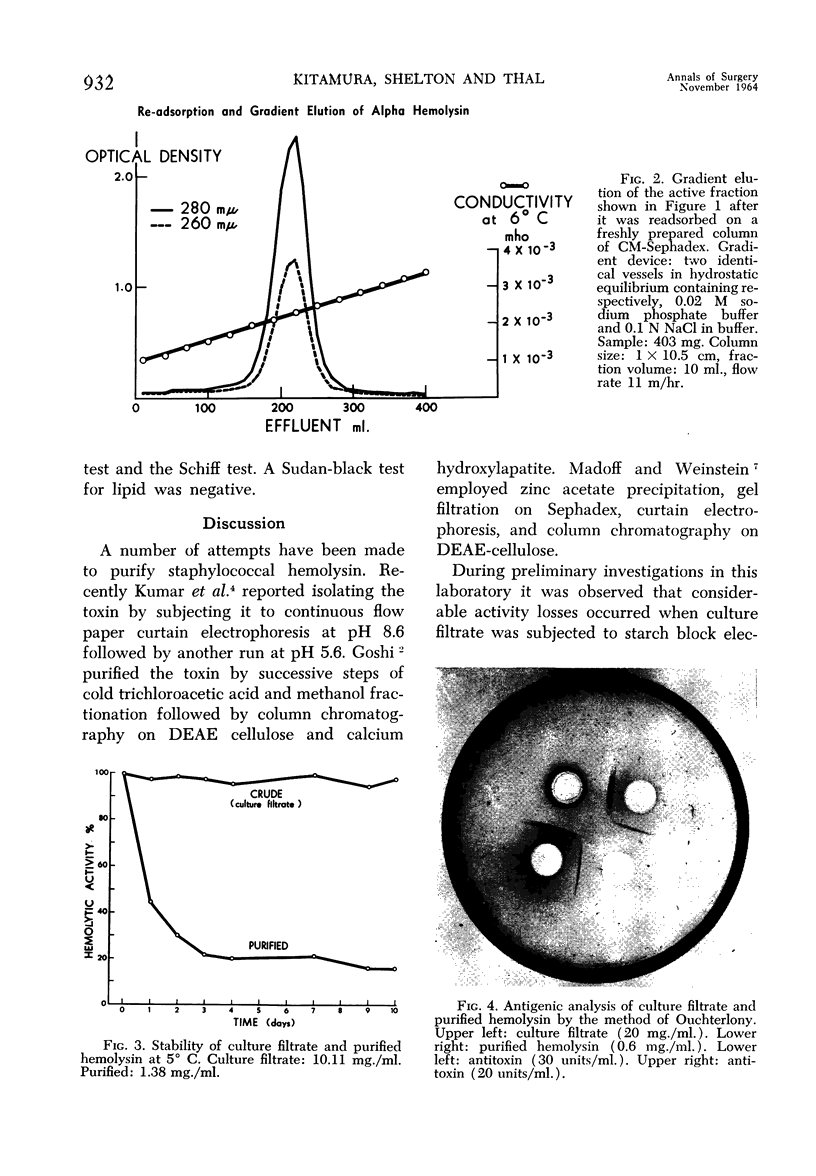

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GOSHI K., CLUFF L. E., NORMAN P. S. Studies on the pathogenesis of staphylococcal infection. V. Purification and characterization of staphylococcal alpha hemolysin. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1963 Jan;112:15–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON A. W., LITTLE R. M. Staphylococcal toxins. I. Factors affecting the hemolytic activity of alpha toxin. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Feb;3(1):47–54. doi: 10.1139/m57-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADOFF M. A., WEINSTEIN L. Purification of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:914–918. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.914-918.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
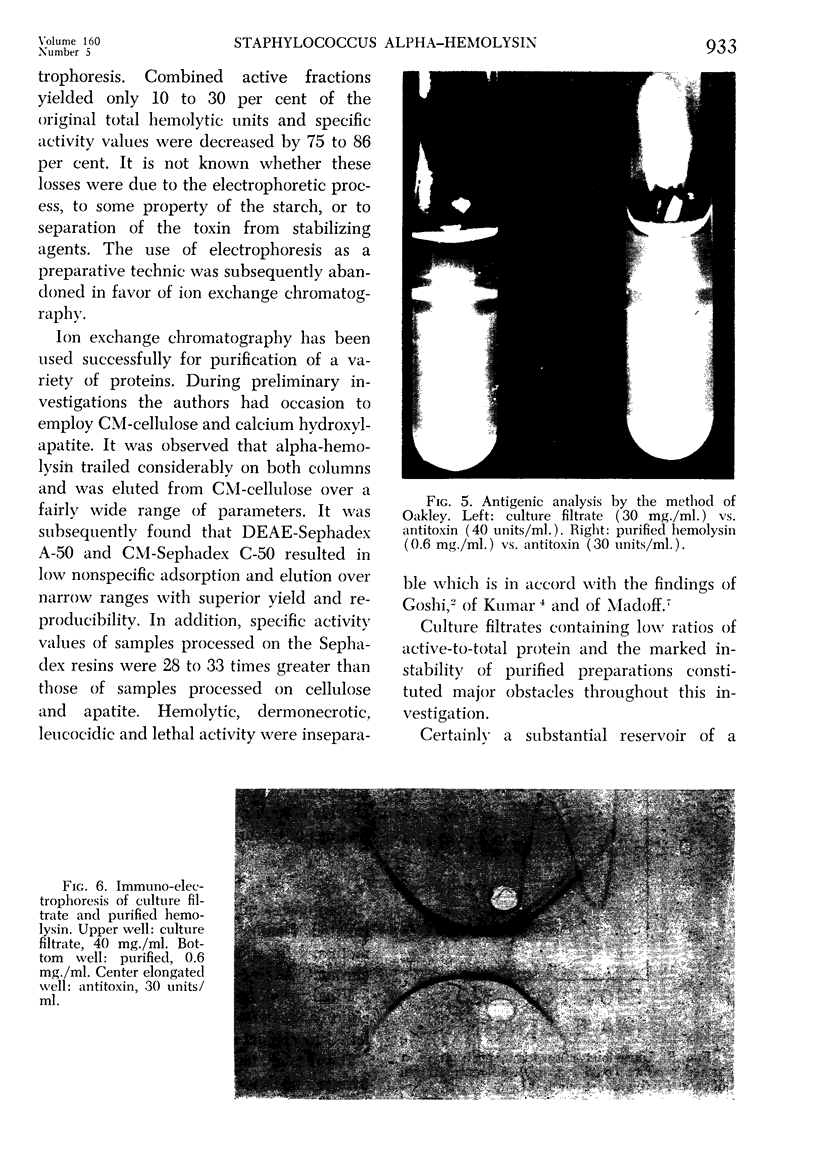
- OAKLEY C. L., FULTHORPE A. J. Antigenic analysis by diffusion. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jan;65(1):49–60. doi: 10.1002/path.1700650105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
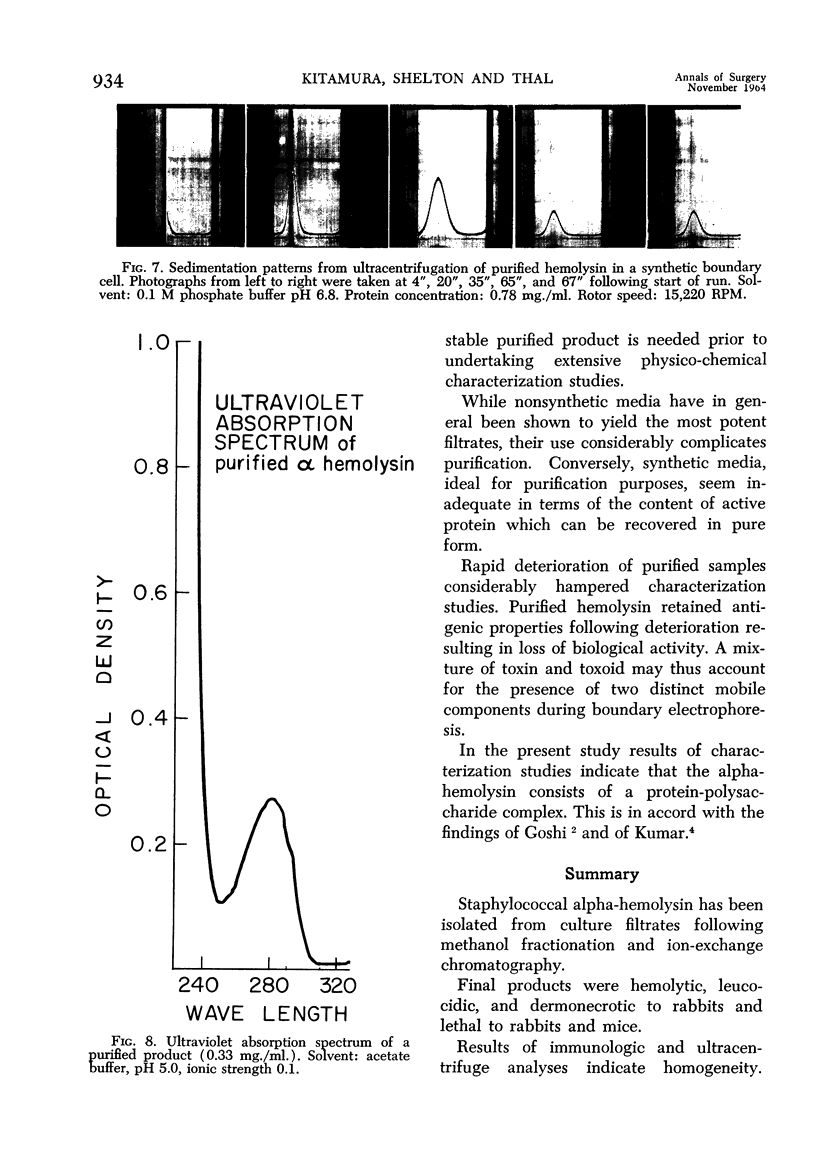
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAL A. P., EGNER W. The site of action of the Staphylococcus alpha toxin. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:67–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODIN A. M. Fractionation of a leucocidin from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1959 Oct;73:225–237. doi: 10.1042/bj0730225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]