Abstract
The cytotoxic effect of normal human blood lymphocytes on Chang cells in tissue culture was investigated. Cell damage was measured by release of 51Cr from pre-labelled tissue culture `target' cells. This method was sensitive and rendered highly reproducible results. Released 51Cr was not re-utilized.
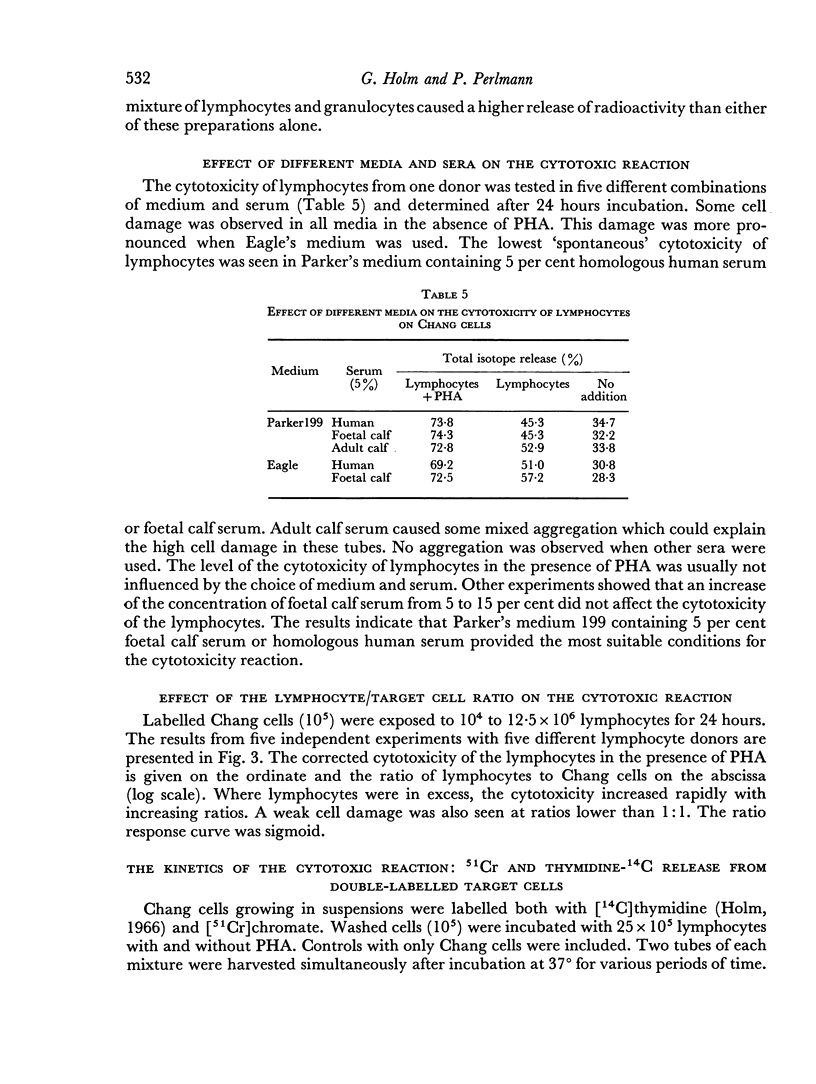
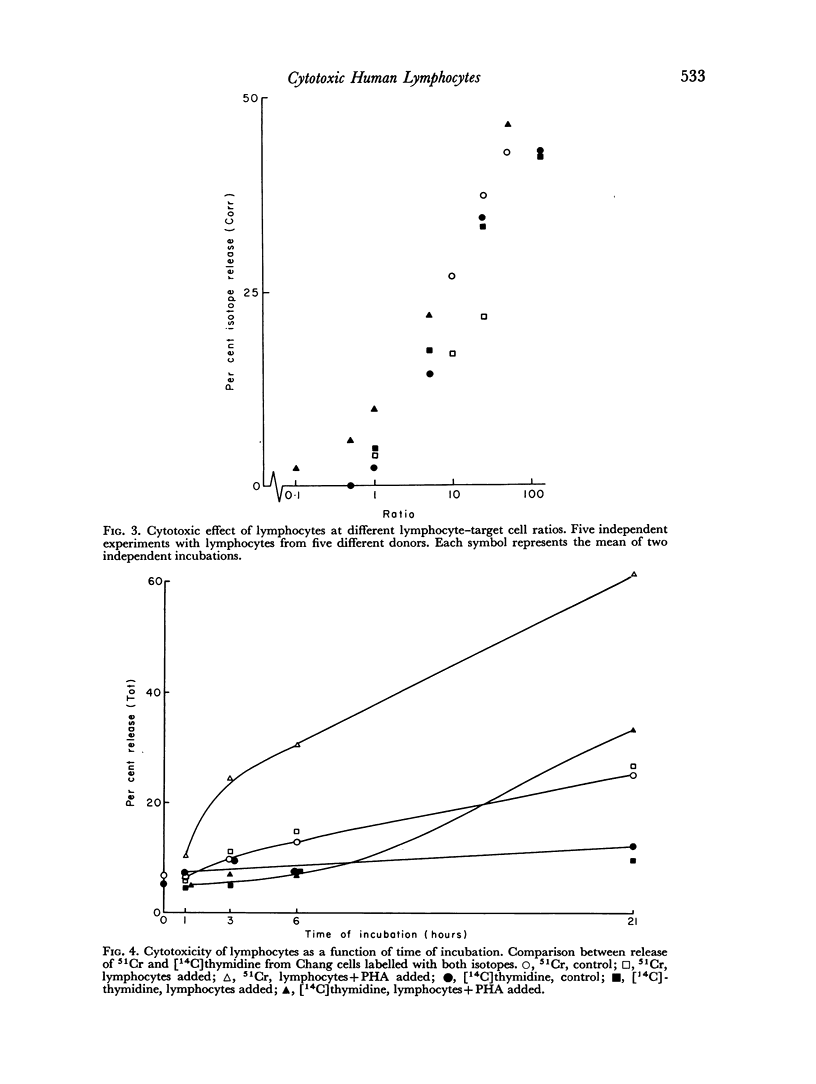
About 25 per cent of the 51Cr was spontaneously released from labelled Chang cells when incubated for 24 hours at 37°. Lymphocytes at a lymphocyte/Chang cell ratio of 25:1 led to a slight increase of this release. When phytohaemagglutinin was also present, about 50–60 per cent of the isotope appeared in the medium. Under these conditions target cells were significantly damaged within 1 hour. At a lymphocyte/Chang cell ratio of only 1:1, weak cytotoxic effects were also noted after 24 hours of incubation. The results of dose—response experiments suggested that a considerable proportion of the lymphocytes participated in the reaction. Individual variation of the cytotoxic effect of lymphocytes from different donors suggested that it could be related to the degree of histoincompatibility between lymphocytes and Chang cells. Under the present conditions contaminating erythrocytes or granulocytes did not interfere with the cytotoxic action of the lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUNTING W. L., KIELY J. M., OWEN C. A., Jr Radiochromiumlabeled lymphocytes in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Jun;113:370–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COULSON A. S., CHALMERS D. G. SEPARATION OF VIABLE LYMPHOCYTES FROM HUMAN BLOOD. Lancet. 1964 Feb 29;1(7331):468–469. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90799-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN H. S. A general method for the quantitation of immune cyotysis. Nature. 1961 Apr 15;190:269–270. doi: 10.1038/190269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLM G., PERLMANN P., WERNER B. PHYTOHAEMAGGLUTININ-INDUCED CYTOTOXIC ACTION OF NORMAL LYMPHOID CELLS ON CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE. Nature. 1964 Aug 22;203:841–843. doi: 10.1038/203841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G. In vitro cytotoxic effects of lymphoid cells from rats with experimental autoimmune nephrosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jan;1(1):45–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Perlmann P. Phytohaemagglutinin-induced cytotoxic action of unsensitized immunologically competent cells on allogeneic and xenogeneic tissue culture cells. Nature. 1965 Aug 21;207(999):818–821. doi: 10.1038/207818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN G., PERLMANN P. IN VITRO CYTOTOXIC EFFECT OF ISOANTIBODY MEASURED AS ISOTOPE RELEASE FROM LABELLED TARGET CELL DNA. Nature. 1963 Aug 3;199:451–453. doi: 10.1038/199451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOELLER E. CONTACT-INDUCED CYTOTOXICITY BY LYMPHOID CELLS CONTAINING FOREIGN ISOANTIGENS. Science. 1965 Feb 19;147(3660):873–879. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3660.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENAU W., MOON H. D. Lysis of homologous cells by sensitized lymphocytes in tissue culture. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1961 Aug;27:471–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON A. R. APPLICATIONS OF ISO-IMMUNE CYTOLYSIS USING RADIOLABELLED TARGET CELLS. Nature. 1964 Oct 17;204:250–253. doi: 10.1038/204250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGZELL H. QUANTITATIVE TITRATIONS OF MOUSE H-2 ANTIBODIES USING CR-51-LABELLED TARGET CELLS. Transplantation. 1965 May;3:423–431. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196505000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


