Abstract
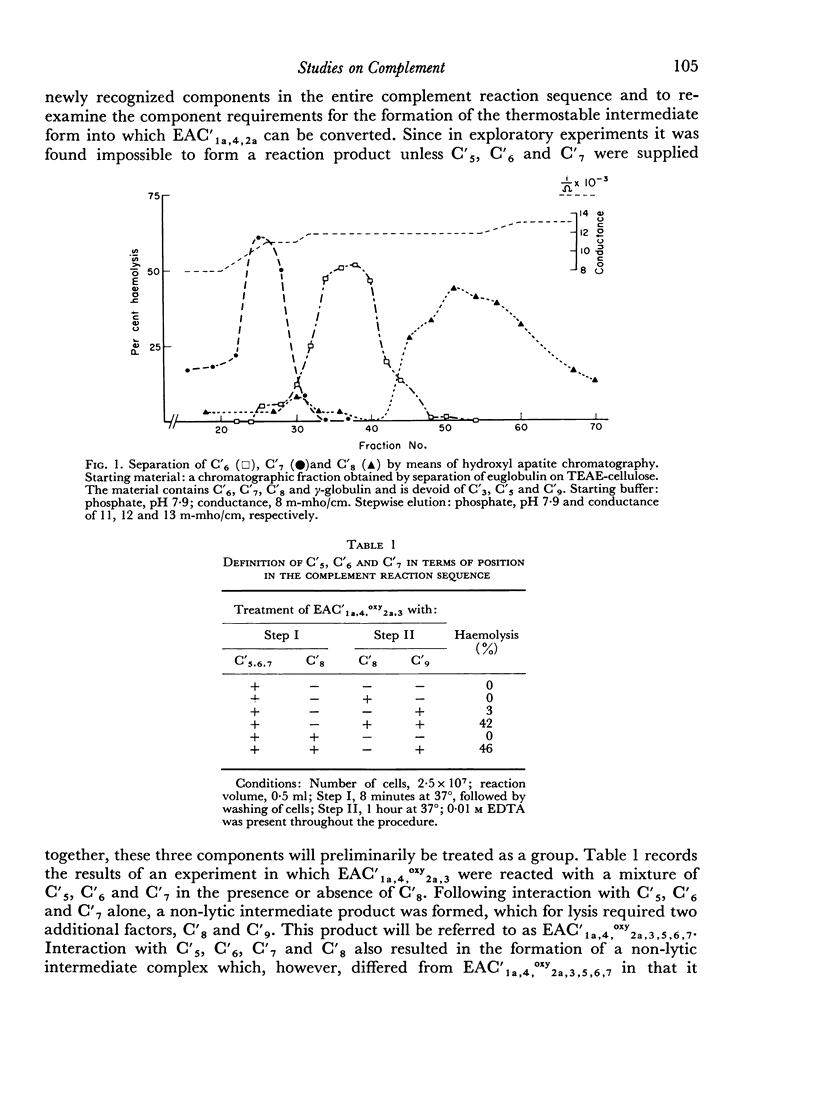
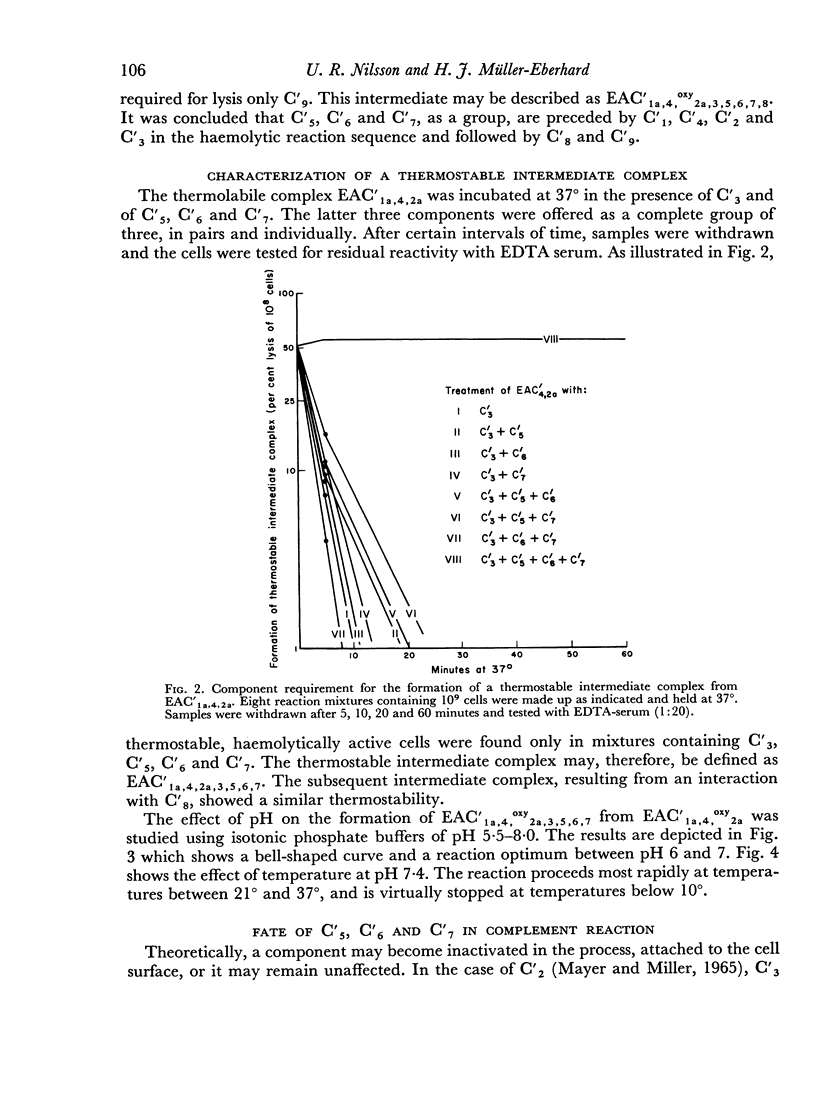
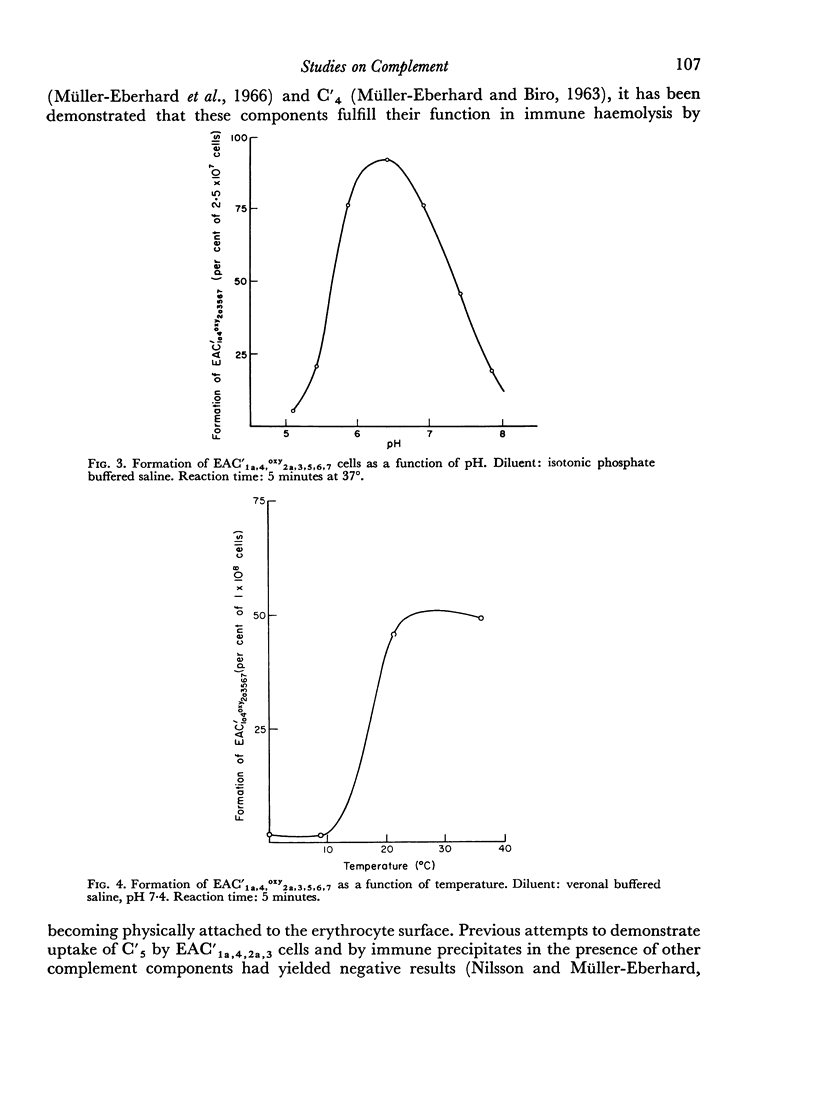
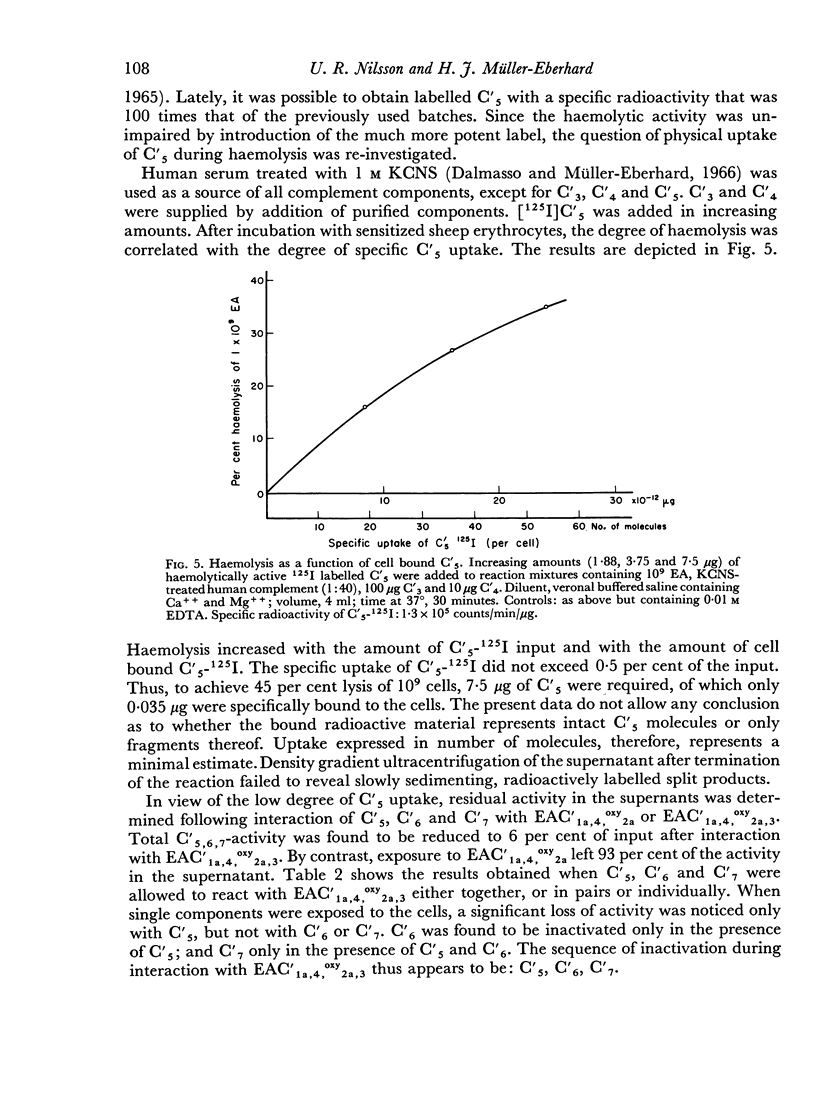
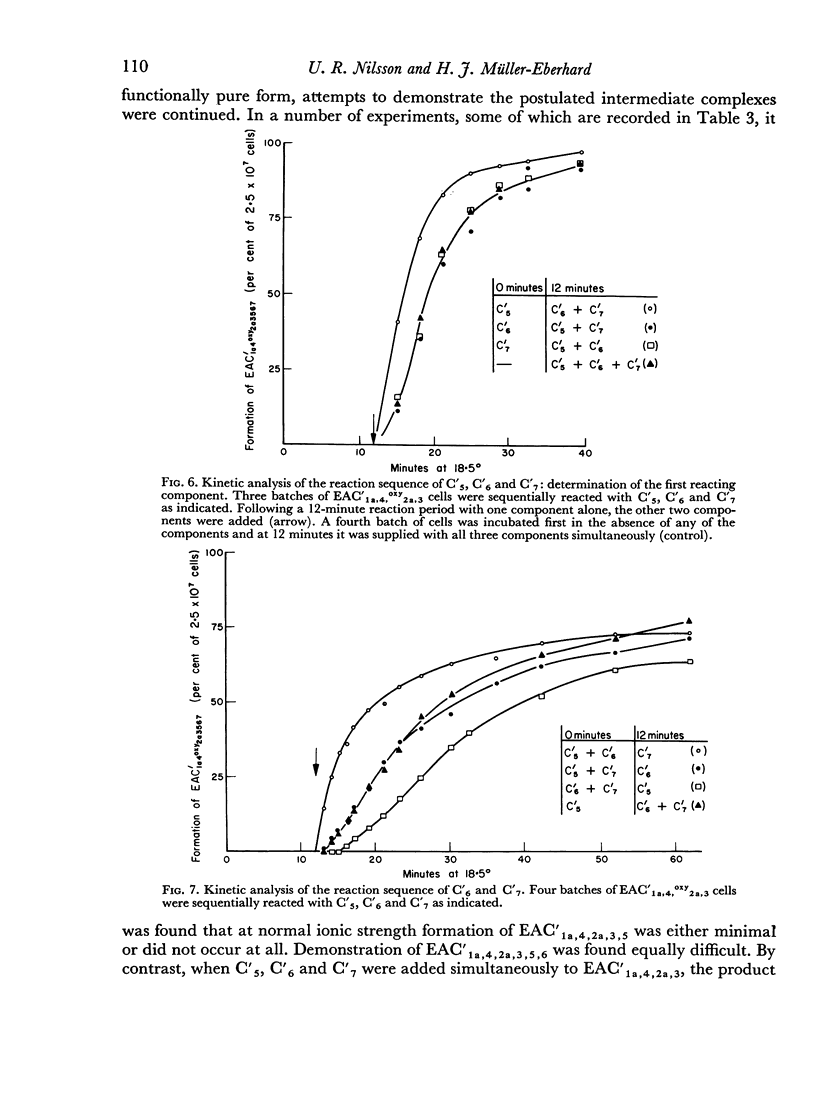
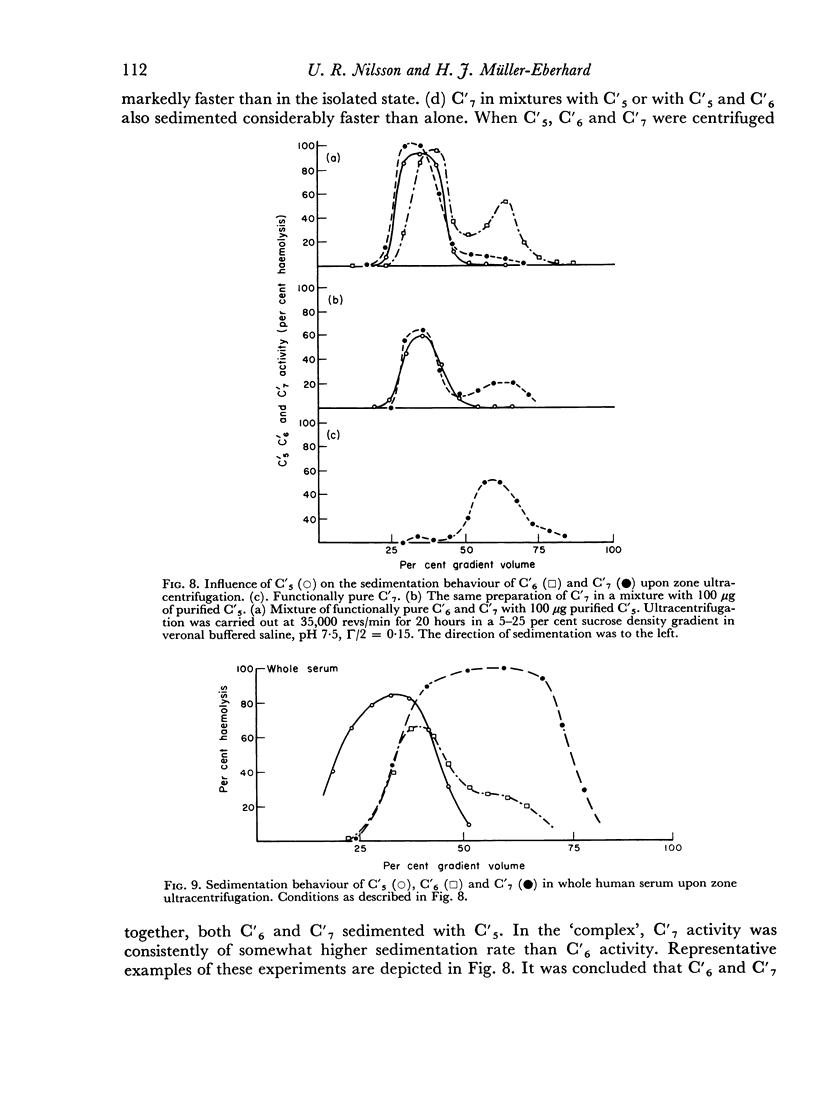
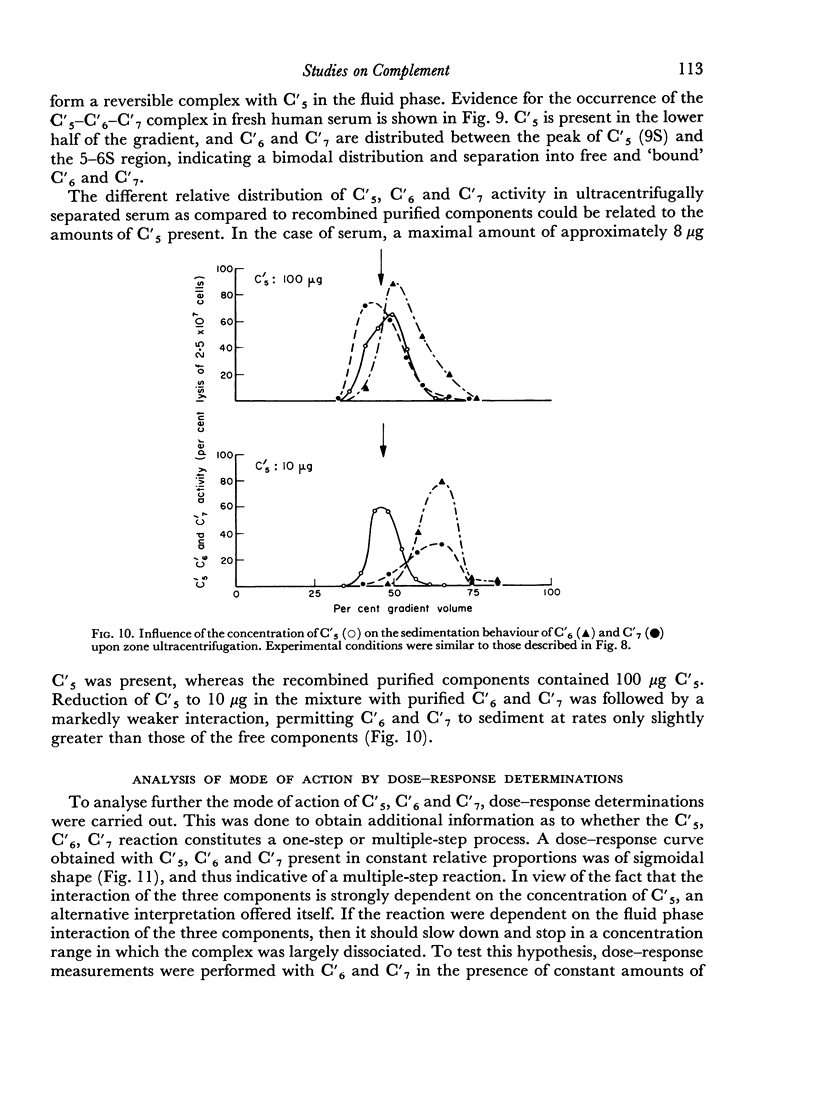
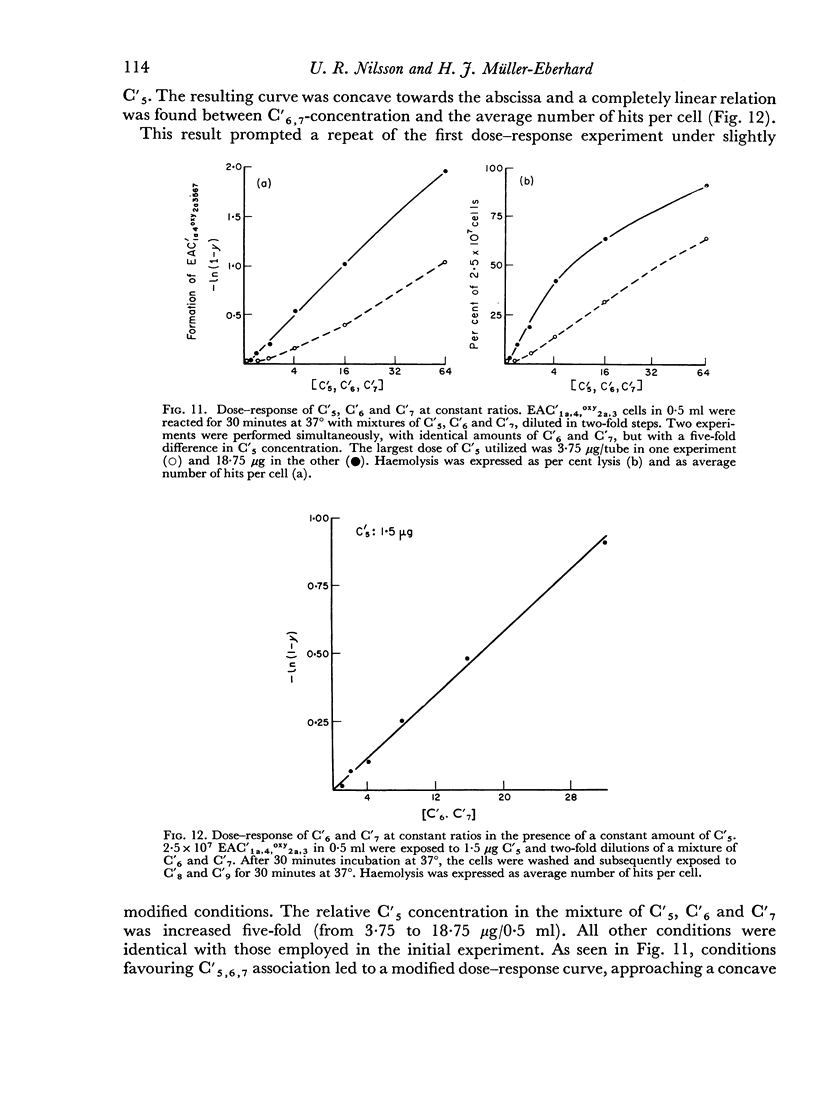
The sixth (C′6), seventh (C′7) and eighth (C′8) components of human complement were separated from each other by chromatography on hydroxyl apatite and obtained in functionally pure form. Density gradient ultracentrifugation revealed that C′6 and C′7 interact with the fifth component of complement (C′5) to form a reversible protein—protein complex. Evidence was obtained that this complex occurs also in unfractionated, fresh human serum. Kinetic analysis of the reaction sequence in immune haemolysis disclosed that C′5, C′6 and C′7 act, in this order, subsequent to the third component (C′3) and prior to C′8. Exploration of the mode of action of C′5, C′6 and C′7 led to the formulation of two alternative hypotheses. The three components act either sequentially or as one functional unit. Their fluid phase interaction, the shape of dose—response curves and the encountered difficulty to isolate intermediate reaction products favour the concept that they act as a functional unit.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Creighton T. E., Yanofsky C. Association of the alpha and beta-2 subunits of the tryptophan synthetase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 25;241(4):980–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalmasso A. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Hemolytic activity of lipoprotein-depleted serum and the effect of certain anions on complement. J Immunol. 1966 Nov;97(5):680–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Nelson R. A., Jr The isolation and characterization of a ninth component of hemolytic complement, C'3f. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):386–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P. G., Wellensiek H. J. Multiple nature of the third component of guinea-pig complement. I. Separation and characterization of three factors a, b, and c, essential for haemolysis. Immunology. 1965 Jun;8(6):590–603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., NAFF G. B., TODD E. W., PENSKY J., HINZ C. F. Chromatographic resolution of the first component of human complement into three activities. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:983–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J., BIRO C. E. ISOLATION AND DESCRIPTION OF THE FOURTH COMPONENT OF HUMAN COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1963 Sep 1;118:447–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M., Miller J. A. Inhibition of guinea pig C'2 by rabbit antibody. Quantitative measurement of inhibition, discrimination between immune inhibition and complement fixation, specificity of inhibition and demonstration of uptake of C'2 by EAC'1a,4. Immunochemistry. 1965 Jun;2(2):71–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Eberhard H. J., Nilsson U. R., Dalmasso A. P., Polley M. J., Calcott M. A. A molecular concept of immune cytolysis. Arch Pathol. 1966 Sep;82(3):205–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Polley M. J., Calcott M. A. Formation and functional significance of a molecular complex derived from the second and the fourth component of human complement. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):359–380. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON U. R., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. ISOLATION OF BETA IF-GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION AS THE FIFTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:277–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. A., Jr, Jensen J., Gigli I., Tamura N. Methods for the separation, purification and measurement of nine components of hemolytic complement in guinea-pig serum. Immunochemistry. 1966 Mar;3(2):111–135. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rother K., Rother U., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Nilsson J. R. Deficiency of the sixth component of complement in rabbits with an inherited complement defect. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):773–785. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellensiek H. J., Klein P. G. Multiple nature of the third component of guinea-pig complement. II. Separation and description of two additional factors beta and d; preparation and characterization of four intermediate products. Immunology. 1965 Jun;8(6):604–617. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



