Abstract
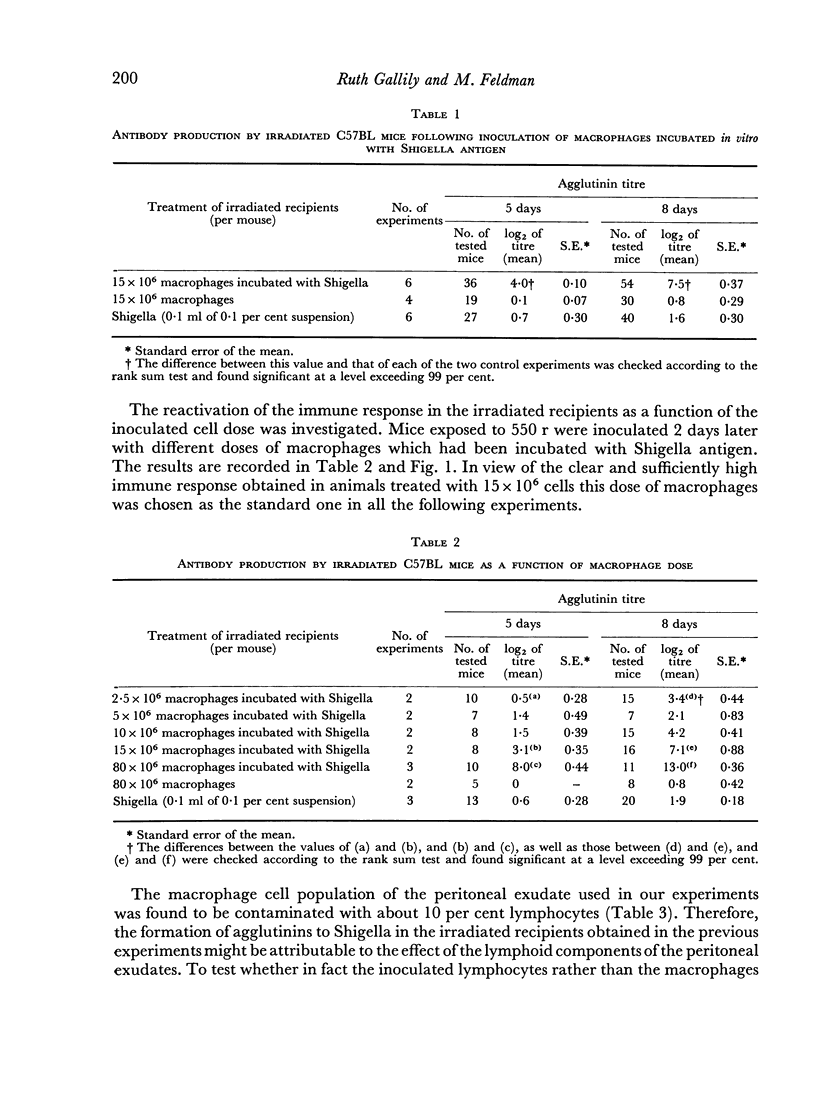
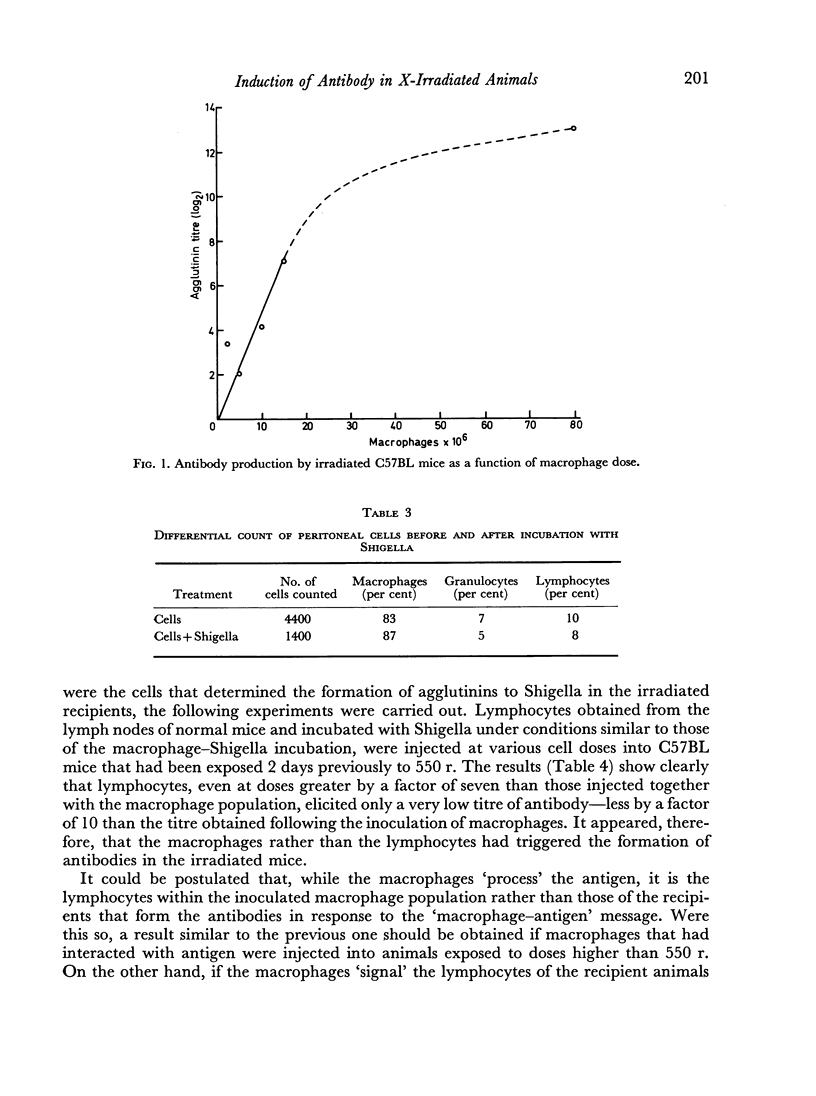
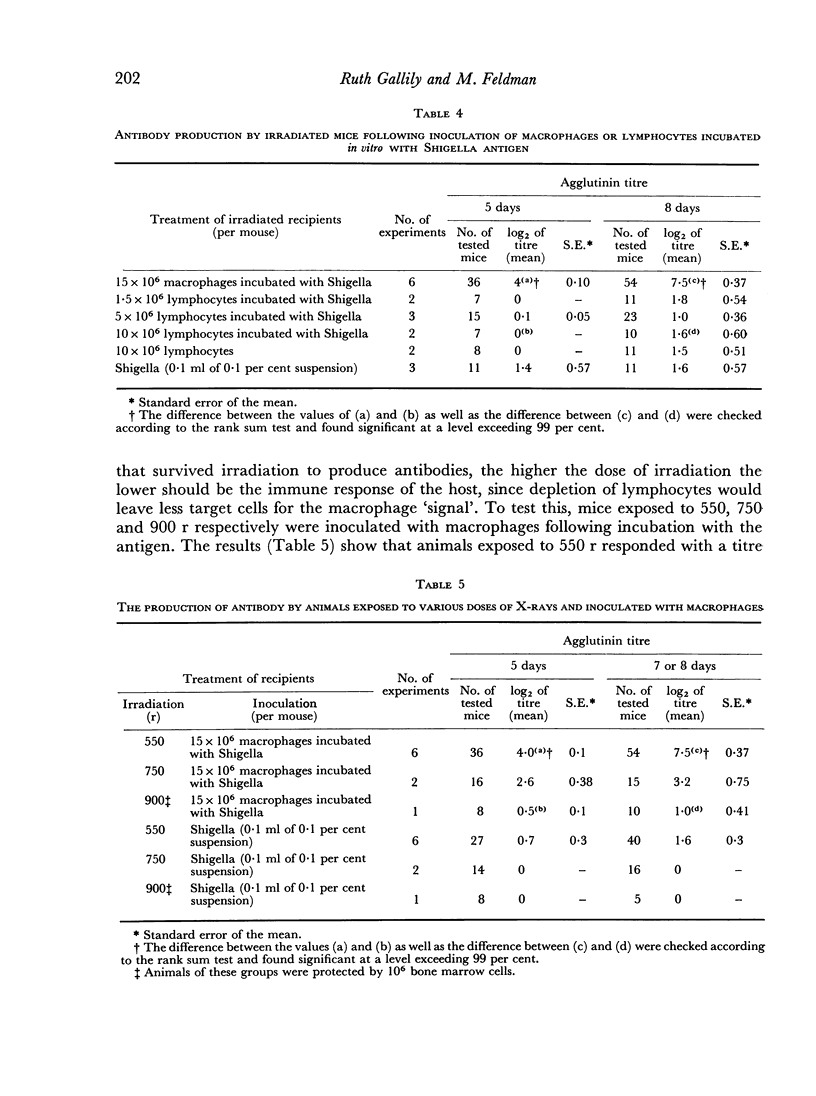
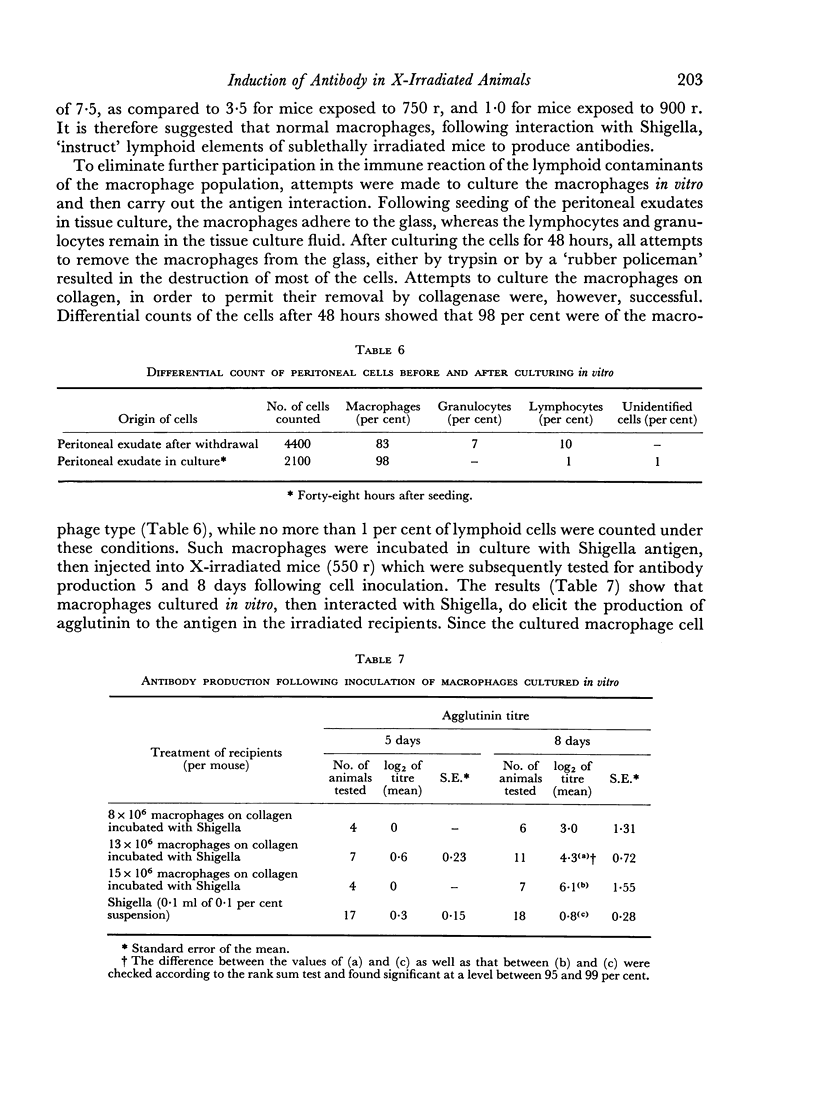
A study was carried out on the function of macrophages in inducing antibody production to Shigella antigen, and on the effect of X-irradiation on the `immunogenic' function of macrophages. Peritoneal macrophages, which had been incubated with Shigella and then injected into mice exposed to 550 r, triggered the formation of agglutinating antibody in animals which did not respond to the injection of the antigen alone. The antibody formed was not produced by `contaminating' lymphocytes of the peritoneal exudate, since: (a) lymph node cells at doses higher than those of the macrophage inocula did not produce antibody when treated and injected under similar conditions, and (b) lymphocyte-free macrophage populations, obtained by culturing in vitro cells of peritoneal exudates, triggered the production of antibody when injected in to X-irradiated recipients after interaction with the antigen. Macrophages from irradiated donors incubated with Shigella were incapable of inducing antibody formation in X-irradiated mice. Animals exposed to higher doses of irradiation (900 r) did not produce antibody following injection of macrophage—antigen complexes. It was, therefore, concluded that macrophages from normal animals elicited the production of antibody by the lymphoid cells of the irradiated recipients.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARROW J., TULLIS J. L., CHAMBERS F. W., Jr Effect of x-radiation and antihistamine drugs on the reticuloendothelial system measured with colloidal radiogold. Am J Physiol. 1951 Mar;164(3):822–831. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.164.3.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., KIVY-ROSENBERG E., SEBESTYEN M. M., ZWEIFACH B. W. The effect of high doses of x-irradiation on the phagocytic, proliferative, and metabolic properties of the reticulo-endothelial system. J Exp Med. 1959 Jul 1;110(1):49–64. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A. Influence of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes and macrophages on the immunogenicity of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1962 Dec 15;196:1066–1068. doi: 10.1038/1961066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI LUZIO N. R. Effect of x-irradiation and choline on the reticulo-endothelial system of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jun;181(3):595–598. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.181.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON D. M., MARCUS S., GYI K. K., PERKINS E. H. The influence of immunization and total body x-irradiation on intracellular digestion by peritoneal phagocytes. J Immunol. 1956 Mar;76(3):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON D. M., MILLER M. L. Depression on normal serum bactericidal activity by nitrogen mustard. J Immunol. 1959 Jan;82(1):69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRMANN R. L., GEY G. O. The growth of cells on a transparent gel of reconstituted rat-tail collagen. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1956 Jun;16(6):1375–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN M. Antibody formation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:837–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GABRIELI E. R., AUSKAPS A. A. The effect of whole body x-irradiation on the reticuloendothelial system as demonstrated by the use of radioactive chromium phosphate. Yale J Biol Med. 1953 Nov;26(2):159–179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLILY R., WARWICK A., BANG F. B. EFFECT OF CORTISONE OF GENETIC RESISTANCE TO MOUSE HEPATITIS VIRUS IN VIVO AND IN VITRO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1158–1164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON L. E., COOPER D. B., MILLER C. P. Clearance of bacteria from the blood of irradiated rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Aug;89(4):577–579. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISH L., FURTH J., SHEPPARD C. W., STOREY R. H. Disappearance rate of tagged substances from the circulation of roentgen irradiated animals. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1952 Apr;67(4):628–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


