Abstract
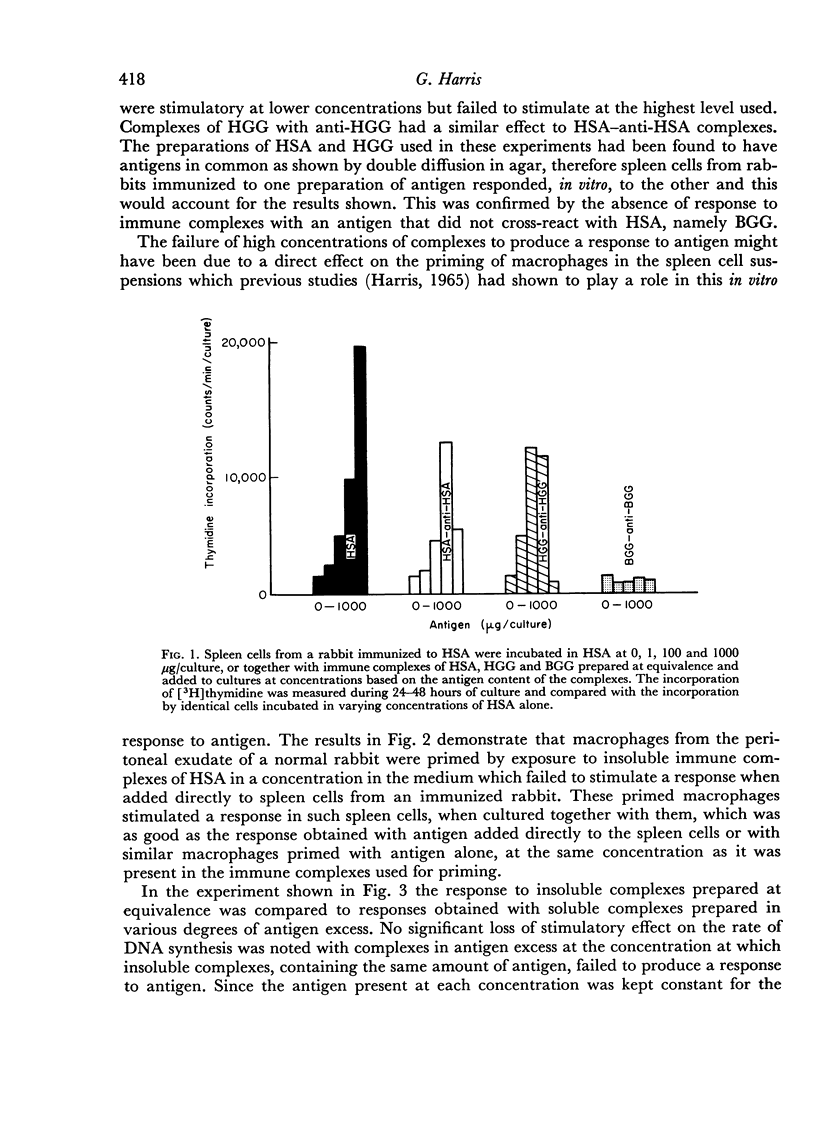
Insoluble immune complexes, prepared with heterologous protein antigens and homologous antibodies, affected the incorporation of [3H]thymidine into spleen cell suspension from rabbits immunized to these proteins. Low concentrations of such complexes stimulated thymidine uptake, this being antigen specific, while high concentrations impaired the response to antigen. The inhibitory effect of high concentrations of immune complexes was found to be non-specific as far as the responses to antigens were concerned, but the PHA-responsiveness of rabbit spleen cells was not significantly impaired by the presence of such complexes.
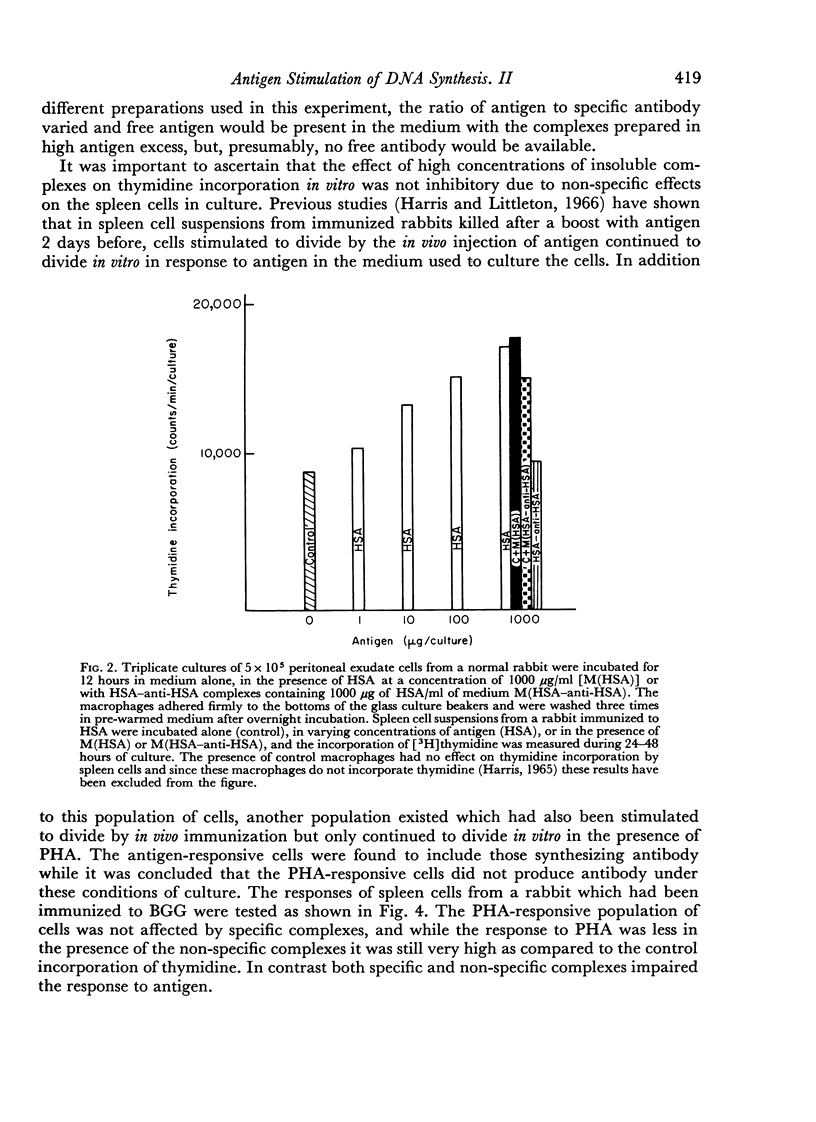
When macrophages from the peritoneal cavities of normal rabbits were incubated with insoluble immune complexes and then washed, such cells were able to stimulate an antigen-specific response by spleen cells from immunized rabbits. It was concluded that, in these experiments, the failure of spleen cells from immunized rabbits to respond to antigen in the presence of immune complexes was the result of a direct inhibition of the mechanism of proliferation by these complexes.
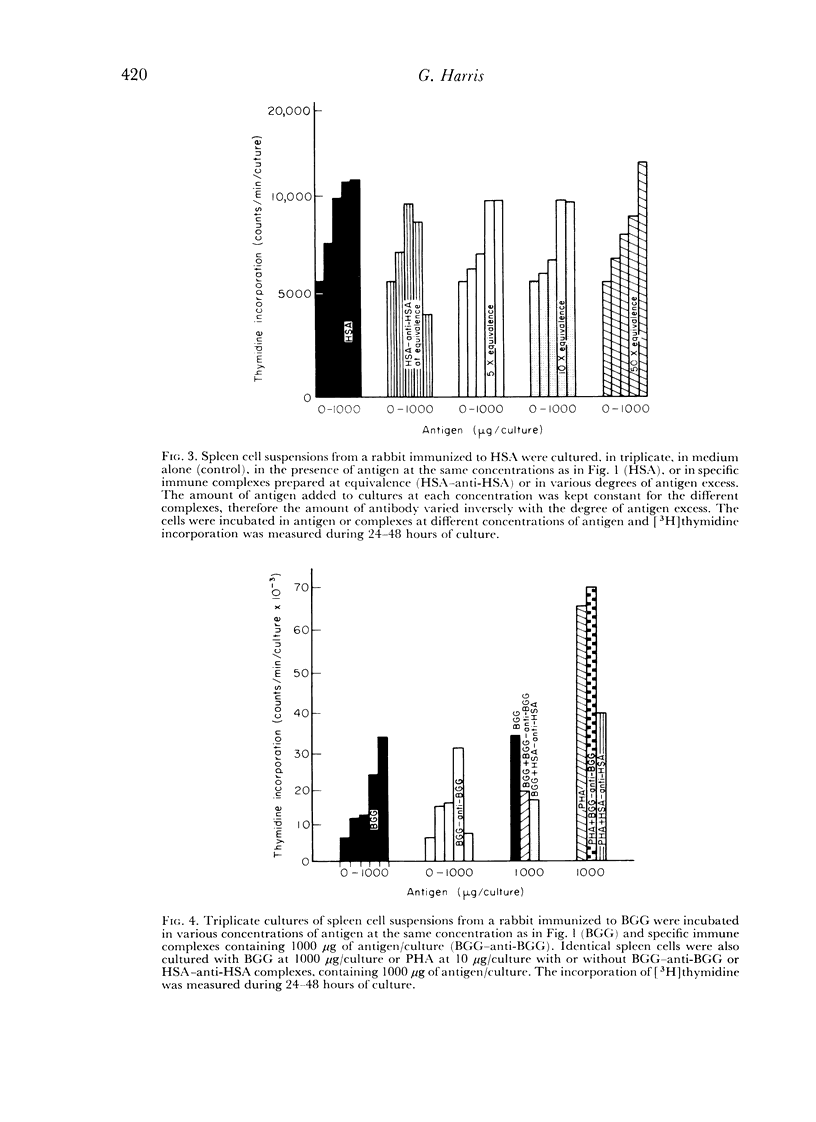
Inhibition of the response to antigen was also produced by the presence of free specific antibodies in the culture medium, even in excess of antigen. It was postulated that, in this situation, antibody reacted with antigen present on the surfaces of cells, particularly macrophages, thus blocking the stimulatory mechanism.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BULLOUGH W. S. The control of mitotic activity in adult mammalian tissues. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1962 Aug;37:307–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1962.tb01615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., TALMAGE D. W. Catabolism of I131 labelled bovine gamma globulin in immune and non-immune rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Oct;78(1):123–125. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-18996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUTTON R. W., EADY J. D. AN IN VITRO SYSTEM FOR THE STUDY OF THE MECHANISM OF ANTIGENIC STIMULATION IN THE SECONDARY RESPONSE. Immunology. 1964 Jan;7:40–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G., Cramp W. A. Further studies of antigen stimulation of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in rabbit spleen cell cultures. I. The effects of centrifuged proteins. Immunology. 1968 Mar;14(3):409–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G., Littleton R. J. The effects of antigens and of phytohemagglutinin on rabbit spleen cell suspensions. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):621–634. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. Studies of the mechanism of antigen stimulation of DNA synthesis in rabbit spleen cultures. Immunology. 1965 Dec;9(6):529–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLER G., WIGZELL H. ANTIBODY SYNTHESIS AT THE CELLULAR LEVEL. ANTIBODY-INDUCED SUPPRESSION OF 19S AND 7S ANTIBODY RESPONSE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jun 1;121:969–989. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.6.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON R., SUSZKO I. M., PRUZANSKY J. J. In vitro uptake of antigen-antibody complexes by phagocytic cells. J Immunol. 1962 Oct;89:471–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLEY D. A., FITCH F. W. HOMEOSTASIS OF ANTIBODY FORMATION IN THE ADULT RAT. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:987–1005. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UHR J. W., BAUMANN J. B. Antibody formation. I. The suppression of antibody formation by passively administered antibody. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:935–957. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE W. O. Elimination of antigen-antibody complexes from sera of rabbits. J Immunol. 1958 Sep;81(3):204–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


