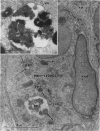
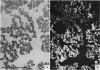
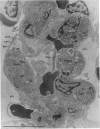
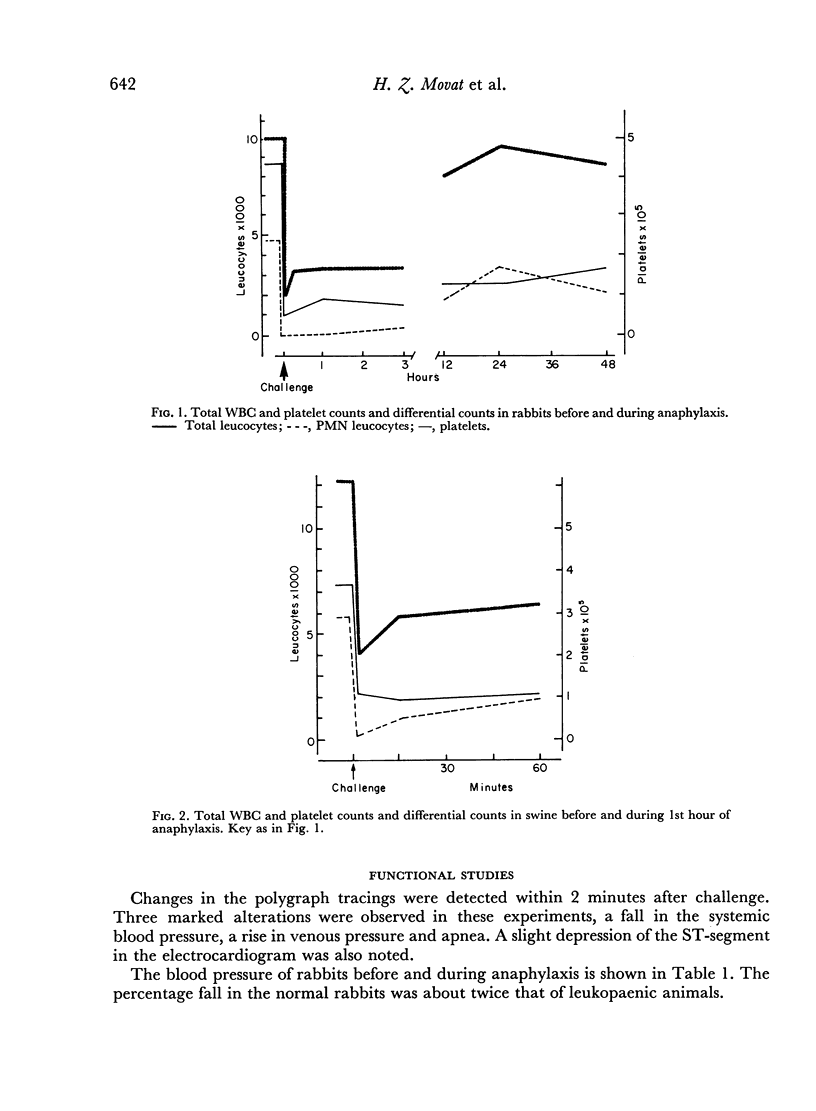
Abstract
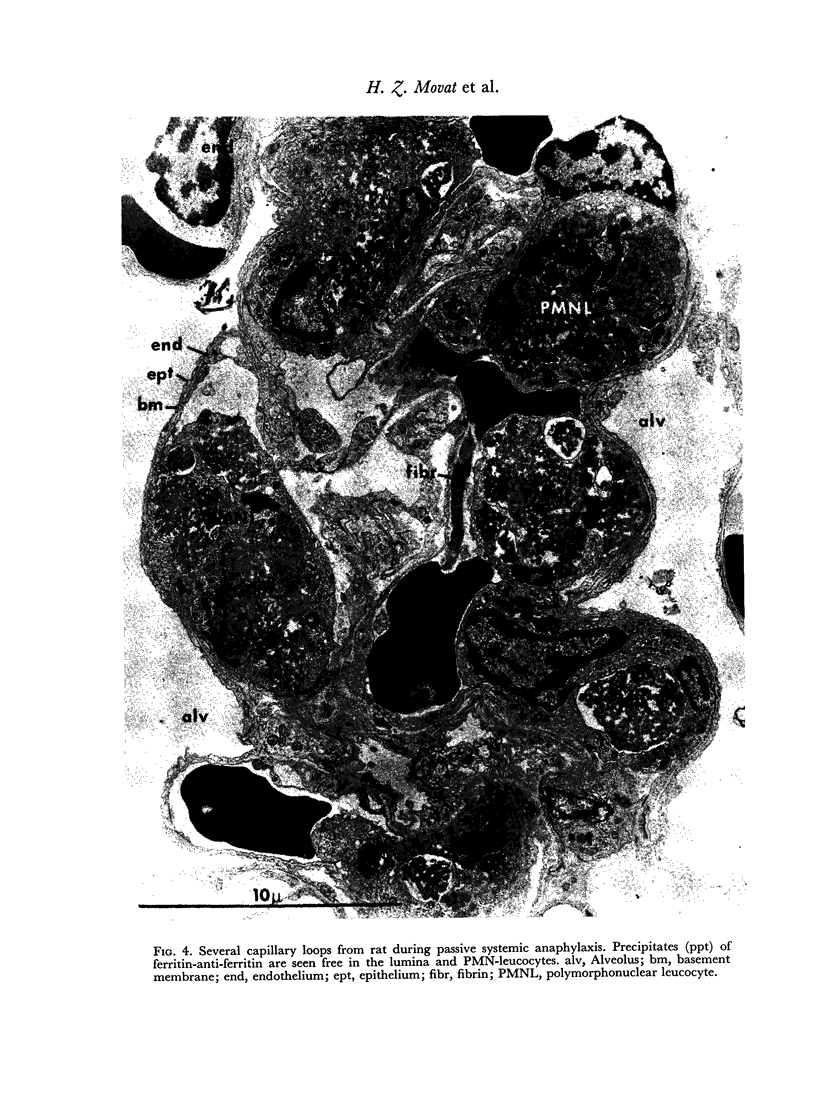
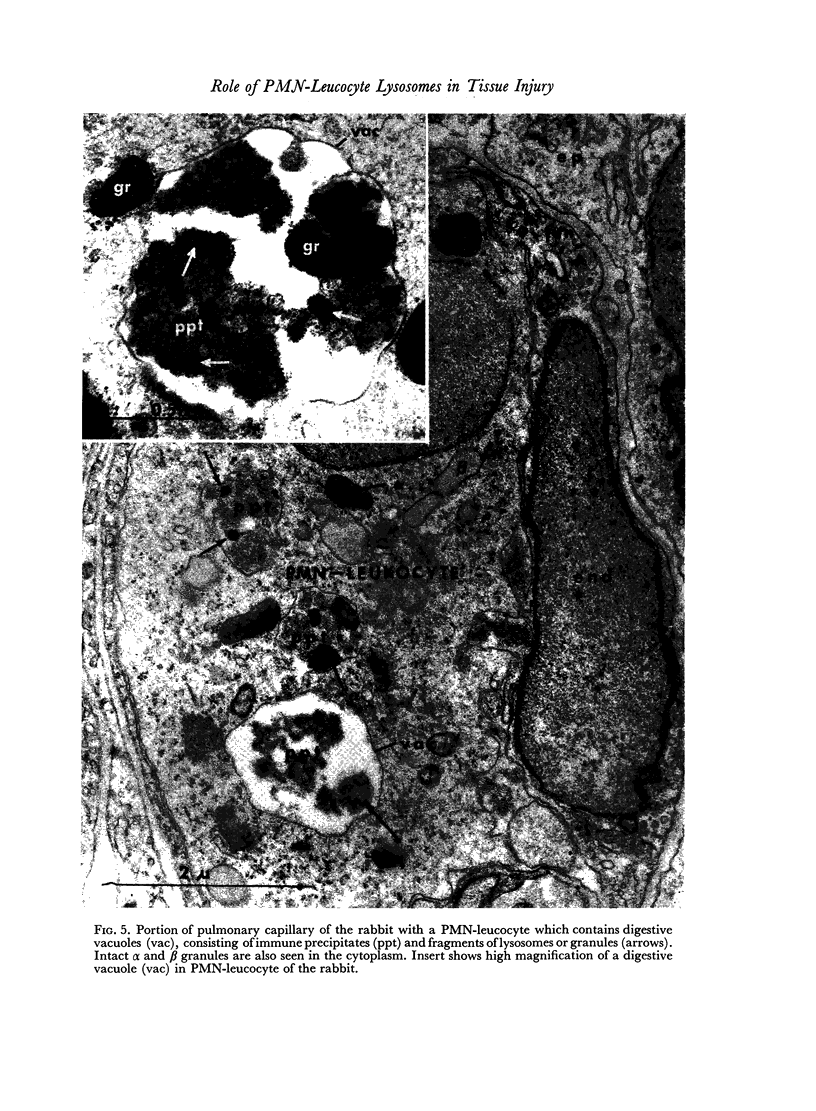
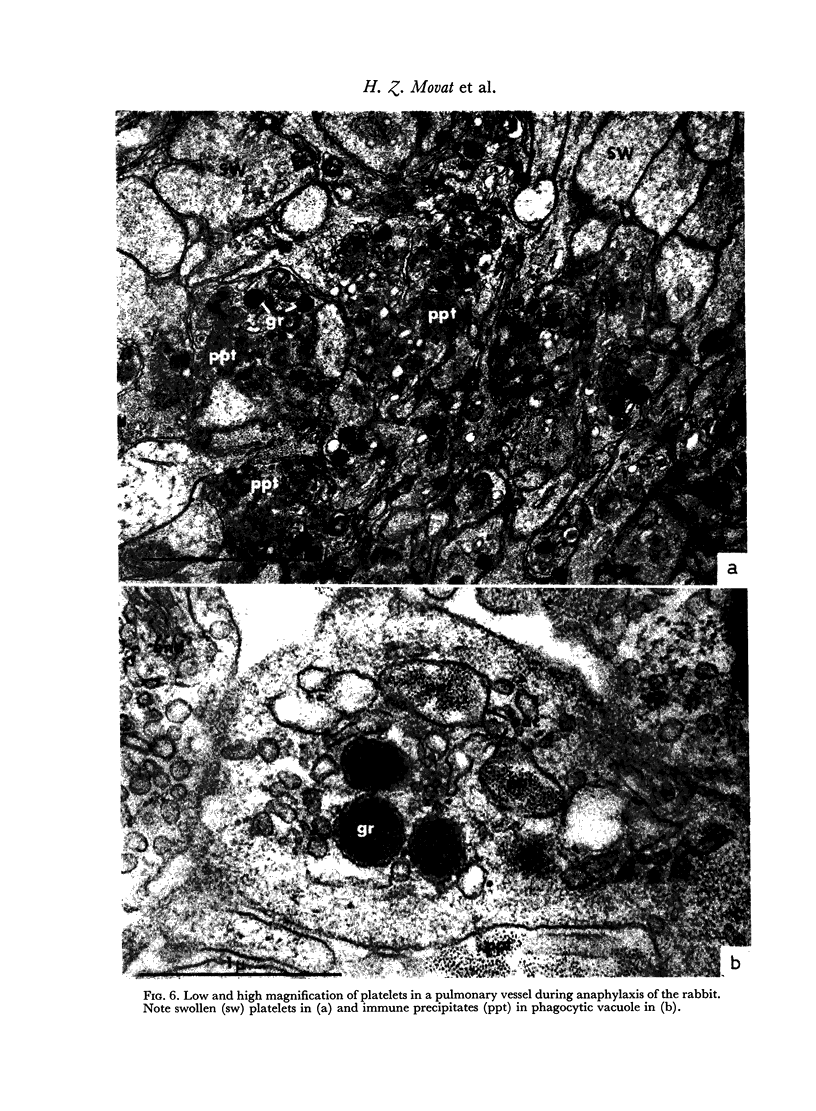
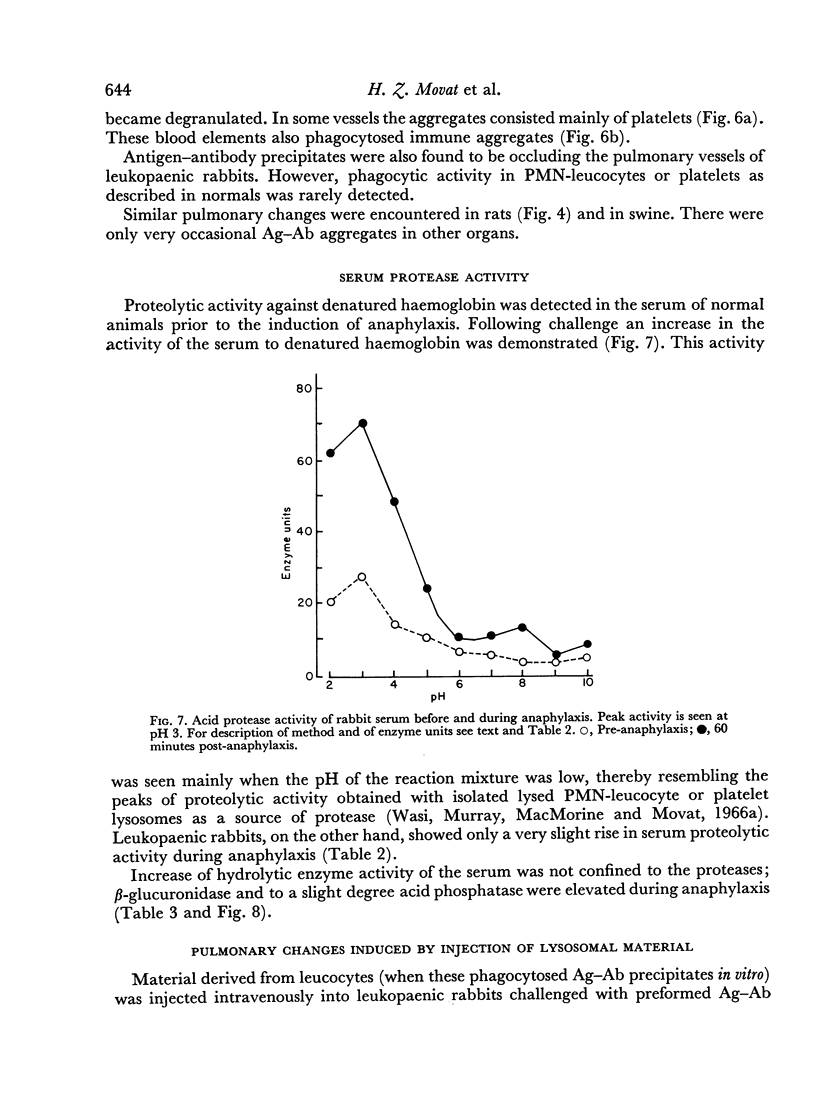
Anaphylaxis due to intravascular interaction of hyperimmune antibody with antigen was studied in rabbits, swine and rats. Obstruction of the pulmonary vessels by the immune precipitates was found to initiate the process. This is followed by aggregation of PMN-leucocytes and platelets in pulmonary vessels and phagocytosis of the precipitates by these blood elements. During this process degranulation of the cells takes place with release of lysosomal contents. As a concomitant a rise in plasma acid protease and other hydrolases was demonstrated, presumably derived from the degranulating PMN-leucocytes and platelets. Unlike leukopaenic animals, normal ones showed a more marked hypotension, a greater tendency to protracted shock and developed focal and confluent haemorrhagic pulmonary lesions. It is suggested that anaphylaxis due to intravascular antigen—antibody interaction or aggregate anaphylaxis is a systemic or pulmonary Arthus reaction, rather than a `true' anaphylaxis.
Full text
PDF






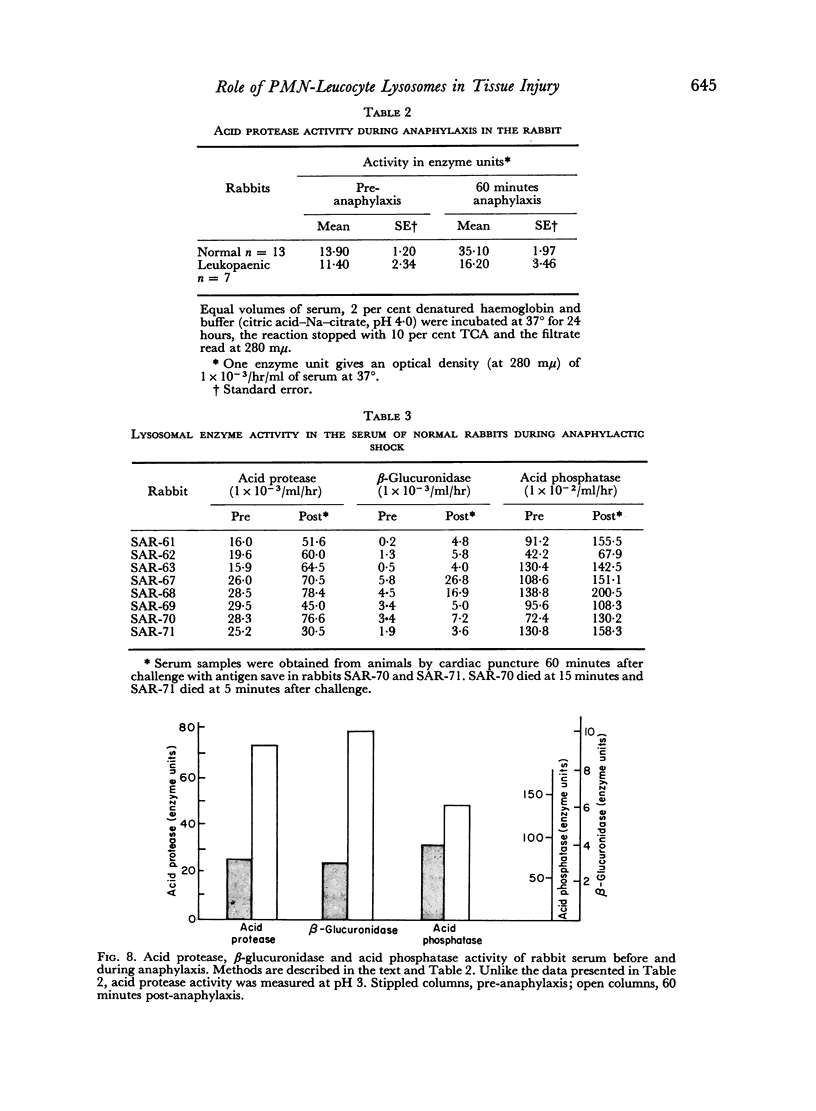



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURKE J. S., URIUHARA T., MACMORINE D. R., MOVAT H. Z. A PERMEABILITY FACTOR RELEASED FROM PHAGOCYTOSING PMN-LEUKOCYTES AND ITS INHIBITION BY PROTEASE INHIBITORS. Life Sci. 1964 Dec;3:1505–1512. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(64)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE C. G., WEIGLE W. O., DIXON F. J. The role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the initiation and cessation of the Arthus vasculitis. J Exp Med. 1959 Sep 1;110:481–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.3.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., HIRSCH J. G. The isolation and properties of the specific cytoplasmic granules of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:983–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Aikin B. S. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes in immunologic reactions. The destruction of vascular basement membrane in vivo and in vitro. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):733–752. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cîrstea M., Suhaciu G., Butculescu I. Bradykinin and anaphylactic shock in dogs, guinea-pigs and rabbits. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1965 Mar;73(2):231–240. doi: 10.3109/13813456509084249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J. The use of I131 in immunologic investigation. J Allergy. 1953 Nov;24(6):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(53)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EBERT R. H., WISSLER R. W. In vivo observations of the vascular reactions to large doses of horse serum using the rabbit ear chamber technique. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Oct;38(4):511–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER P., LECOMTE J. Choc anaphylactique chez le lapin traité par réserpine. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1956 Sep 26;150(5):1026–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., JAQUES R. The release of histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) from platelets by antigen-antibody reactions (in vitro). J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):9–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H. The mechanism of Arthus reactions. I. The role of polymorphonuclear leucocytes and other factors in reversed passive Arthus reactions in rabbits. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Jun;36(3):268–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz G. HISTAMINE RELEASE FROM BLOOD CELLS IN ANAPHYLAXIS IN VITRO. Science. 1940 Mar 1;91(2357):221–221. doi: 10.1126/science.91.2357.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOVAT H. Z., FERNANDO N. V., URIUHARA T., WEISER W. J. ALLERGIC INFLAMMATION. III. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF COLLAGEN FIBRILS AT SITES OF ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY INTERACTION IN ARTHUS-TYPE LESIONS. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:557–564. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOVAT H. Z., URIUHARA T., MACMORINE D. L., BURKE J. S. A PERMEABILITY FACTOR RELEASED FROM LEUKOCYTES AFTER PHAGOCYTOSIS OF IMMUNE COMPLEXES AND ITS POSSIBLE ROLE IN THE ARTHUS REACTION. Life Sci. 1964 Sep;3:1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(64)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKINNON G. E., ANDREWS E. C., Jr, HEPTINSTALL R. H., GERMUTH F. G., Jr An immunohistologic study on the occurrence of intravascular antigen-antibody precipitation and its role in anaphylaxis in the rabbit. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1957 Nov;101(5):258–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Mustard J. F., Taichman N. S., Uriuhara T. Platelet aggregation and release of ADP, serotonin and histamine associated with phagocytosis of antigen-antibody complexes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Oct;120(1):232–237. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F., Bloch K. J. Antibodies involved in antigen-induced release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) in the guinea pig and rat. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):127–147. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAALKES T. P., WEISSBACH H., BOZICEVICH J., UDENFRIEND S. Serotonin and histamine release during anaphylaxis in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jul;36(7):1115–1120. doi: 10.1172/JCI103507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE W. O., COCHRANE C. G., DIXON F. J. Anaphylactogenic properties of soluble antigen-antibody complexes in the guinea pig and rabbit. J Immunol. 1960 Nov;85:469–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasi S., Uriuhara T., Taichman N. S., Murray R. K., Movat H. Z. Proteolytic activity in the serum of rabbits during anaphylaxis. Experientia. 1966 Mar 15;22(3):196–198. doi: 10.1007/BF01897735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]