Abstract
Sera of rabbits immunized with rat or guinea-pig lymph node cell extract were fractionated by column chromatography. In all cases the fractions which contained antibody were able to suppress the inflammatory response of delayed hypersensitivity reactions, whereas fractions devoid of antibody had no activity. Furthermore, rabbit antiserum to guinea-pig serum, or its fraction rich in antibody, were unable to suppress delayed hypersensitivity reactions, indicating that antibodies to the serum proteins present in the cell extract were not responsible for the anti-inflammatory activity of the anti-cell extract serum, in spite of the close association of LNPF activity with plasma protein in the lymph node extract. Haemagglutination inhibition experiments detected in the anti-cell extract antisera a small titre of specifc antibody which may be responsible for the inflammatory suppression.
Full text
PDF



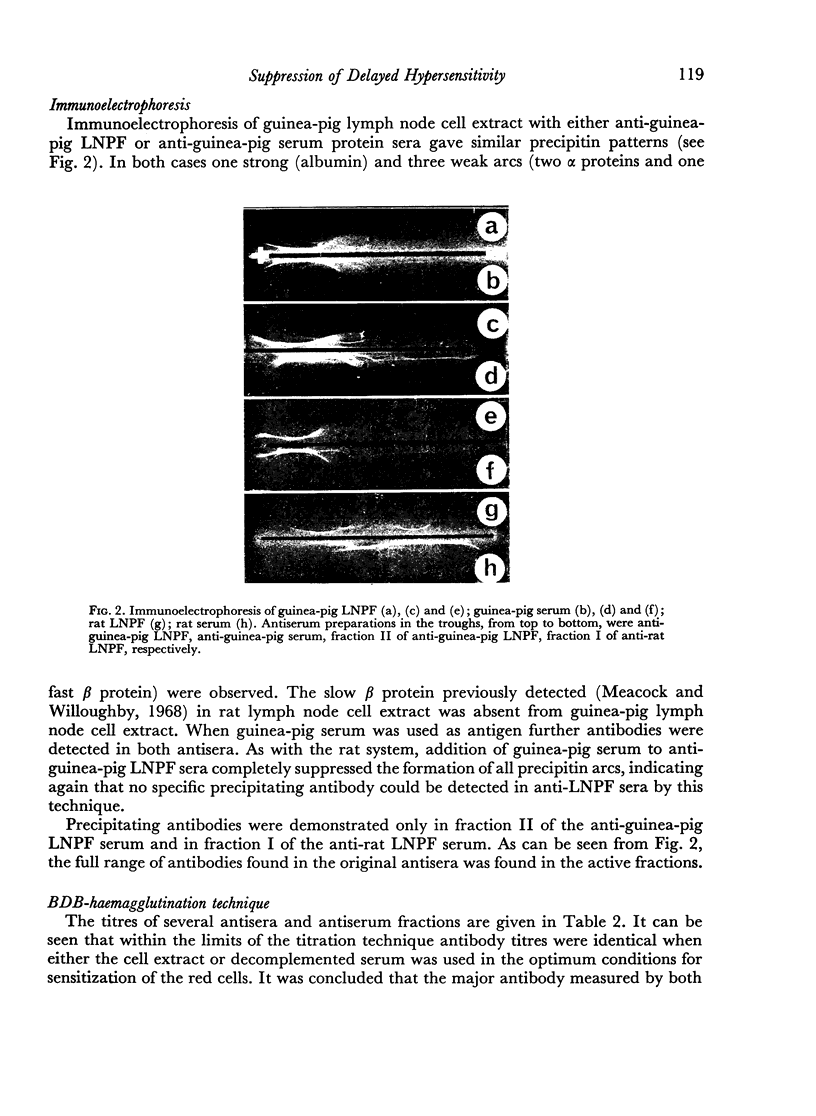
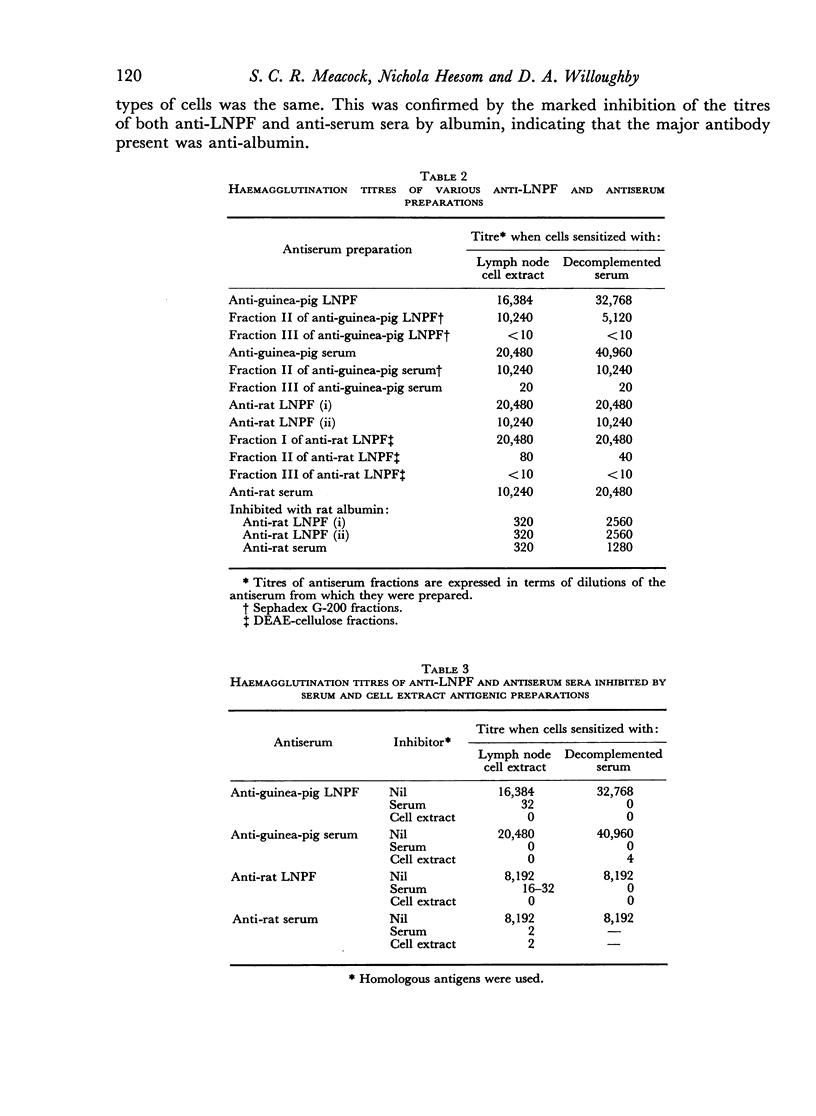


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GELOTTE B., FLODIN P., KILLANDER J. Fractionation of human plasma proteins by gel filtration and zone electrophoresis or ion-exchange chromatography. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:319–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON J., ROSE B., SEHON A. H. Detection of non-precipitating antibodies in sera of individuals allergic to ragweed pollen by an in vitro method. J Exp Med. 1958 Jul 1;108(1):37–51. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEACOCK S. C., SHULMAN R., FREEDMAN S. O., SEHON A. H. IMMUNOLOGIC AND CLINICAL PROPERTIES OF TWO PURIFIED RAGWEED FRACTIONS. J Allergy. 1965 Jan-Feb;36:1–11. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(65)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacock S. C., Willoughby D. A. Purification of serum proteins from lymph node cell extracts with permeability activity characteristic of the lymph node permeability factor. Immunology. 1968 Jul;15(1):101–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKATSY G. The use of spiral loops in serological and virological micro-methods. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;3(1-2):191–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLOUGHBY D. A., SPECTOR W. G., BOUGHTON B. A LYMPH-NODE PERMEABILITY FACTOR IN THE TUBERCULIN REACTION. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:353–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1700870216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby D. A., Coote E. The lymph-node permeability factor: a possible mediator of experimental allergic thyroiditis in the rat. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(2):281–289. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby D. A. The mechanism of cutaneous hypersensitivity in the rat and its suppression by immunological methods. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):139–150. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby D. A., Walters M. N., Spector W. G. Lymph node permeability factor in the dinitrochlorobenzene skin hypersensitivity reaction in guinea-pigs. Immunology. 1965 Jun;8(6):578–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





