Abstract
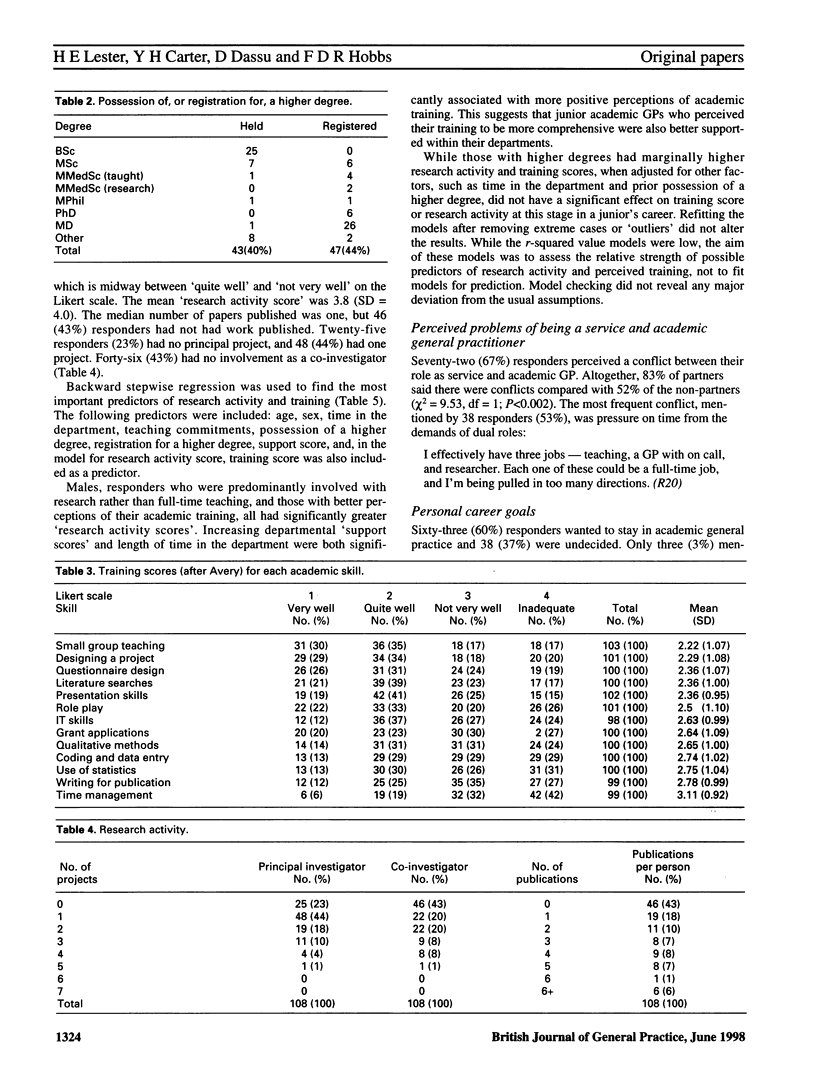
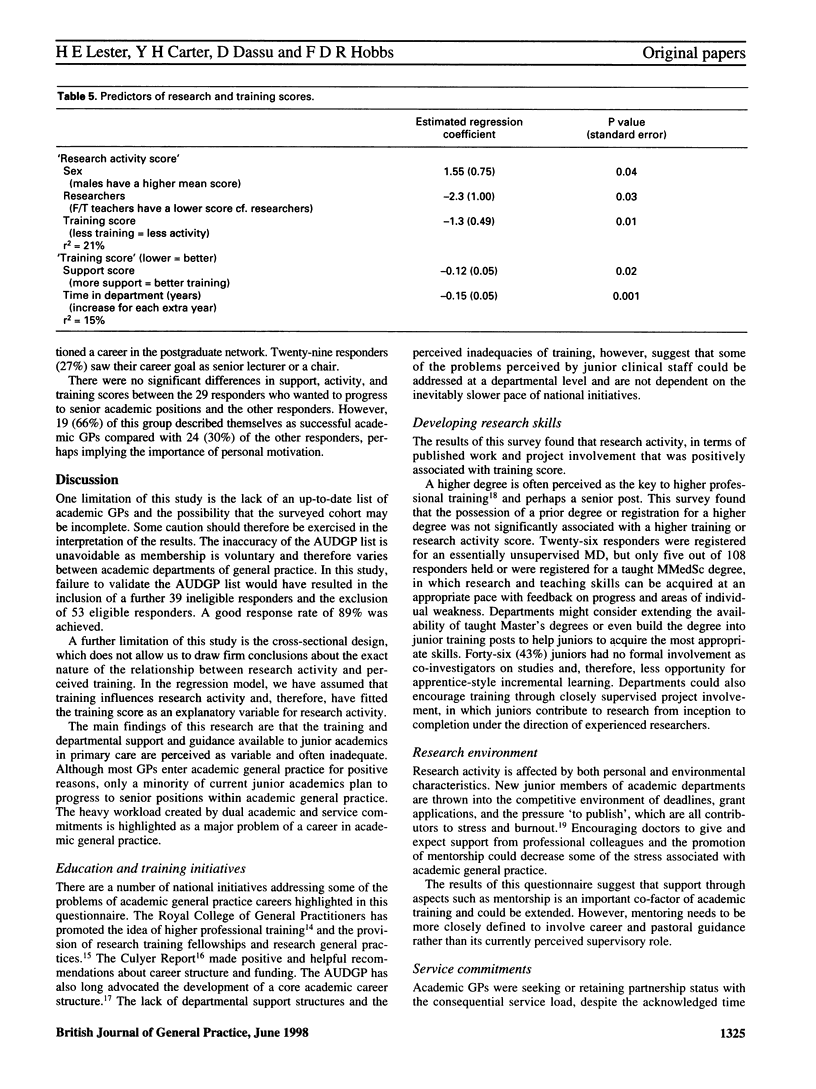
BACKGROUND: Recent changes in the organization of the National Health Service have created new roles and responsibilities for academic general practice. Previous work on the constraints and opportunities of a career in academic general practice is largely anecdotal and is often based on the views of more senior members of the profession. AIM: To survey the research activity, perceived level of training, support needs, and career intentions of junior academic general practitioners (GPs). METHOD: A postal, validated, semistructured questionnaire was sent to the 121 eligible junior academic GPs in the academic departments of general practice in the United Kingdom and Dublin. Main outcome measures were 'research activity score', as measured by publications in peer-reviewed journals and involvement in research projects, 'training score' devised from 13 skills required for both research and teaching, and perceived level of departmental support assessed by six different support mechanisms. RESULTS: Response rate was 89% (n = 108). Forty-six responders (43%) had no publications. Twenty-five responders (23%) had no principal project. Thirty-nine responders (37%) had a mentor. Research activity appeared to be dependent on sex, having a predominantly research role rather than a full-time teaching role, and a positive perception of academic training (P < 0.05). Increasing departmental 'support scores' and length of time in the department were both significantly associated with more positive perceptions of academic training (P < 0.05). Only 29 (27%) responders wanted to progress to senior positions within academic general practice. CONCLUSION: Training and departmental support and guidance available to junior academics in primary care are perceived as variable and often inadequate. If academic general practice is to thrive, improved academic training is required, such as taught Master's degrees, supervised personal projects or 'apprenticeship' as a co-investigator, and improved methods of departmental support.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin C. D., Levine H. G., McCormick D. P. Meeting the faculty development needs of generalist physicians in academia. Acad Med. 1995 Jan;70(1 Suppl):S97–103. doi: 10.1097/00001888-199501000-00032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley E. G. Research for all in general practice. Br J Gen Pract. 1990 Sep;40(338):357–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers R. Avoiding burnout in general practice. Br J Gen Pract. 1993 Nov;43(376):442–443. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. P. Research in general practice: law of inverse opportunity. BMJ. 1991 Jun 8;302(6789):1380–1382. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6789.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handysides S. Morale in general practice: is change the problem or the solution. BMJ. 1994 Jan 1;308(6920):32–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.308.6920.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper J., Dowell A. C., Kinnersley P. Academic departments of general practice at the crossroads? Br J Gen Pract. 1990 Jul;40(336):268–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashid A., Allen J., Styles B., Gray D. P. Careers in academic general practice: problems, constraints, and opportunities. BMJ. 1994 Nov 12;309(6964):1270–1272. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6964.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. F. Higher professional training in general practice: provision of master's degree courses in the United Kingdom in 1993. BMJ. 1994 Jun 25;308(6945):1679–1682. doi: 10.1136/bmj.308.6945.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



