Abstract
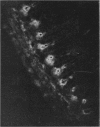
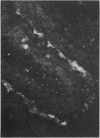
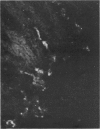
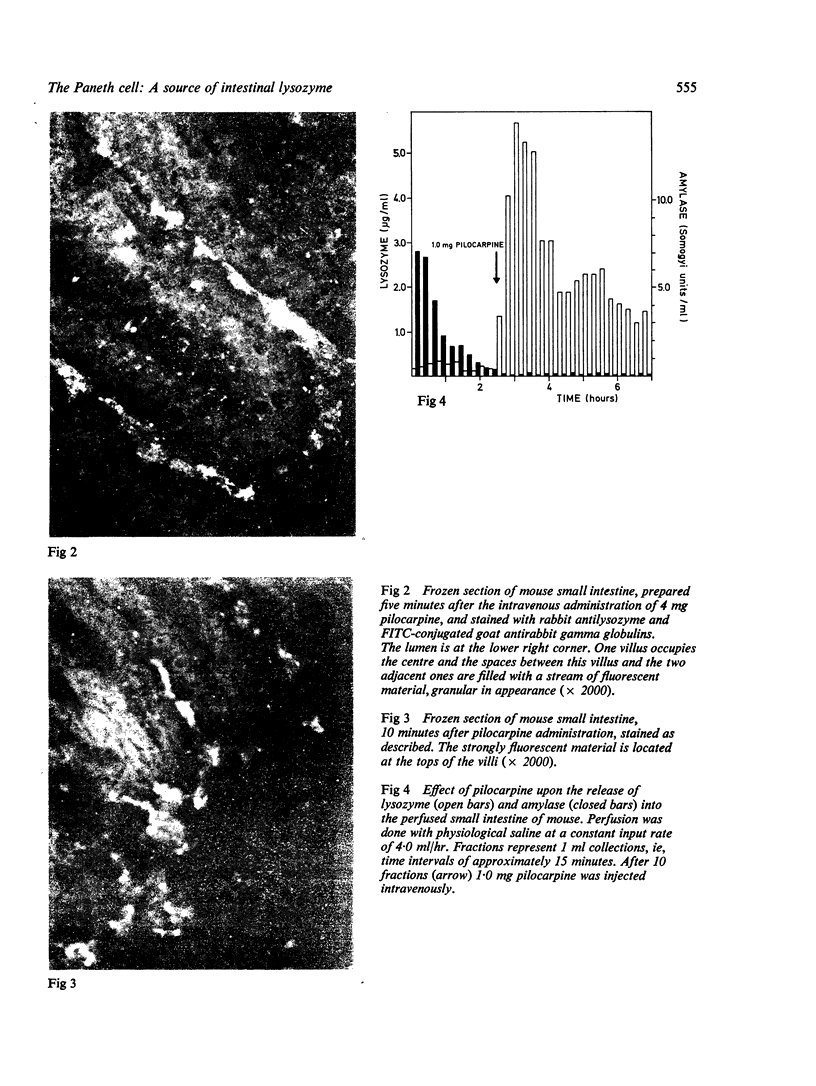
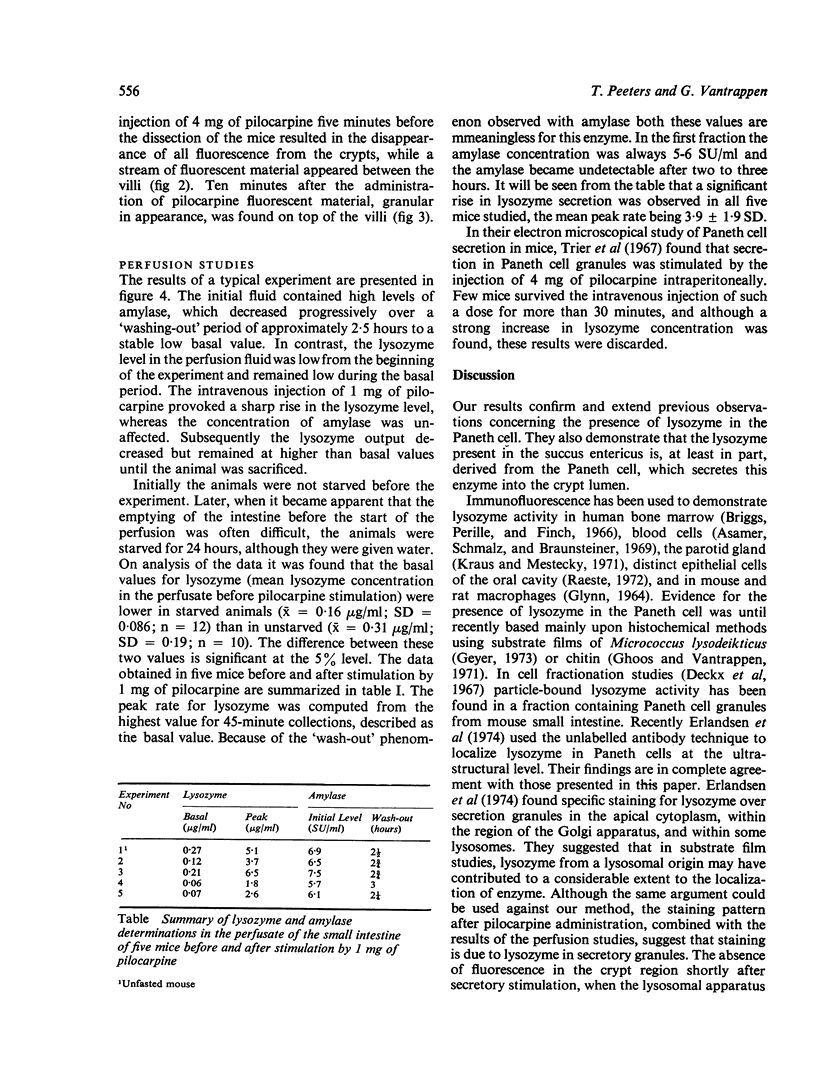
An antiserum prepared against lysozyme isolated from mucosal scrapings of mouse small intestine was used to stain sections of mouse small intestine with the indirect fluorescent antibody technique. Mucosal fluorescence was confined to the base of the crypts of Lieberkuhn, where Paneth cells are located. After the intravenous administration of 4 mg of pilocarpine fluorescence was no longer found in the Paneth cell but in the crypt lumen. Perfusion studies confirmed these findings. The basal lysozyme output of 0-1 to 0-4 mug/ml was raised to peak rates of 1-8 to 6-5 mug/ml after the intravenous administration of 1 mg of pilocarpine. Our results demonstrate that the lysozyme of the succus entericus is, at least in part, derived from the Paneth cell, and is probably present in the Paneth cell granules. Its secretion is stimulated by pilocarpine. Our model could be very useful for studying the function of the Paneth cell, which probably forms part of an intestinal defence system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asamer H., Schmalzl F., Braunsteiner H. Der immunzytologische Lysozymnachweis in menschlichen Blutzellen. Acta Haematol. 1969;41(1):49–54. doi: 10.1159/000208830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladen H., Hageage G., Harr R., Pollock F. Lysis of certain organisms by the synergistic action of complement and lysozyme. J Dent Res. 1973 Mar-Apr;52(2):371–376. doi: 10.1177/00220345730520023101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs R. S., Perillie P. E., Finch S. C. Lysozyme in bone marrow and peripheral blood cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Feb;14(2):167–170. doi: 10.1177/14.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARAWAY W. T. A stable starch substrate for the determination of amylase in serum and other body fluids. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Jul;32(1):97–99. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/32.1_ts.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creamer B. Paneth-cell function. Lancet. 1967 Feb 11;1(7485):314–316. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91245-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckx R. J., Vantrappen G. R., Parein M. M. Localization of lysozyme activity in a Paneth cell granule fraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):204–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Chase D. G. Paneth cell function: phagocytosis and intracellular digestion of intestinal microorganisms. I. Hexamita muris. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Nov;41(3):296–318. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Chase D. G. Paneth cell function: phagocytosis and intracellular digestion of intestinal microorganisms. II. Spiral microorganism. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Nov;41(3):319–333. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Parsons J. A., Taylor T. D. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of lysozyme in the Paneth cells of man. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Jun;22(6):401–413. doi: 10.1177/22.6.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gent A. E., Creamer B. Paneth cell secretion. Digestion. 1972;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1159/000197258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer G. Lysozyme in Paneth cell secretions. Acta Histochem. 1973;45(1):126–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoos Y., Vantrappen G. The cytochemical localization of lysozyme in Paneth cell granules. Histochem J. 1971 May;3(3):175–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01002560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A. Lysozyme: antigen, enzyme and antibacterial agent. Sci Basis Med Annu Rev. 1968:31–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin G., Wang S. F., Papapavlou L. Assay of lysozyme by its lytic action on M. lysodeikticus cells. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):113–127. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90467-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus F. W., Mestecky J. Immunohistochemical localization of amylase, lysozyme and immunoglobulins in the human parotid gland. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Jul;16(7):781–789. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin K. Histochemical observations on Paneth cells. J Anat. 1969 Jul;105(Pt 1):171–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeste A. M. Lysozyme (muramidase) activity of leukocytes and exfoliated epithelial cells in the oral cavity. Scand J Dent Res. 1972;80(5):422–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1972.tb00307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riecken E. O., Pearse A. G. Histochemical study on the Paneth cell in the rat. Gut. 1966 Feb;7(1):86–93. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEECE A. J. HISTOCHEMICAL DISTRIBUTION OF LYSOZYME ACTIVITY IN ORGANS OF NORMAL MICE AND RADIATION CHIMERAS. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 May;12:384–391. doi: 10.1177/12.5.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]