Abstract
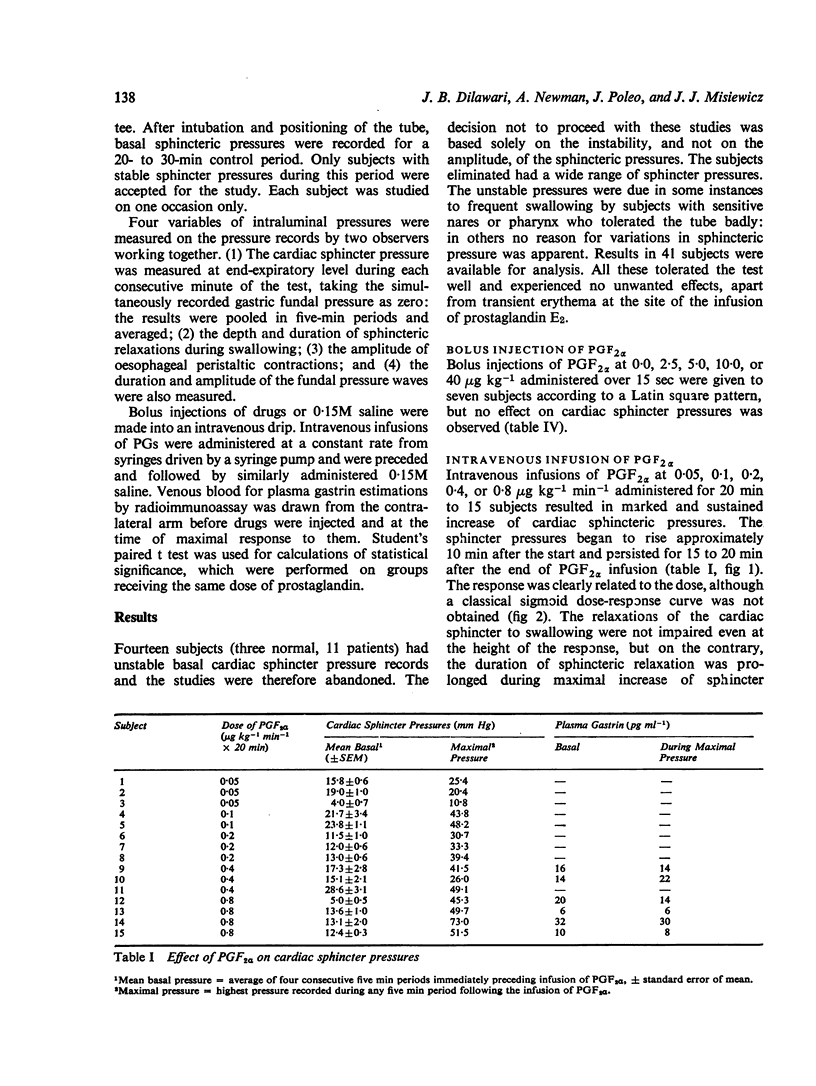
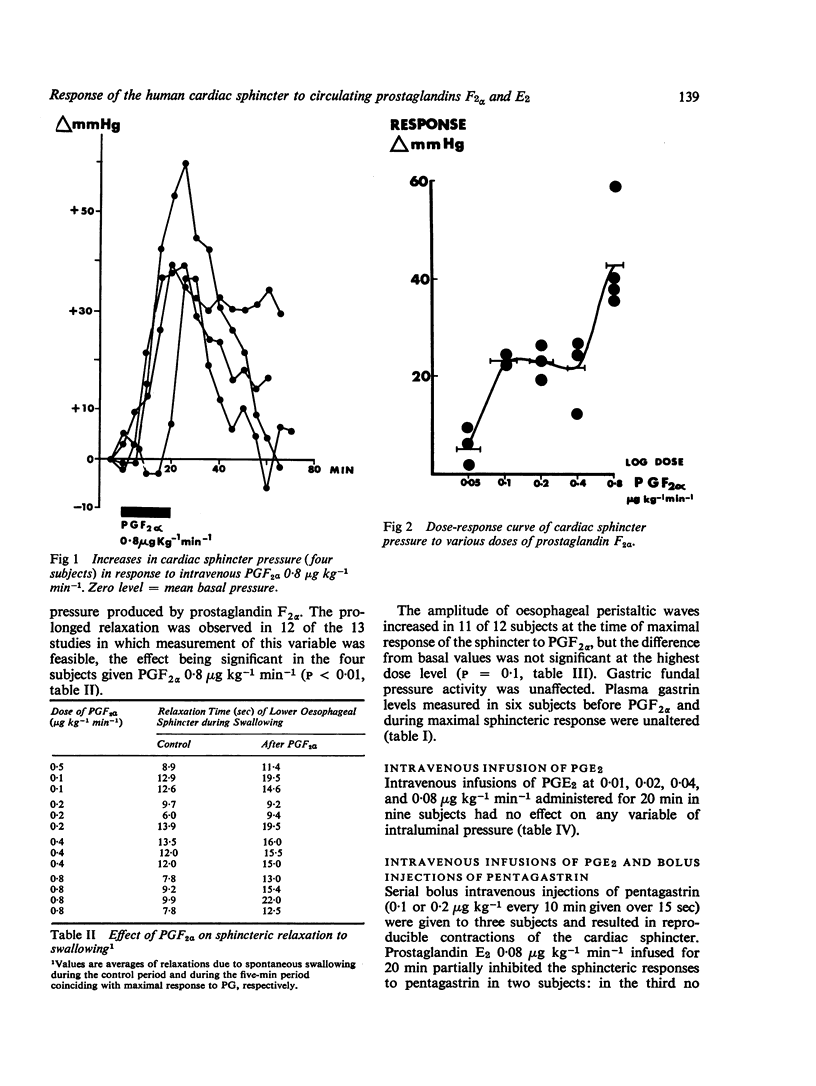
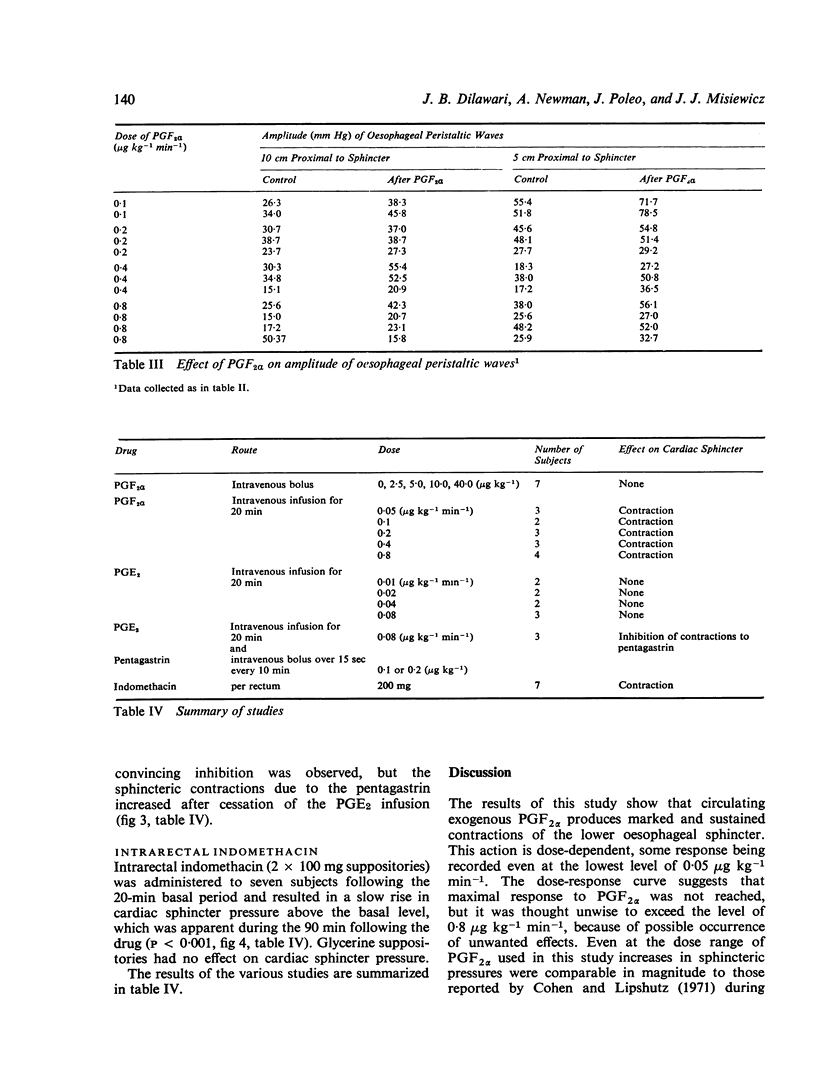
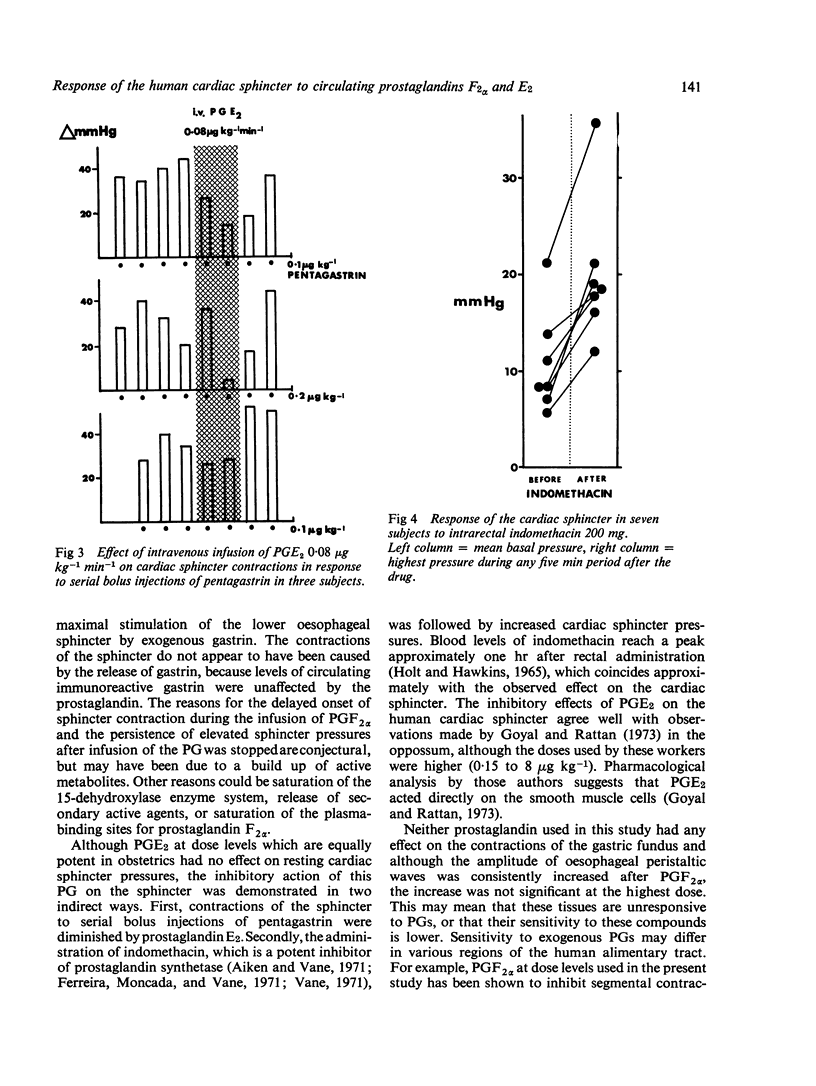
The effects on intraluminal pressure in the oesophagus, the cardiac sphincter, and the gastric fundus of intravenous prostaglandin F2alpha, E2, And of rectal indomethacin were studies in 41 subjects. Intravenous infusion of prostaglandin F2alpha (0-05 to 0-8 mug kg-minus1) produced marked, dose-related and sustained elevation of cardiac sphincter pressure without significantly affecting oesophageal peristalsis or gastric fundal motility. Sphincteric relaxation during swallowing was prolonged. Plasma gastrin levels were unchanged. Intravenous infusion of PGE2 (0-08 mug kg-minus1 min-minus) inhibited sphincter contractions to serial bolus intravenous injections of pentagastrin (0-1 or 0-2 mug kg-minus 1). Rectal indomethacin (200 mg) resulted in a riseof cardiac sphincter pressure, suggesting that endogenous synthesis of an inhibitory (E-type) prostaglandin was suppressed. The results indicate that prostaglandin E2 may be concerned in the regulation of cardiac sphincter tone in man, whilst prostaglandin F2alpha may be useful in the treatment of gastrooesphageal reflux.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A., Eley K. G., Scholes G. B. Effects of prostaglandins E1 and E2 on human, guinea-pig and rat isolated small intestine. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):630–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Friedmann C. A., Vane J. R. Release of prostaglandin E-1 from the rat stomach. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):873–876. doi: 10.1038/216873a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Murray J. G., Wyllie J. H. Occurrence of prostaglandin E2 in the human stomach, and a study of its effects on human isolated gastric muscle. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Feb;32(2):339–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Posner J. Studies on prostaglandin antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Aug;42(4):584–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell D. O., Harris L. D. Hormonal control of gastroesophageal-sphincter strength. N Engl J Med. 1970 Apr 16;282(16):886–889. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197004162821602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Daniel E. E. Effects of some autonomic drugs on circular esophageal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Feb;159(2):243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Dons R. F. Regional variations in response of cat esophageal muscle to stimulation with drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 May;161(1):55–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J. Pharmacologic identification of the lower esophageal sphincter. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):681–691. doi: 10.1172/JCI106280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Pace-Asciak C., Volta F., Wolfe L. S. Effect of nerve stimulation on prostaglandin formation and release from the rat stomach. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):1056–1064. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Lipshutz W. Hormonal regulation of human lower esophageal sphincter competence: interaction of gastrin and secretin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):449–454. doi: 10.1172/JCI106512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Newman A., Misiewicz J. J., Milton-Thompson G. J., Billings J. A. Effect of intravenous prostaglandin F 2 on small intestinal function in man. Nature. 1973 May 18;243(5403):169–171. doi: 10.1038/243169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P., Ramwell P. W., Willis A. L. Inhibition of intestinal tone and prostaglandin synthesis by 5,8,11,14 tetraynoic acid. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Nov;46(3):547P–548P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMarino A. J., Cohen S. The adrenergic control of lower esophageal sphincter function. An experimental model of denervation supersensitivity. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2264–2271. doi: 10.1172/JCI107413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenfels A., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins, oxygen tension and smooth muscle tone. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;45(3):451–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08101.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Herman A., Vane J. R. Proceedings: Prostaglandin generation maintains the smooth muscle tone of the rabbit isolated jejunum. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;44(2):328P–329P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H. Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and analgesia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):200–203. doi: 10.1038/newbio240200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung W. P., Karim S. M., Tye C. Y. Effect of 15(R)15 methylprostaglandin E2 methyl ester on healing of gastric ulcers. Controlled endoscopic study. Lancet. 1974 Jul 6;2(7871):10–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles G. R., Mason M. C., Humphries C., Clark C. G. Action of gastrin on the lower oesophageal sphincter in man. Gut. 1969 Sep;10(9):730–734. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.9.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal R. K., Rattan S. Mechanism of the lower esophageal sphincter relaxation. Action of prostaglandin E 1 and theophylline. J Clin Invest. 1973 Feb;52(2):337–341. doi: 10.1172/JCI107189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman M. I. Letters: What is physiological? Gastroenterology. 1973 Dec;65(6):994–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT L. P., HAWKINS C. F. INDOMETHACIN: STUDIES OF ABSORPTION AND OF THE USE OF INDOMETHACIN SUPPOSITORIES. Br Med J. 1965 May 22;1(5446):1354–1356. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5446.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis J. B., Levine S. M., Castell D. O. Differential sensitivity of the human esophagus to pentagastrin. Am J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(4):870–874. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.4.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt R. H., Dilawari J. B., Misiewicz J. J. The effect of intravenous prostaglandin F2 alpha and E2 on the motility of the sigmoid colon. Gut. 1975 Jan;16(1):47–49. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg J., Csendes A., Walsh J. H. Resting and pentagastrin-stimulated gastroesophageal sphincter pressure in patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1971 Nov;61(5):655–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim S. M., Carter D. C., Bhana D., Ganesan P. A. Effect of orally administered prostaglandin E 2 and its 15-methyl analogues on gastric secretion. Br Med J. 1973 Jan 20;1(5846):143–146. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5846.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipshutz W., Hughes W., Cohen S. The genesis of lower esophageal sphincter pressure: its identification through the use of gastrin antiserum. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):522–529. doi: 10.1172/JCI106840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misiewicz J. J., Waller S. L., Anthony P. P., Gummer J. W. Achalasia of the cardia: pharmacology and histopathology of isolated cardiac sphincteric muscle from patients with and without achalasia. Q J Med. 1969 Jan;38(149):17–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E. Prostaglandin inhibition of gastric secretion. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):34P–36P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashid S. The release of prostaglandin from the oesophagus and the stomach of the frog (Rana temporaria). J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;23(6):456–457. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roling G. T., Farrell R. L., Castell D. O. Cholinergic response of the lower esophageal sphincter. Am J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(4):967–972. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.4.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuch A., Cohen S. Lower esophageal sphincter relaxation: studies on the neurogenic inhibitory mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):14–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI107157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


