Abstract
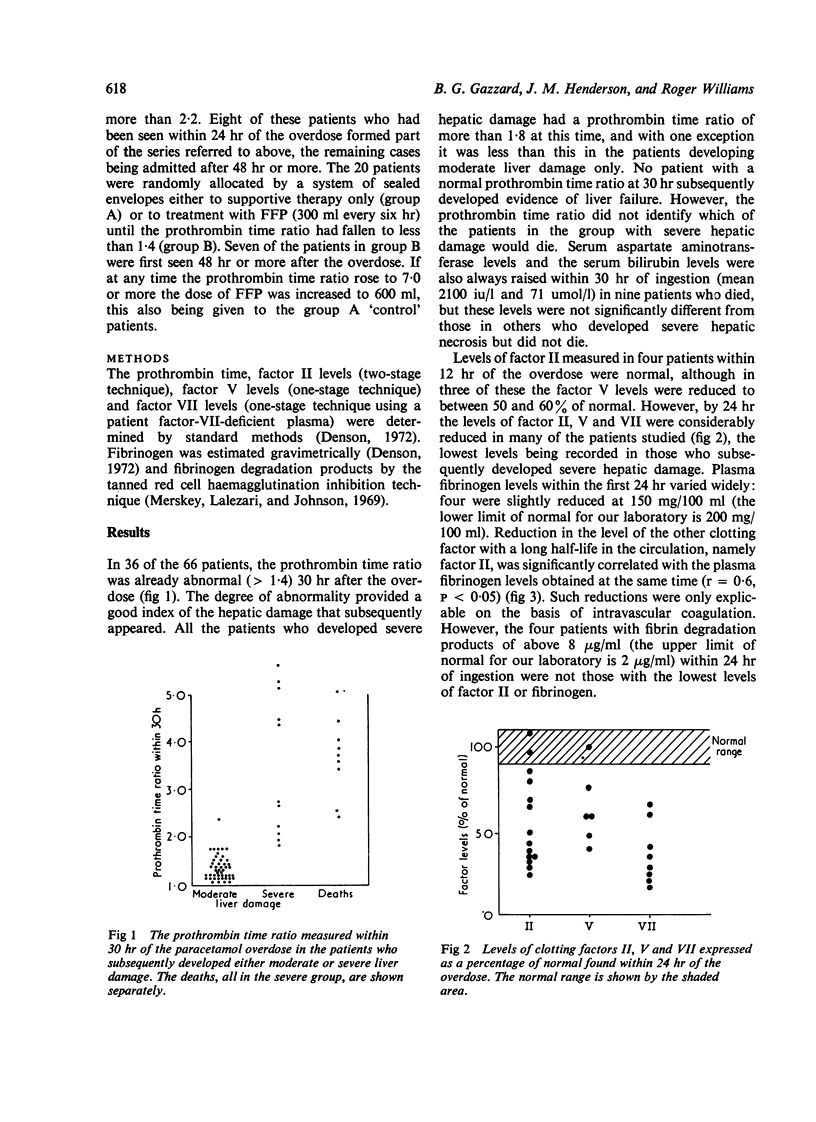
Early changes in coagulation were found in patients following a paracetamol overdose. Low levels of clotting factors II, V and VII were present within 24 hours of the overdose. As the levels of factor II correlated with plasma fibrinogen values at this time, it is possible that they were consumed in the process of intravascular coagulation, although this was not supported by the presence of raised titres of fibrin degradation products. The prothrombin time ratio was greater than 2-2 within 30 hours of ingestion of the overdose in all patients who eventually died, whereas it was less than this in those developing only moderate liver damage. The administration of fresh frozen plasma to patients did appear to reduce the maximum abnormality of the prothrombin time ratio, which was significantly less three days after the overdose in the group receiving fresh frozen plasma. However, the coagulation disturbance was of short duration, and the prothrombin time ratio had also returned to normal within one week of the overdose in the control patients, and the administration of fresh frozen plasma did not appear to reduce the morbidity or mortality in the treated patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark R., Borirakchanyavat V., Davidson A. R., Thompson R. P., Widdop B., Goulding R., Williams R. Hepatic damage and death from overdose of paracetamol. Lancet. 1973 Jan 13;1(7794):66–70. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90466-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R., Borirakchanyavat V., Gazzard B. G., Rake M. O., Shilkin K. B., Flute P. T., Williams R. Disorderd hemostasis in liver damage from paracetamol overdose. Gastroenterology. 1973 Nov;65(5):788–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzard B. G., Clark R., Borirakchanyavat V., Williams R. A controlled trial of heparin therapy in the coagulation defect of paracetamol-induced hepatic necrosis. Gut. 1974 Feb;15(2):89–93. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.2.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzard B. G., Hughes R. D., Portmann B., Dordoni B., Williams R. Protection of rats against the hepatotoxic effect of paracetamol. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Dec;55(6):601–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzard B. G., Lewis M. L., Ash G., Rizza C. R., Bidwell E., Williams R. Coagulation factor concentrate in the treatment of the haemorrhagic diathesis of fulminant hepatic failure. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):993–998. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin G. A., Montoya C. A., Sierra J. L., Senior J. R. Evaluation of corticosteroid and exchange-transfusion treatment of acute yellow-phosphorus intoxication. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jan 21;284(3):125–128. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197101212840303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Lalezari P., Johnson A. J. A rapid, simple, sensitive method for measuring fibrinolytic split products in human serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):871–875. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Roscoe P., Wright N., Brown S. S. Plasma-paracetamol half-life and hepatic necrosis in patients with paracetamol overdosage. Lancet. 1971 Mar 13;1(7698):519–522. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rake M. O., Flute P. T., Pannell G., Shilkin K. B., Williams R. Experimental hepatic necrosis: studies on coagulation abnormalities, plasma clearance, and organ distribution of 125I-labelled fibrinogen. Gut. 1973 Jul;14(7):574–580. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.7.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rake M. O., Flute P. T., Shilkin K. B., Lewis M. L., Winch J., Williams R. Early and intensive therapy of intravascular coagulation in acute liver failure. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1215–1218. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90540-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. P., Blendis L. M., Williams R. Frequency and type of renal and electrolyte disorders in fulminant hepatic failure. Br Med J. 1974 Feb 2;1(5900):186–189. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5900.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


