Abstract
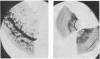
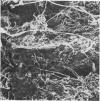
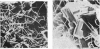
A number of gallstones have been studied using methods which have not previously been applied to gallstones. In particular, the use of scanning electron microscopy and micro-x-radiography have allowed detailed observations to be made on the structure of the stones and the distribution of the various components within the stones. Large differences in structure have been shown to exist between stones having similar overall chemical compositions. In cholesterol gallstones containing calcium carbonate the crystalline nature, distribution and method of deposition of the calcium carbonate was studied and was found to vary from stone to stone. Evidence was found for the presence of fibrous material in the centre of many stones and it is possible that this material acted as a nucleus for the deposition of the other stone components.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouchier I. A. Gallstone formation. Lancet. 1971 Apr 10;1(7702):711–715. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91985-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freston J. W., Bouchier I. A., Newman J. Biliary mucous substances in dihydrocholesterol-induced cholelithiasis. Gastroenterology. 1969 Dec;57(6):670–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy-Robb I. W. Cholesterol gallstones. Scott Med J. 1973 Sep;18(5):157–165. doi: 10.1177/003693307301800506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAINS A. J., BARSON G. J., CRAWFORD N., SHREWSBURY J. F. A chemical and bacteriological study of gallstones. The presence of an actinomycete. Lancet. 1960 Sep 17;2(7151):614–618. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)91691-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutor D. J., Wooley S. E. A statistical survey of the composition of gallstones in eight countries. Gut. 1971 Jan;12(1):55–64. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutor D. J., Wooley S. E. The sequential deposition of crystalline material in gallstones: evidence for changing gallbladder bile composition during the growth of some stones. Gut. 1974 Feb;15(2):130–131. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.2.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]