Abstract
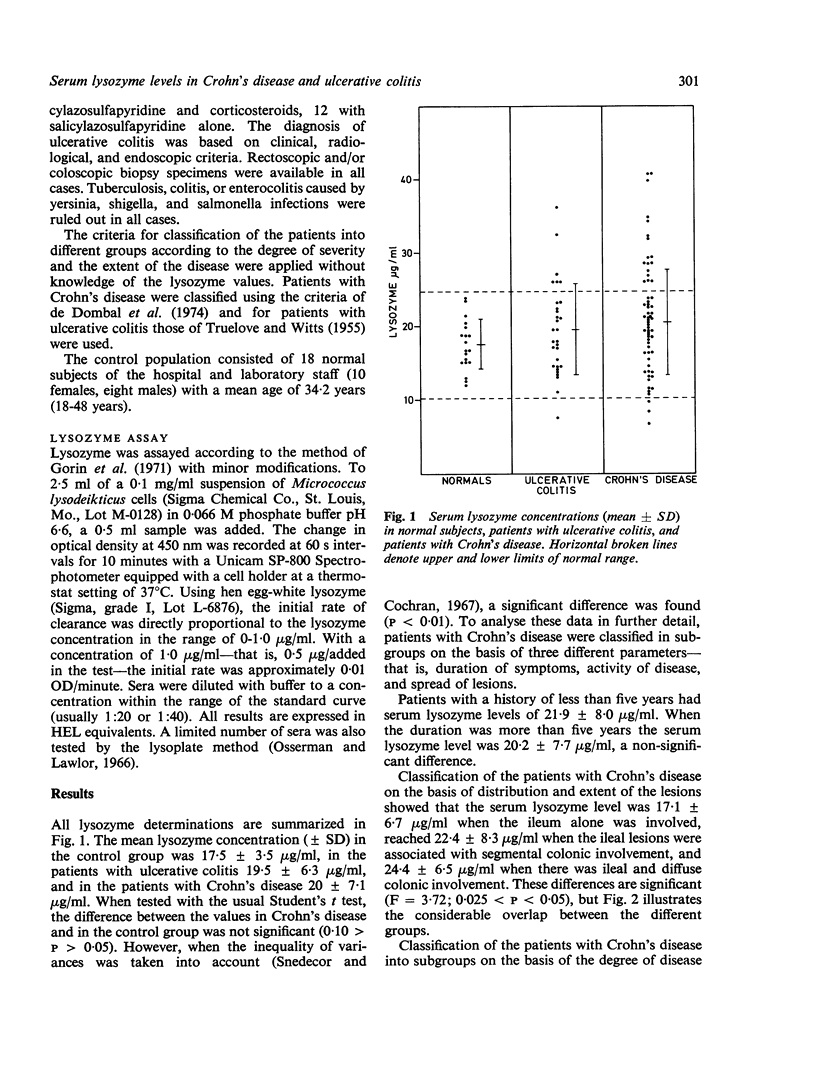
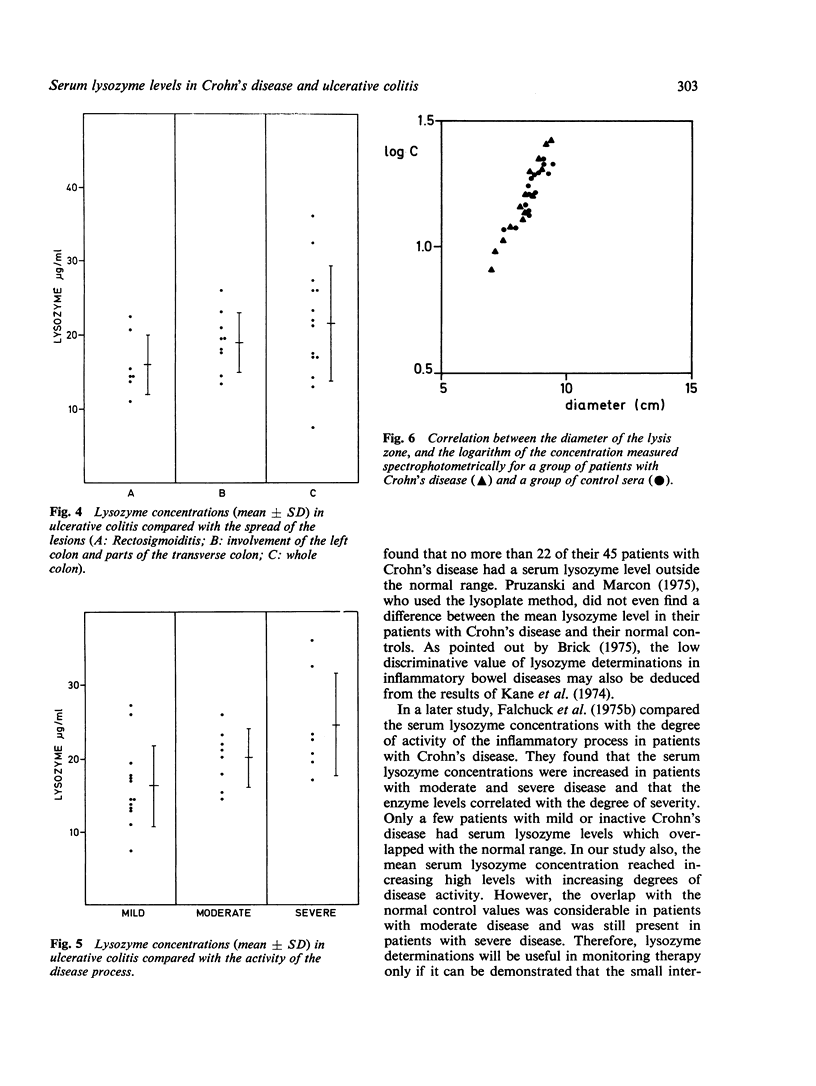
Serum lysozyme levels were determined in healthy volunteers, patients with Crohn's disease, and patients with ulcerative colitis. The mean concentration in Crohn's disease was significantly greater than in the other groups. In patients with Crohn's disease, as well as in patients with ulcerative colitis, the lysozyme levels correlated with the severity of the disease process and with the extent of the lesions: the more severe the disease and the more extensive the involvement, the higher the lysozyme levels. However, the lysozyme values of the different groups overlapped considerably. Our results indicate that lysozyme determinations have only limited discriminative value for the diagnosis of Crohn's disease and for determining the severity and the extent of the disease process in the individual patient.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brick I. B. Letter: Serum lysosyme levels in Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 15;292(20):1079–1080. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505152922016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Dombal F. T., Burton I. L., Clamp S. E., Goligher J. C. Short-term course and prognosis of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1974 Jun;15(6):435–443. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.6.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk K. R., Perrotto J. L., Isselbacher K. J. Serum lysozyme in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 20;292(8):395–397. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502202920805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk K. R., Perrotto J. L., Isselbacher K. J. Serum lysozyme in Crohn's disease. A useful index of disease activity. Gastroenterology. 1975 Oct;69(4):893–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin G., Wang S. F., Papapavlou L. Assay of lysozyme by its lytic action on M. lysodeikticus cells. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):113–127. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90467-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen N. E. Plasma lysozyme--a measure of neutrophil turnover. An analytical review. Ser Haematol. 1974;7(1):1–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. P., Hoffbrand A. V., Neale G. Indices of granulocyte activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):953–959. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman E. F., Lawlor D. P. Serum and urinary lysozyme (muramidase) in monocytic and monomyelocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1966 Nov 1;124(5):921–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual R. S., Gee J. B., Finch S. C. Usefulness of serum lysozyme measurement in diagnosis and evaluation of sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Nov 15;289(20):1074–1076. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311152892007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perillie P. E., Khan K., Finch S. C. Serum lysozyme in pulmonary tuberculosis. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Apr;265(4):297–302. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197304000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pounder R. E., Avella J. R., McCallum H., Misiewicz J. J. Letter: Serum lysozyme in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1975 Aug 2;2(7927):228–229. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90696-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Marcon N. Letter: Lysozyme in Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 18;293(12):611–612. doi: 10.1056/nejm197509182931219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUELOVE S. C., WITTS L. J. Cortisone in ulcerative colitis; final report on a therapeutic trial. Br Med J. 1955 Oct 29;2(4947):1041–1048. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4947.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker S., Hanes D. J., Vogler W. R., Eanes R. Z. Plasma muramidase: a study of methods and clinical applications. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jan;75(1):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


