Abstract
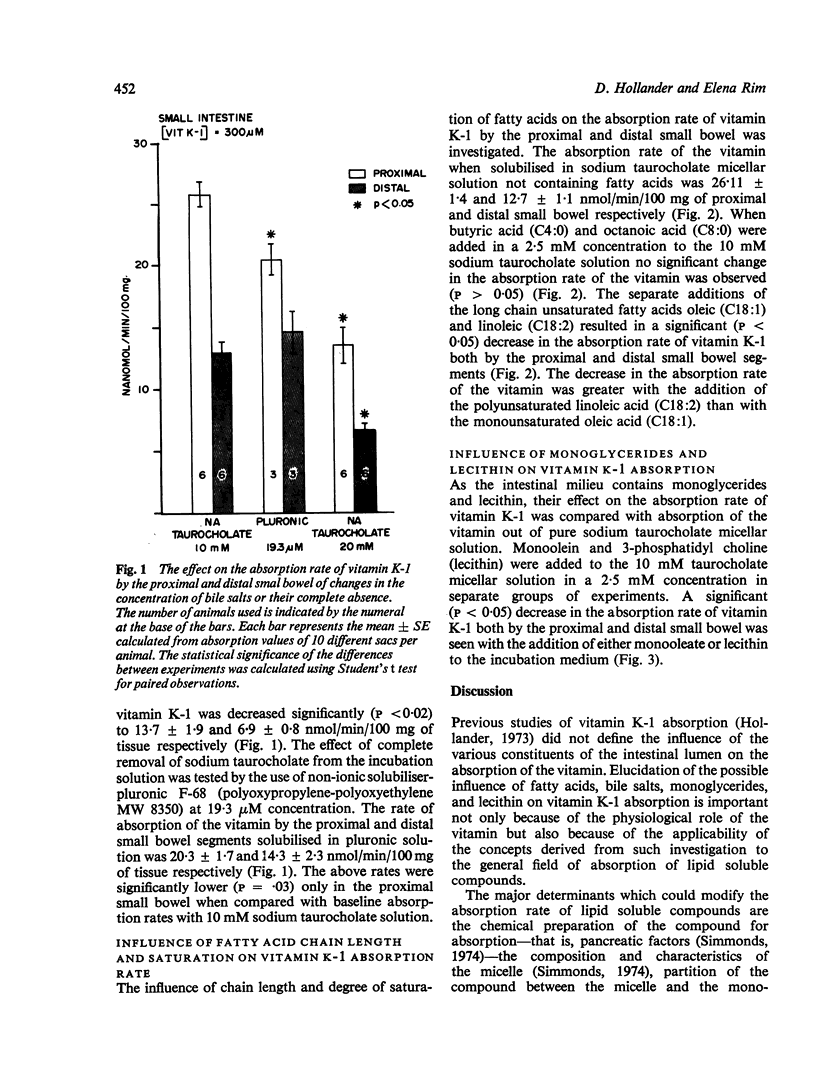
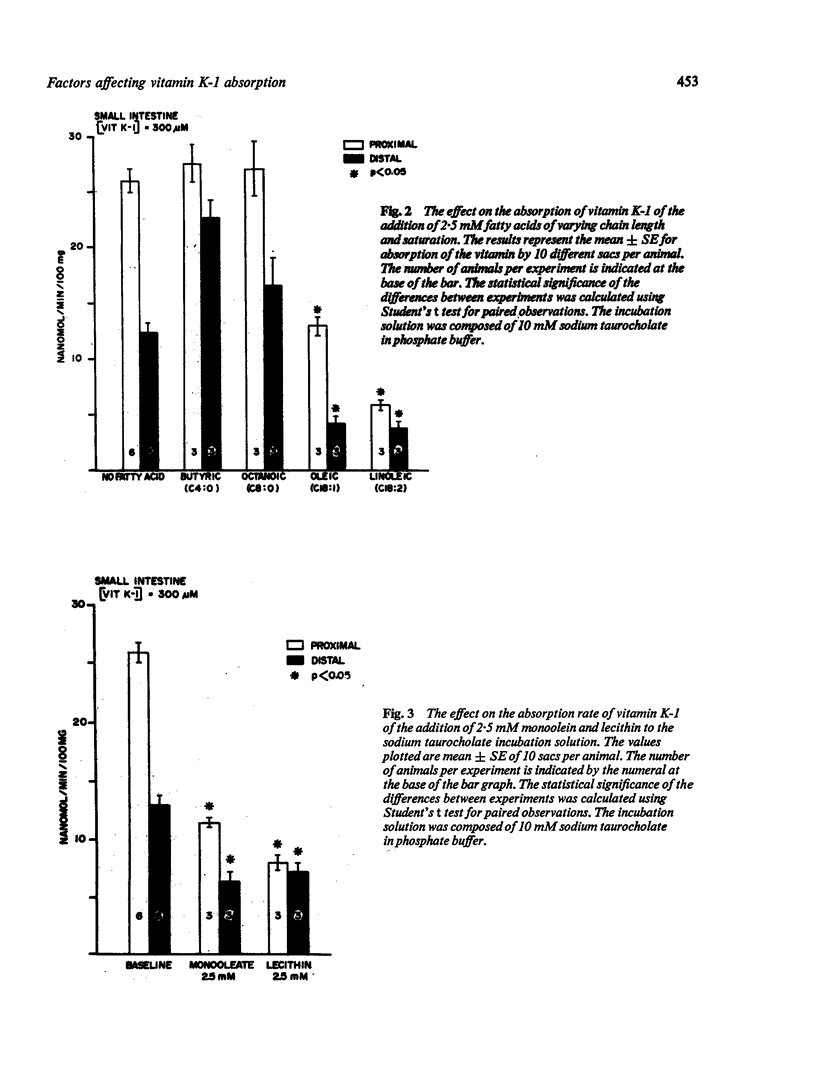
Factors which might affect the absorption of vitamin K of dietary origin were investigated using everted small bowel sacs. Increasing the bile salt concentration to 20 mM or the addition of long chain fatty acids, monoolein, or lecithin all resulted in significant (P less than 0-05) decrease in the absorption rate of the vitamin. The addition of 2-5 mM short and medium chain fatty acids did not change the absorption rate of vitamin K-1 (P greater than 0-05). The absorption rate of vitamin K-1 appears to be modified by the presence of compounds in the incubation medium which either alter the partition of the vitamin between the micelle and the cell membrane or which change the permeation characteristics of the compound through the unstirred water layer or modify the physical characteristics of the cell membrane itself. It is possible that some of the above factors modify the absorption of lipid soluble compounds in general.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Diamond J. M., Katz Y. Interpretation of nonelectrolyte partition coefficients between dimyristoyl lecithin and water. J Membr Biol. 1974;17(2):121–154. doi: 10.1007/BF01870176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:581–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito G., Csáky T. Z. Extracellular space in the epithelium of rats' small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jan;226(1):50–55. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg J. A. New solvent systems for thin-layer chromatography of bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):579–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries J. T., Sladen G. E. The effects of different bile salts on the absorption of fluid, electrolytes, and monosaccharides in the small intestine of the rat in vivo. Gut. 1972 Aug;13(8):596–603. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.8.596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander D. Vitamin K1 absorption by everted intestinal sacs of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1973 Aug;225(2):360–364. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.2.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. J. Transport of short chain fatty acids. Biomembranes. 1974;4B(0):673–709. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3336-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. Y., Simmonds W. J., Hoffman N. E. The effect of partition of fatty acid between oil and micelles on its uptake by everted intestinal sacs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):548–555. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschiner J. T., Taggart W. V., Amelotti J. M. The vitamin K content of beef liver. Detection of a new form of vitamin K. Biochemistry. 1967 May;6(5):1243–1248. doi: 10.1021/bi00857a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. R., Ockner R. K., Isselbacher K. J. Effect of mixed micellar lipid on the absorption of cholesterol and vitamin D3 into lymph. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):87–95. doi: 10.1172/JCI105977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenheuvel F. A. Structure of membranes and role of lipids therein. Adv Lipid Res. 1971;9:161–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard H., Dietschy J. M. Delineation of the dimensions and permeability characteristics of the two major diffusion barriers to passive mucosal uptake in the rabbit intestine. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):718–732. doi: 10.1172/JCI107810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. A., Dietschy J. M. The intestinal unstirred layer: its surface area and effect on active transport kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 21;363(1):112–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


