Abstract
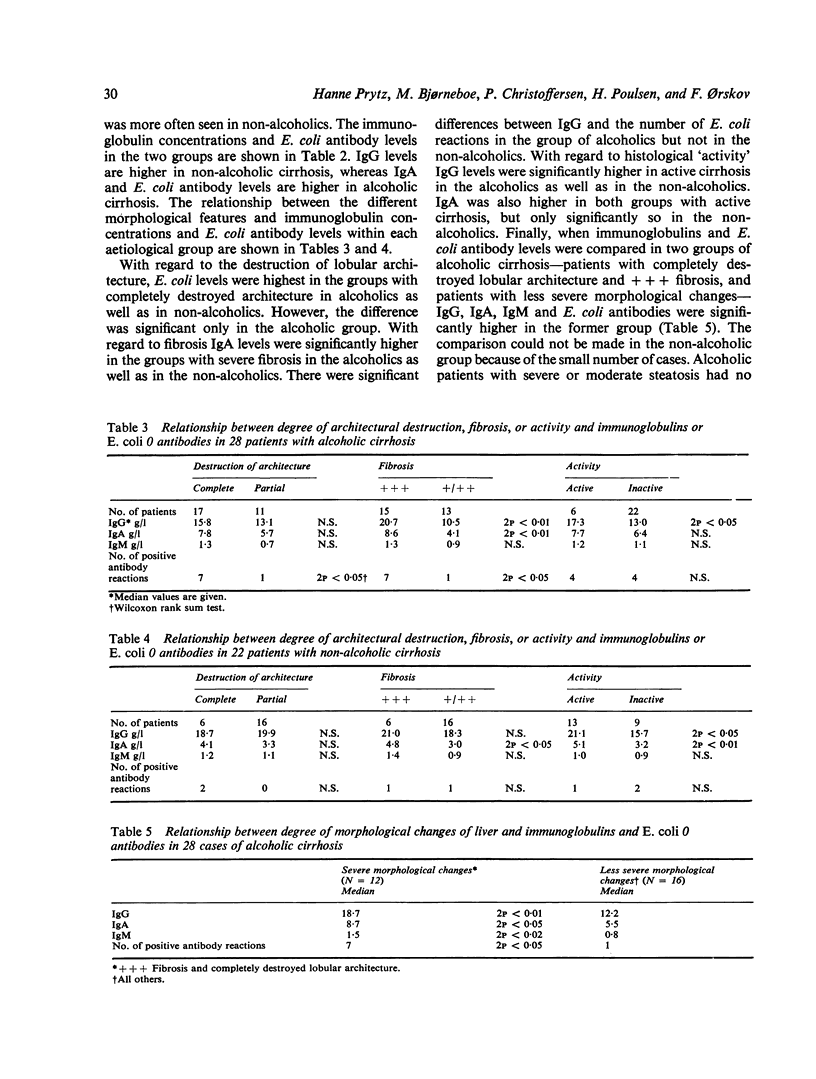
Increased antibody production and hypergammaglobulinaemia in cirrhosis are probably to a large extent due to decreased hepatic extraction of antigens. The deceased extraction is presumably related to changed microcirculation caused by damaged anatomical structure of the liver. It is therefore to be expected that immunoglobulin and antibody levels in serum in cirrhotic patients are related to the degree of certain morphological changes of the liver. This hypothesis has been tested. In 50 patients with cirrhosis, 28 alcoholics and 22 non-alcoholics, the degree of architectural destruction, the degree of fibrosis, the degree of fatty infiltration, and the degree of "activity" were compared with immunoglobulins G, A, and M and E. coli O antibody levels. The comparison was carried out within each of the aetiological groups. Identical relationships were found in both groups. Patients with completely destroyed lobular architecture had higher levels of E. coli O antibodies than patients with partly destroyed architecture. Patients with severe fibrosis had higher IgA and E. coli O antibody levels than patients with moderate or slight fibrosis. Patients with moderate and severe steatosis and patients with no or slight steatosis had the same immunoglobulin and E. coli O antibody levels. Patients with active cirrhosis had higher IgG levels than patients with inactive cirrhosis. When architectural destruction and fibrosis were combined significantly higher IgG, IgA, IgM, and E. coli antibodies were found in the group with the most severe changes. These findings support the hypothesis that immunoglobulin and antibody levels are related to the degree of morphological changes in the liver--namely, destruction of lobular architecture, fibrosis, and "activity".
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer S. J., Wust C. J. Comparison of immunogenic RNA extracted from peritoneal exudate cells and Kupffer cells of the rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 May 31;207:241–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb47487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., Meima F., Van der Meulen G. M., van Ewijk W. Antibody formation in mouse bone marrow. III. Effects of route of priming and antigen dose. Immunology. 1974 Nov;27(5):747–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorneboe M., Prytz H., Orskov F. Antibodies to intestinal microbes in serum of patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Lancet. 1972 Jan 8;1(7741):58–60. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksley W. G., Powell L. W., Halliday J. W. Reticuloendothelial phagocytic function in human liver disease and its relationship to haemolysis. Br J Haematol. 1973 Aug;25(2):147–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01725.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzl R. E. The primary immune response in mice. 3. Retention of sheep red blood cell immunogens by the spleen and liver. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):469–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.469-482.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN B. N., BIOZZI G., PEQUIGNOT G., DELALOYE B., STIFFEL C., MOUTON D. [Measurement of the blood circulation of the liver and of the phagocytic activity of the reticuloendothelial system in the normal subject and the cirrhotic patient]. Pathol Biol. 1959 Aug;7:1637–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchley C. J. The actvity of mouse Kupffer cells following intravenous injection of T4 bacteriophage. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jul;5(1):173–187. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEEVY C. M., ZINKE M., BABER J., CHEY W. Y. Observations on the influence of medical therapy on portal hypertension in hepatic cirrhosis. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Oct;49(4):837–851. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-49-4-837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. S., Triger D. R. Studies on hepatic uptake of antigen. III. Studies of liver macrophage function in normal rats and following carbon tetrachloride administration. Immunology. 1975 Aug;29(2):253–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prytz H., Bjorneboe M., Johansen T. S., Orskov F. The influence of portosystemic shunt operation on immunoglobulins and Escherichia coli antibodies in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Acta Med Scand. 1974 Jul-Aug;196(1-2):109–112. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1974.tb00976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prytz H., Björneboe M., Orskov F., Hilden M. Antibodies to Escherichia coli in alcoholic and non-alcoholic patients with cirrhosis of the liver or fatty liver. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1973;8(5):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANKIN J. G., PLAYOUST M. R., BEAL R. W. Significance of alterations in extraction and distribution of colloidal chromic phosphate in patients with liver disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Dec;58:920–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport A. M., Black R. G., Lucas C. C., Ridout J. H., Best C. H. Normal and pathologic microcirculation of the living mammalian liver. Rev Int Hepatol. 1966;16(4):813–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds T. B., Hidemura R., Michel H., Peters R. Portal hypertension without cirrhosis in alcoholic liver disease. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Mar;70(3):497–506. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-3-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHALDON S., CHIANDUSSI L., GUEVARA L., CAESAR J., SHERLOCK S. The estimation of hepatic blood flow and intrahepatic shunted blood flow by colloidal heat-denatured human serum albumin labeled with I-131. J Clin Invest. 1961 Jul;40:1346–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI104365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. L., Addison I. E., Bradfield J. W. Increased antibody production following depression of hepatic phagocytosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Apr;20(1):155–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souhami R. L. The effect of colloidal carbon on the organ distribution of sheep red cells and the immune response. Immunology. 1972 Apr;22(4):685–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., McSween R. N., White R. G. Role of the liver in controlling the immunogenicity of commensal bacteria in the gut. Lancet. 1973 Jun 9;1(7815):1288–1291. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triger D. R., Alp M. H., Wright R. Bacterial and dietary antibodies in liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Jan 8;1(7741):60–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triger D. R., Wright R. Studies on hepatic uptake of antigen. II. The effect of hepatotoxins on the immune response. Immunology. 1973 Dec;25(6):951–956. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. Origin and molecular size of immunoglobulin-A in the mesenteric lymph of the dog. Immunology. 1970 Jan;18(1):27–38. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


