Abstract
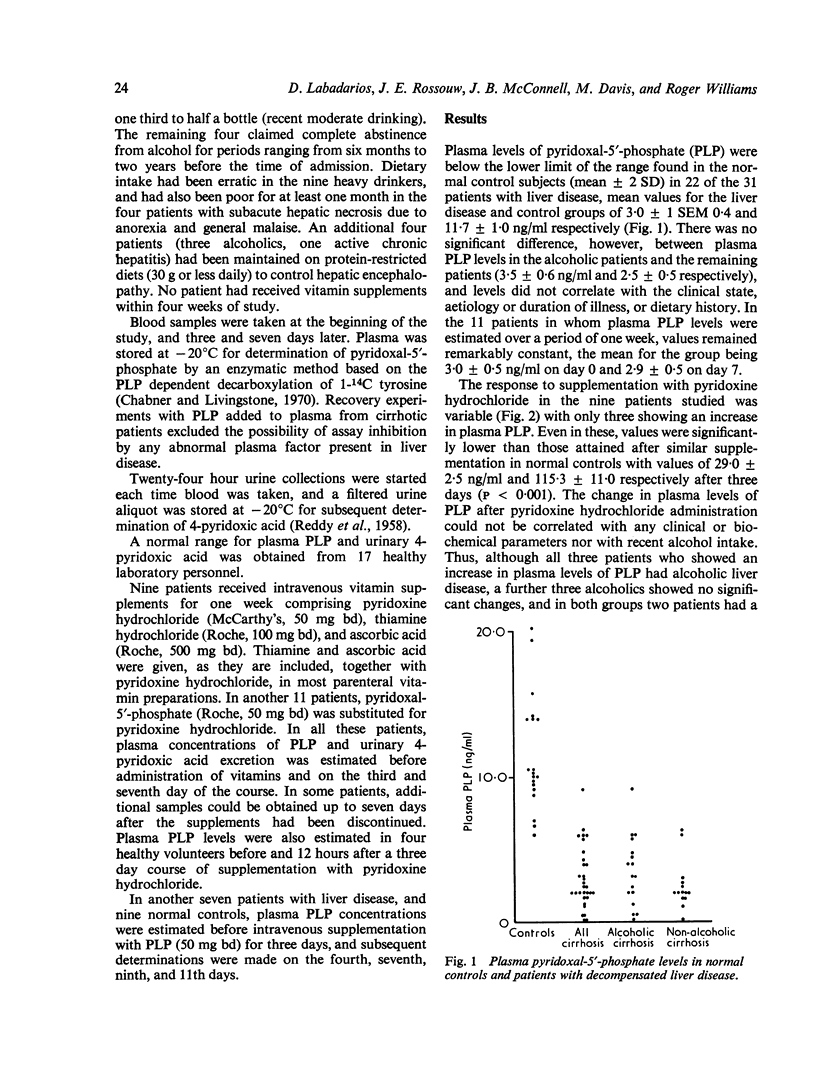
Plasma levels of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP), the active coenzyme form of vitamin B6, were found to be significantly lower than normal in 22 out of 31 patients with decompensated cirrhosis or subacute hepatic necrosis. There was no significant difference in plasma PLP levels between those with liver disease due to alcohol and those with other varieties. When intravenous supplements with pyridoxine hydrochloride were given only 33% responded with an increase in plasma PLP. In contrast, all patients given PLP responded, although peak plasma levels were variable, the response being significantly less than that found in normal control subjects. After supplementation with pyridoxine hydrochloride, and with PLP, the urinary excretion of 4-pyridoxic acid, which is derived from the degradation of PLP, was higher in patients who showed the least increase in plasma PLP levels. Although impaired phosphorylation of pyridoxine hydrochloride may be one factor, the most likely explanation for these findings is an increased rate of PLP degradation which may be important in the pathogenesis of vitamin B6 deficiency in patients with severe liver disease.
Full text
PDF
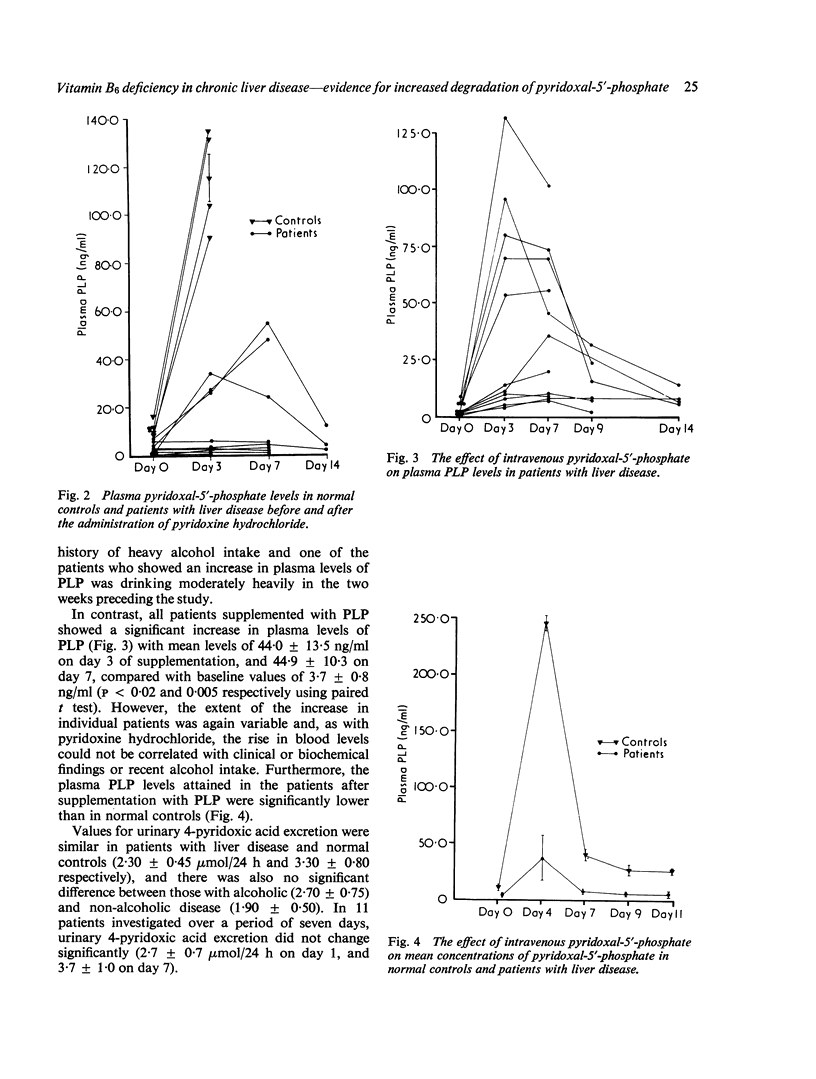


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chabner B., Livingston D. A simple enzymic assay for pyridoxal phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1970 Apr;34(2):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombini C. E., McCoy E. E. Vitamin B6 metabolism. The utilization of [14C]pyridoxine by the normal mouse. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 3;9(3):533–538. doi: 10.1021/bi00805a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contractor S. F., Shane B. 4-pyridoxic acid 5'-phosphate: a metabolite of pyridoxol in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970;39(6):1175–1181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90684-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamfelt A. Enzymatic determination of pyridoxal phosphate in plasma by decarboxylation of L-tyrosine-14 C (U) and a comparison with the tryptophan load test. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1967;20(1):1–10. doi: 10.1080/00365516709076912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamfelt A. Pyridoxal phosphate concentration and aminotransferase activity in human blood cells. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 Apr;16(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90264-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines J. D., Cowan D. H. Studies on the pathogenesis of alcohol-induced sideroblastic bone-marrow abnormalities. N Engl J Med. 1970 Aug 27;283(9):441–446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197008272830901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEEVY C. M., BAKER H., TENHOVE W., FRANK O., CHERRICK G. R. B-COMPLEX VITAMINS IN LIVER DISEASE OF THE ALCOHOLIC. Am J Clin Nutr. 1965 Apr;16:339–346. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/16.4.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevy C. M., Thompson A., Baker H. Vitamins and liver injury. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Apr;23(4):493–499. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumeng L., Li T. K. Vitamin B6 metabolism in chronic alcohol abuse. Pyridoxal phosphate levels in plasma and the effects of acetaldehyde on pyridoxal phosphate synthesis and degradation in human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):693–704. doi: 10.1172/JCI107607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REDDY S. K., REYNOLDS M. S., PRICE J. M. The determination of 4-pyridoxic acid in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1958 Sep;233(3):691–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauberlich H. E., Canham J. E., Baker E. M., Raica N., Jr, Herman Y. F. Biochemical assessment of the nutritional status of vitamin B 6 in the human. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Jun;25(6):629–642. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.6.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


