Abstract
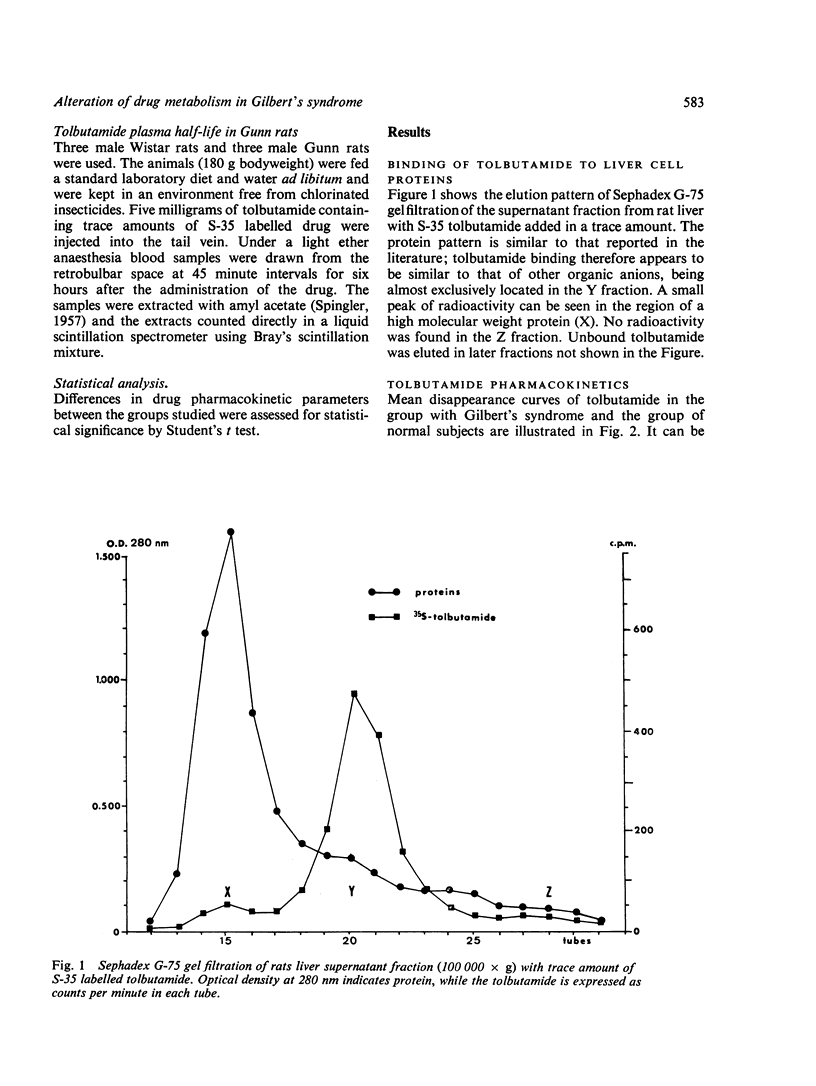
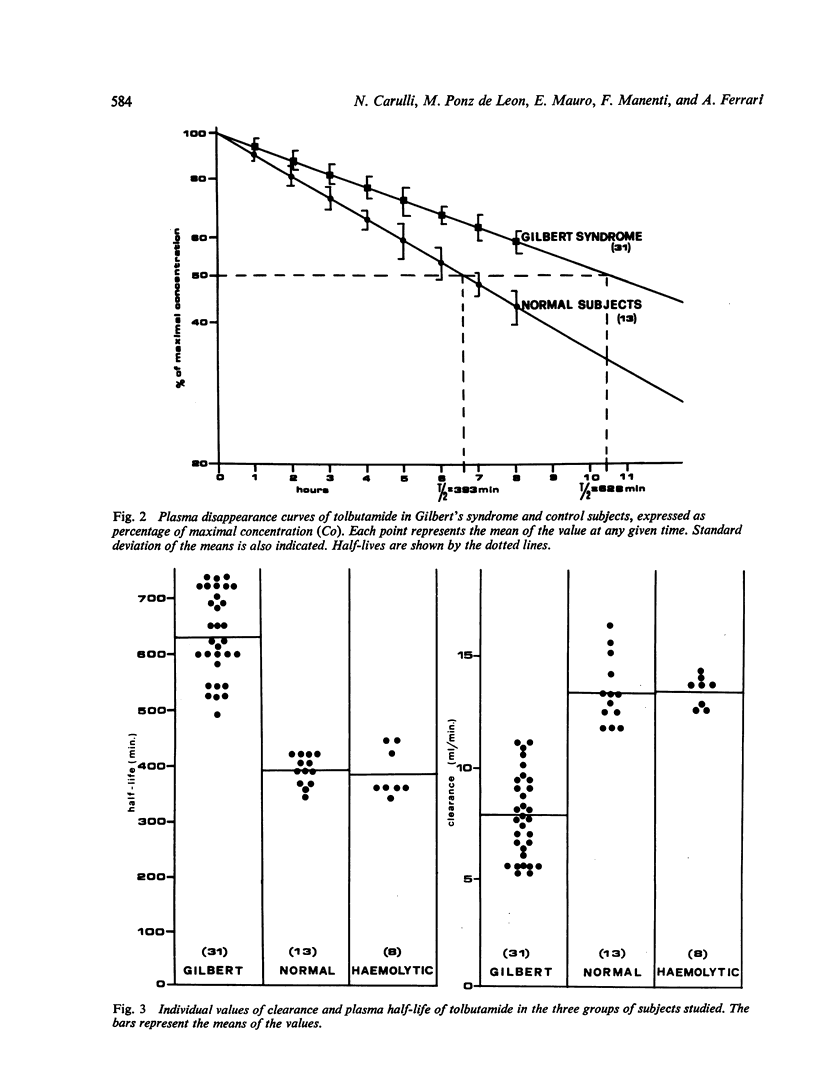
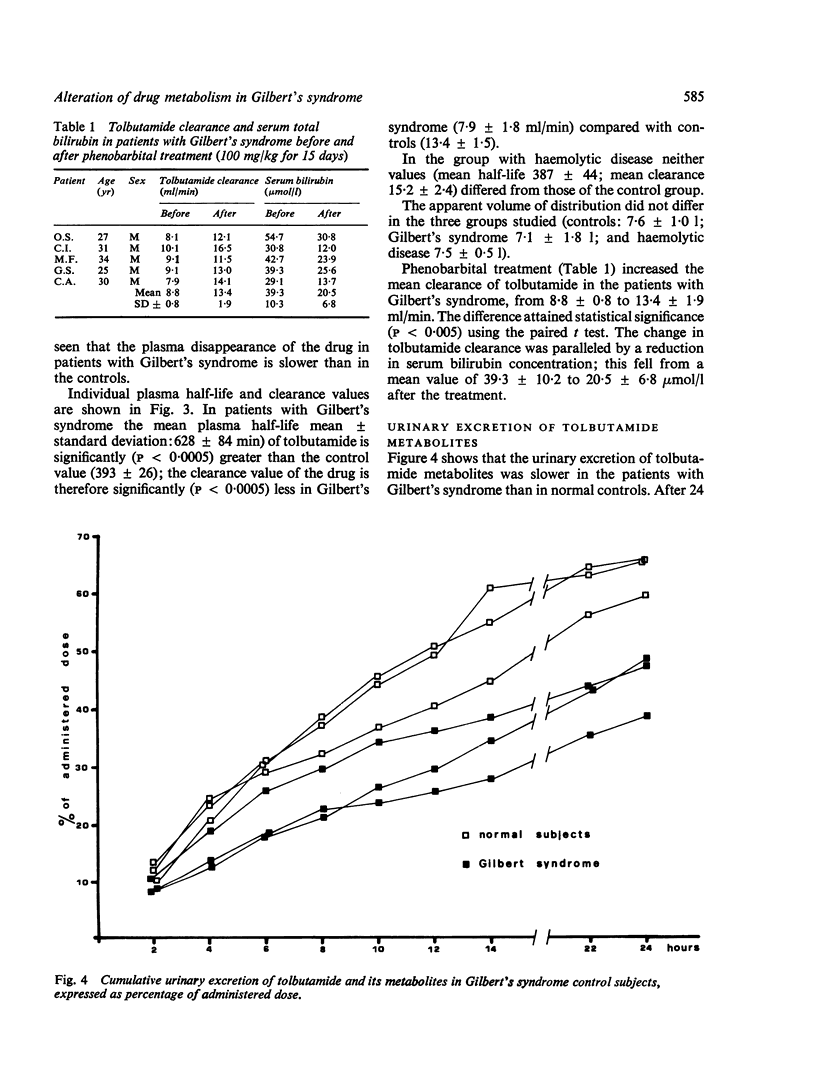
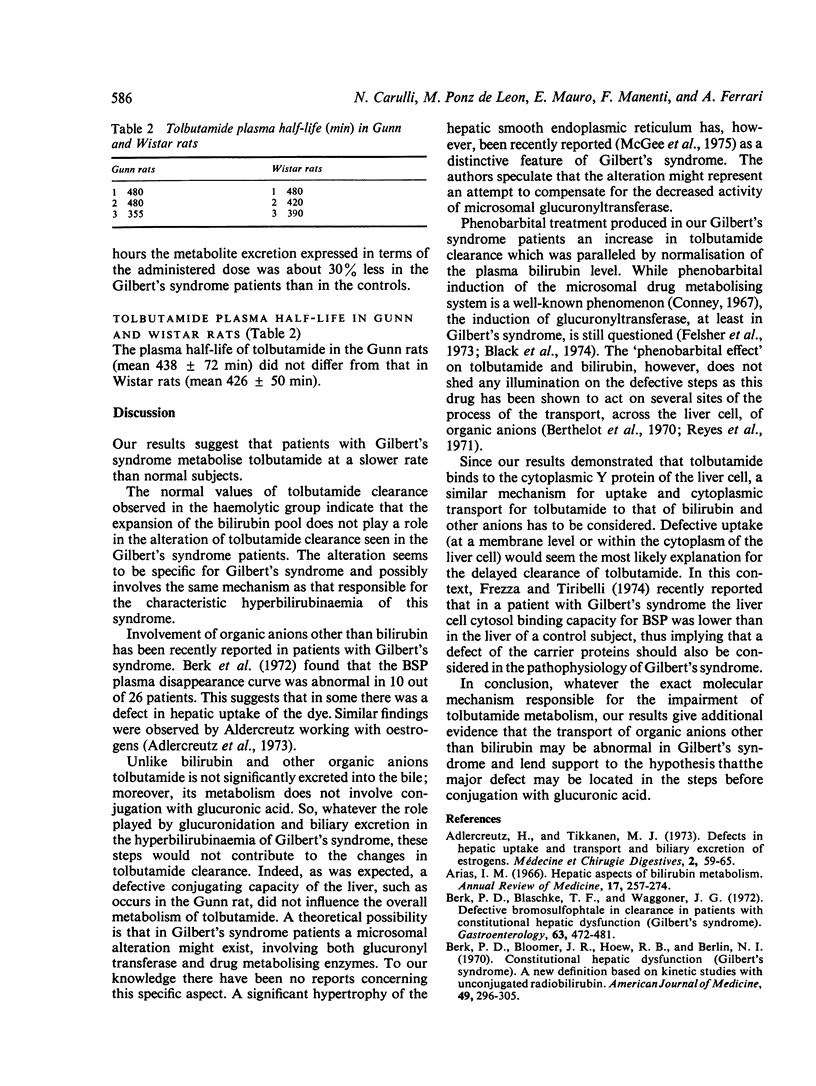
The pathophysiology of Gilbert's syndrome was studied by investigating the metabolism of the drug tolbutamide, which is metabolised by the liver but does not undergo glucuronidation. Using rat liver cell supernatant, tolbutamide was shown to bind to the hepatic cytoplasmic Y protein in a manner similar to other organic anions, but not to Z protein. In 31 patients with Gilbert's syndrome the plasma disappearance (plasma half-life, mean +/- SD: 628+/-84 min) and metabolic clearance (7-9+/-1-8 ml/min) were significantly (P less than 0-0005) altered compared with the 13 controls (mean half-life 393+/-26 and mean clearance 13-4+/-1-5). The eight patients with hyperbilirubinaemia due to haemolytic disease showed no difference from the normal control subjects. In three patients with Gilbert's syndrome the cumulative urinary excretion of tolbutamide metabolites, 24 hours after the administration of the drug, was 30% lower than in the controls. In the five patients with Gilbert's syndrome, phenobarbital administration (100 mg/day) produced a significant increase in clearance of the drug from 8-8+/-0-8 to 13-4+/-1-9 ml/min; this was paralleled by a fall in serum bilirubin concentration. The plasma half-life of tolbutamide was similar in Gunn rats and Wistar rats. The results suggest that the metabolic defect(s) of Gilbert's syndrome affects compounds other than bilirubin and that defective uptake is probably the major factor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlercreutz H., Tikkanen M. J. Defects in hepatic uptake and transport and biliary excretion of estrogens. Some new concepts of liver metabolism. Med Chir Dig. 1973;2(2):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias I. M. Hepatic aspects of bilirubin metabolism. Annu Rev Med. 1966;17:257–274. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.17.020166.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLING B. H., WILLIAMS R., RICHARDS T. G. DEFECTS IN HEPATIC TRANSPORT OF BILIRUBIN IN CONGENITAL HYPERBILIRUBINAEMIA: AN ANALYSIS OF PLASMA BILIRUBIN DISAPPEARANCE CURVES. Clin Sci. 1964 Oct;27:245–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Blaschke T. F., Waggoner J. G. Defective bromosulfophthalein clearance in patients with constitutional hepatic dysfunction (Gilbert's syndrome). Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(3):472–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk P. D., Bloomer J. R., Howe R. B., Berlin N. I. Constitutional hepatic dysfunction (Gilbert's syndrome). A new definition based on kinetic studies with unconjugated radiobilirubin. Am J Med. 1970 Sep;49(3):296–305. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthelot P., Erlinger S., Dhumeaux D., Preaux A. M. Mechanism of phenobarbital-induced hypercholeresis in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1970 Sep;219(3):809–813. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.3.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M., Billing B. H. Hepatic bilirubin udp-glucuronyl transferase activity in liver disease and gilbert's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jun 5;280(23):1266–1271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196906052802303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M., Fevery J., Parker D., Jacobson J., Billing B. H., Carson E. R. Effect of phenobarbitone on plasma (14C)bilirubin clearance in patients with unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Jan;46(1):1–17. doi: 10.1042/cs0460001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):317–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby F. J., Grundy R. K., Evans D. A. Apparent Michaelis constants for the metabolism of (ureyl- 14 C)tolbutamide by human liver microsomal preparations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Feb 1;21(3):407–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90352-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsher B. F., Craig J. R., Carpio N. Hepatic bilirubin glucuronidation in Gilbert's syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Jun;81(6):829–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Two hepatic cytoplasmic protein fractions, Y and Z, and their possible role in the hepatic uptake of bilirubin, sulfobromophthalein, and other anions. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2156–2167. doi: 10.1172/JCI106182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Allan J. G., Russell R. I., Patrick R. S. Liver ultrastructure in Gilbert's syndrome. Gut. 1975 Mar;16(3):220–224. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.3.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON E., O'REILLY I. Kinetics of carboxytolbutamide excretion following tolbutamide and carboxytolbutamide administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Apr;132:103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nistrup Madsen S., Fog-Moller F., Persson I. Distribution of tolbutamide and chlorpropamide after administration to non-diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971;13(3):374–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Studies of Y and Z, two hepatic cytoplasmic organic anion-binding proteins: effect of drugs, chemicals, hormones, and cholestasis. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2242–2252. doi: 10.1172/JCI106721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPINGLER H. Uber eine Möglichkeit zur colorimetrischen Bestimmung von N-(4-Methyl-benzolsulfonyl)-N'-butyl-harnstoff in Serum. Klin Wochenschr. 1957 May 15;35(10):533–535. doi: 10.1007/BF01480893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C., Ikeda G. J. The metabolic fate of tolbutamide in man and in the rat. J Med Chem. 1966 Jul;9(4):507–510. doi: 10.1021/jm00322a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


