Abstract
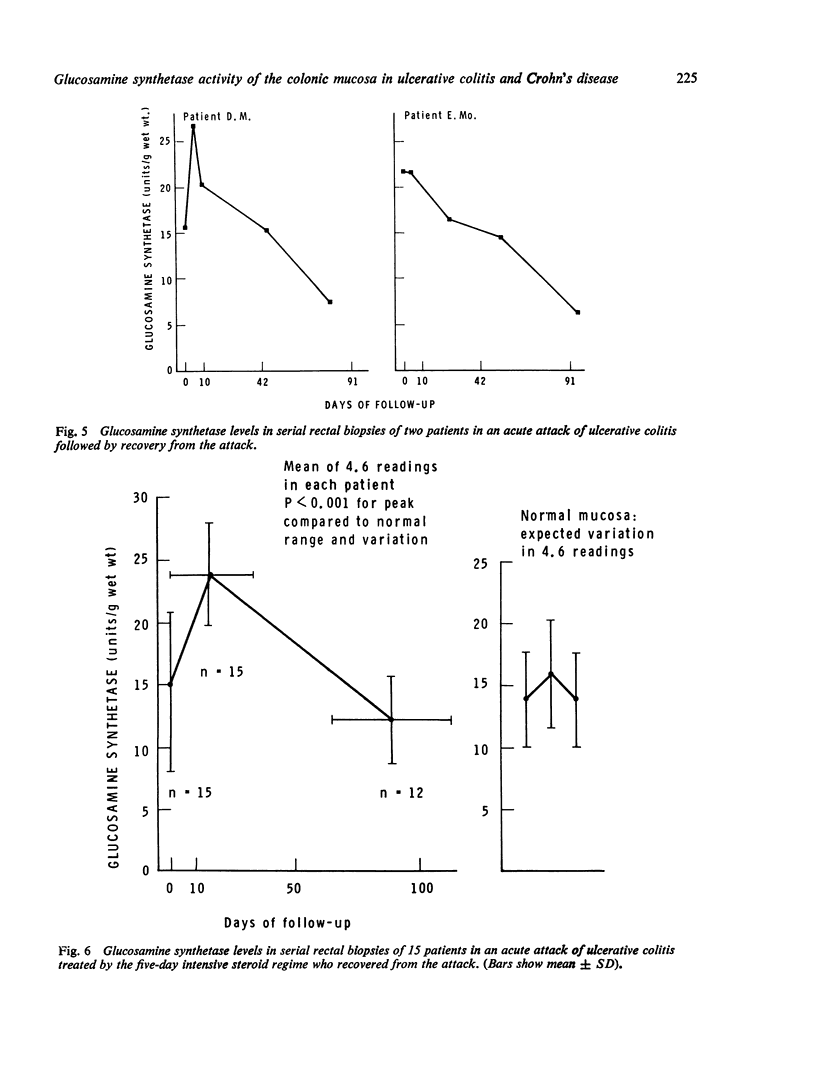
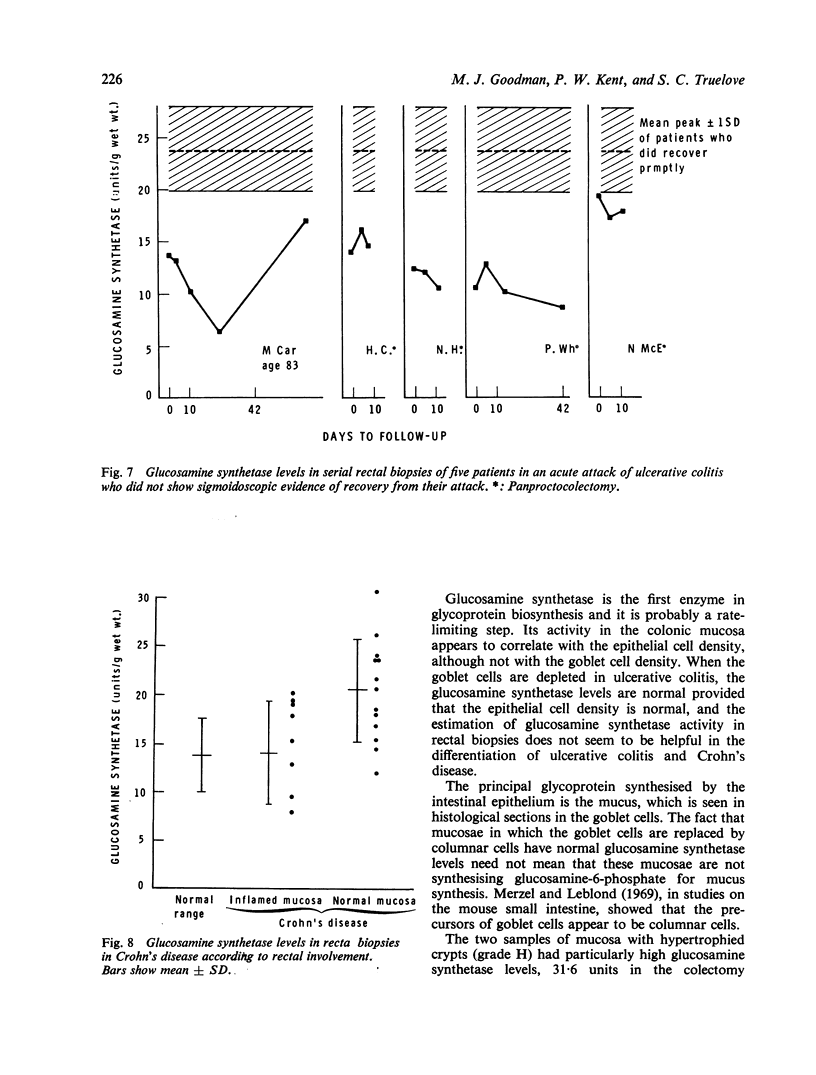
Glucosamine synthetase is the first enzyme in glycoprotein biosynthesis, catalysing the formation of glucosamine-6-phosphate, from which N-acetylglucosamine is formed. The levels of this enzyme in normal human colonic mucosa (in colectomy specimens and rectal biopsies) were found to be 13-8 +/- 4-0 micron mol glucosamine synthesised/h/g wet wt. In the colonic mucosa in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's colitis the enzyme level was diminished when there was loss of epithelial cells in the mucosa, although not when there was just loss of goblet cells. In patients recovering from an acute attack of ulcerative colitis, the enzyme levels rose to a peak above the normal range, an effect which did not occur in patients who did not recover promptly. This recovery peak may be related to the synthesis of gastrointestinal mucus, or immunoglobulin, or the secretory component of IgA, all of which contain large amounts of N-acetylglucosamine.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akamatsu N., Maeda H. R. Formation of glucosamine 6-phosphate in regenerating rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 19;244(2):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates C. J., Adams W. R., Handschumacher R. E. Control of the formation of uridine diphospho-N-acetyl-hexosamine and glycoprotein synthesis in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1705–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bley R. L., Okubo H., Chandler A. M. Regulation of glucosamine synthesis in injury and partial hepatectomy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Oct 1;144(1):134–140. doi: 10.3181/00379727-144-37542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. G., Dixon M. F. An analysis of the reliability of detection and diagnostic value of various pathological features in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1973 Apr;14(4):255–262. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.4.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. M., Burdett K. The use of isolated cells to assess the contribution of the mucosal epithelium to the metabolism of the intestinal wall. Gut. 1973 Feb;14(2):98–103. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.2.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G. (1-14C)glucosamine incorporation by subcellular fractions of small intestinal mucosa. Identification by precursor labeling of three functionally distinct glycoprotein classes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3584–3592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner J., Taichman N., Kalnins V., Forstner G. Intestinal goblet cell mucus: isolation and identification by immunofluorescence of a goblet cell glycoprotein. J Cell Sci. 1973 Mar;12(2):585–602. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.2.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. J., Skinner J. M., Truelove S. C. Abnormalities in the apparently normal bowel mucosa in Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1976 Feb 7;1(7954):275–278. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91404-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNFELD S., KORNFELD R., NEUFELD E. F., O'BRIEN P. J. THE FEEDBACK CONTROL OF SUGAR NUCLEOTIDE BIOSYNTHESIS IN LIVER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:371–379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman M., Yip M. C., Knox W. E. Glucosamine 6-phosphate synthesis in normal and neoplastic rat tissues. Enzyme. 1971;12(5):537–544. doi: 10.1159/000459583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent P. W. Structure and function of glycoproteins. Essays Biochem. 1967;3:105–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi H., Kobayashi Y., Tsuiki S. L-glutamine:D-fructose 6-phosphate amidotransferase in tumors and the liver of tumor-bearing animals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 22;237(3):412–421. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm M. E., Greenberg J. Human secretory component. Comparison of the form occurring in exocrine immunoglobulin A to the free form. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2744–2750. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukie B. E., Forstner G. G. Synthesis of intestinal glycoprotein. Incorporation of (I- 14 C) glucosamine in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 28;261(2):353–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzel J., Leblond C. P. Origin and renewal of goblet cells in the epithelium of the mouse small intestine. Am J Anat. 1969 Mar;124(3):281–305. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001240303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T., Elson L. A. A colorimetric method for the determination of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylchrondrosamine. Biochem J. 1934;28(3):988–995. doi: 10.1042/bj0280988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poger M. E., Lamm M. E. Localization of free and bound secretory component in human intestinal epithelial cells. A model for the assembly of secretory IgA. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):629–642. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönhöfer P., Anspach K. F. Die Aktivität der L-Glutamin-D-fructose-6-phosphat-aminotransferase im Verlauf einer durch Carrageenin induzierten Entzündung und ihre Hemmbarkeit durch Phenylbutazon. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1967 Apr;166(2):382–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truelove S. C., Jewell D. P. Intensive intravenous regimen for severe attacks of ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1974 Jun 1;1(7866):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90552-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterburn P. J., Phelps C. F. Purification and some kinetic properties of rat liver glucosamine synthetase. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):701–709. doi: 10.1042/bj1210701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


