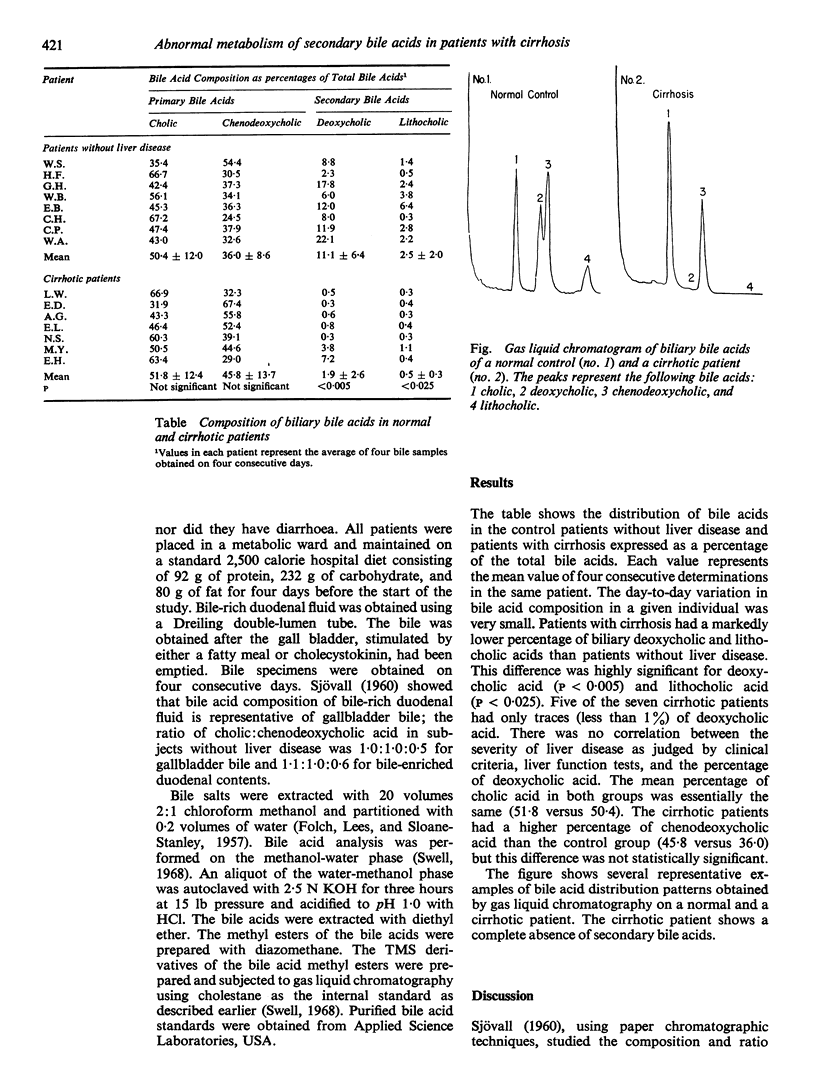
Abstract
The composition of bile acids in human bile was determined in bile-rich duodenal fluid on four consecutive days in a group of seven patients with cirrhosis and eight control patients with no liver disease. There was a marked reduction of secondary biliary bile acids in cirrhotic patients. Possible mechanisms for these changes are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- EKDAHL P. H., SJOVALL J. Metabolism of desoxycholic acid in the rabbit. Bile acids and steroids, 28. Acta Physiol Scand. 1955 Oct 27;34(2-3):287–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1955.tb01248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKDAHL P. H., SJOVALL J. On the conjugation and formation of bile acids in the human liver. I. On the excretion of bile acids by patients with postoperative choledochostomy drainage; bile acids and steroids 61. Acta Chir Scand. 1958 May 10;114(6):439–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSSON B. E., BERGSTROM S., LINDSTEDT S., NORMAN A. Turnover and nature of fecal bile acids in germfree and infected rats fed cholic acid-24-14C; bile acids and steroids 41. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Mar;94(3):467–471. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON J. G. The effect of oral neomycin on the conversion of cholic acid to deoxycholic in man. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Apr;101:7–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90527-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J., Drasar B. S. Degradation of bile salts by human intestinal bacteria. Gut. 1968 Feb;9(1):22–27. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


