Abstract
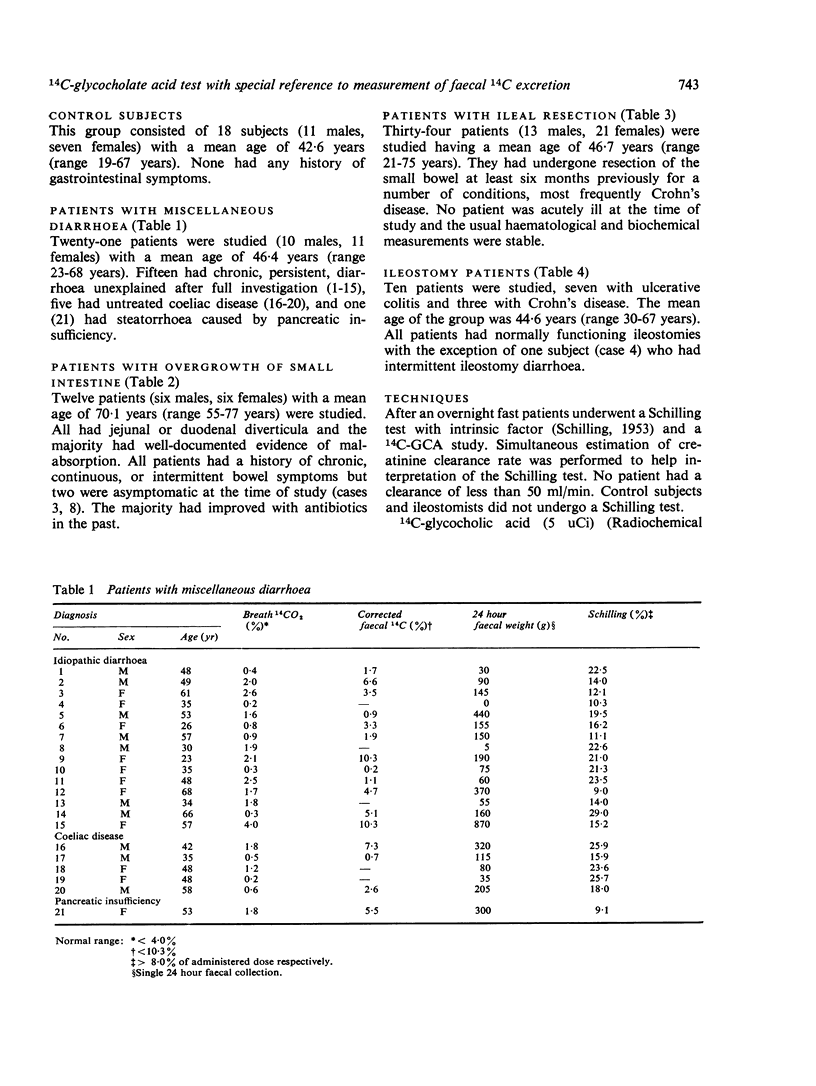
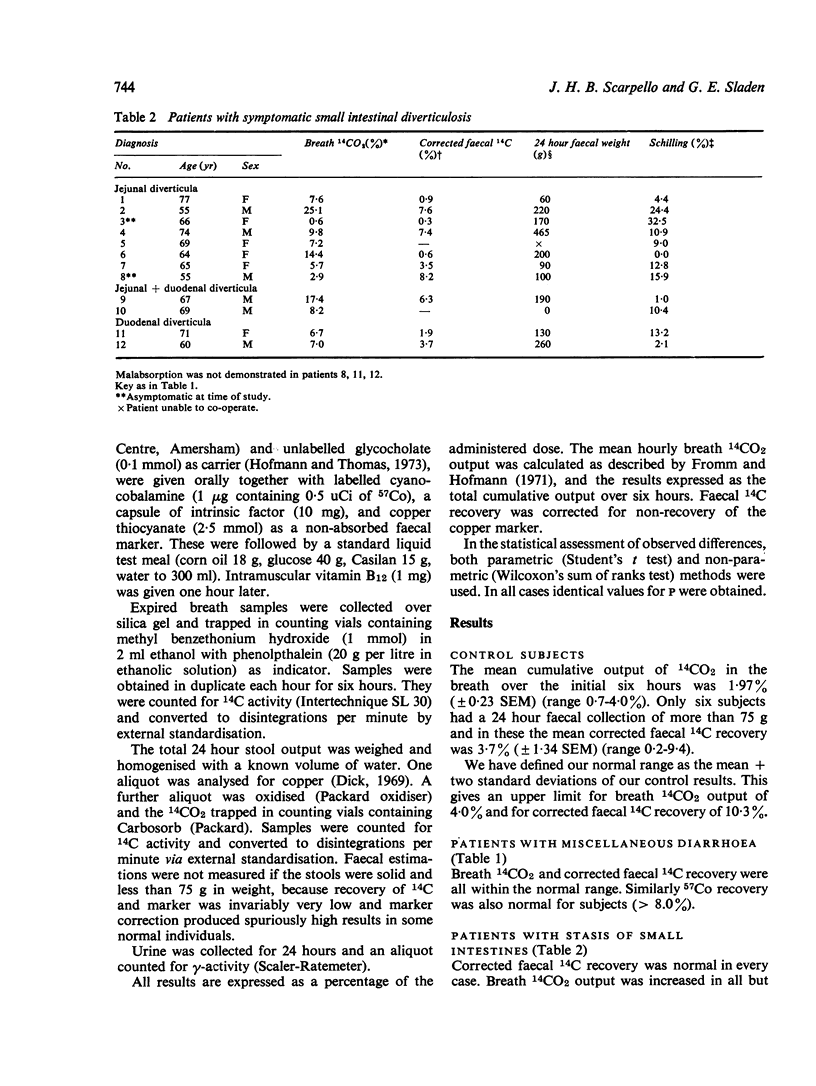
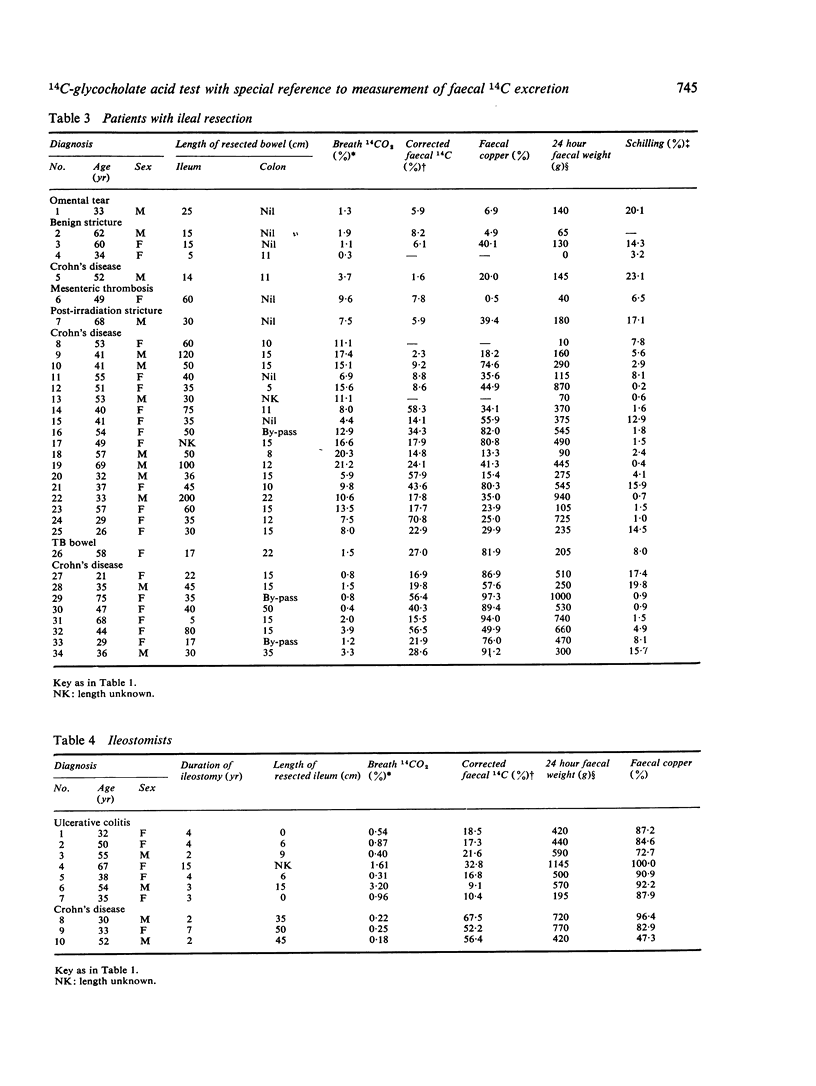
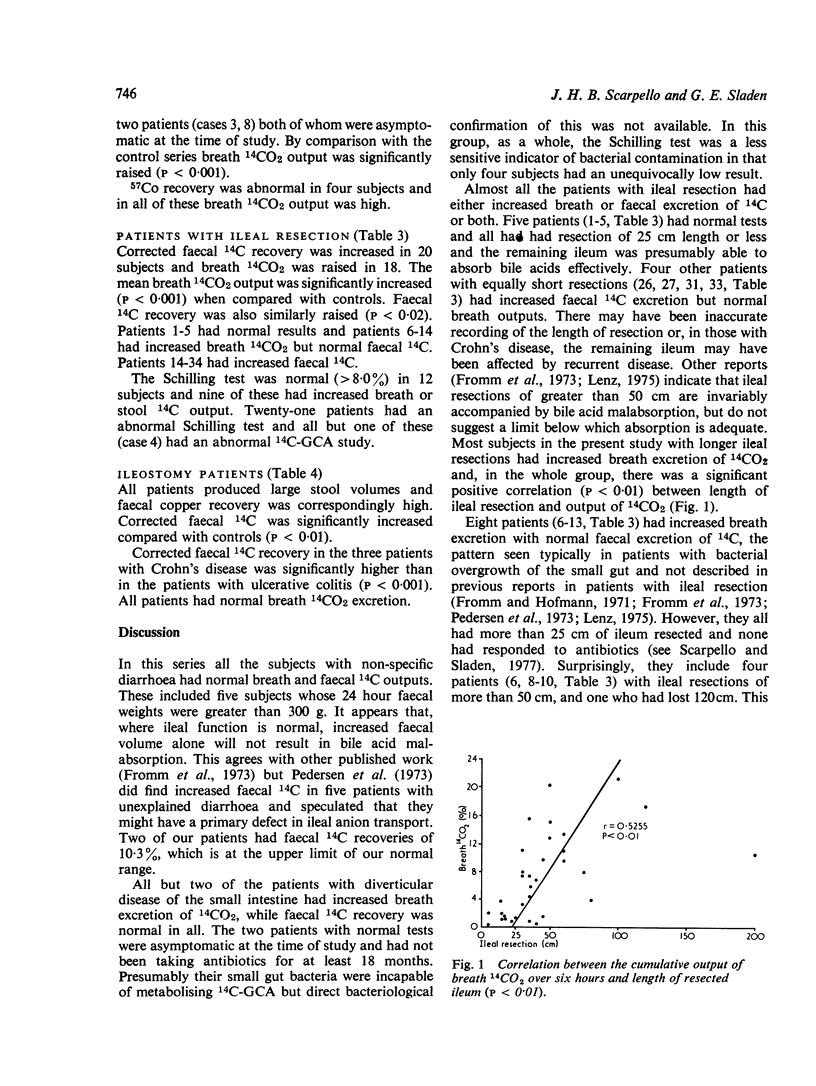
The 14C-glycocholate test, including the measurement of marker corrected faecal 14C, has been assessed in the following groups of subjects: normal controls (18), patients with diarrhoea not attributable to altered bile acid metabolism (21), patients with diverticula of the small intestine (12), patients with previous resection of ileum and often proximal colon (34), and established ileostomists (10). Patients with diverticular disease had increased breath 14CO2 excretion, but normal faecal excretion of 14C, and this test was more frequently abnormal than the Schilling test. Ileostomists excreted increased amounts of faecal 14C, even when the ileum was intact and apparently normal. The pattern after resection was complex. Breath 14C output was normal if the ileal resection was less than 25 cm in length, although some of these patients had increased faecal 14C excretion if, in addition, at least 15 cm of proximal colon had been resected or by-passed. Longer ileal resections were associated with increased breath and/or faecal 14C excretion, depending in part on the length of colon resected or by-passed and the 24 hour faecal volume. Fewer than half these patients had both increased breath and faecal excretion of isotope and faecal 14C alone was occasionally normal with an ileal resection of 50 cm of more. The 14C-glycocholate test was more frequently abnormal than the Schilling test in this group. The use of faecal marker correction had only a minor impact on the results. These data suggest that, in patients with ileal resection, faecal 14C, like faecal weight, is determined by the extent of colonic resection as well as by the amount of ileum resected.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan R., Steinberg D. M., Dixon K., Cooke W. T. Changes in the bidirectional sodium flux across the intestinal mucosa in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1975 Mar;16(3):201–204. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.3.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., James W. P., Wiggins H. S. Role of the colon in ileal-resection diarrhoea. Lancet. 1973 Feb 17;1(7799):344–347. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick M. Use of cuprous thiocyanate as a short-term continuous marker for faeces. Gut. 1969 May;10(5):408–412. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.5.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm D. Ileal resection, or disease, and the blind loop syndrome: current concepts of pathophysiology. Surgery. 1973 May;73(5):639–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Hofmann A. F. Breath test for altered bile-acid metabolism. Lancet. 1971 Sep 18;2(7725):621–625. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)80068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Thomas P. J., Hofmann A. F. Sensitivity and specificity in tests of distal ileal function: prospective comparison of bile acid and vitamin B 12 absorption in ileal resection patients. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jun;64(6):1077–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Nahas L., Weinstein L., Levitan R., Patterson J. F. Studies of intestinal microflora. IV. The microflora of ileostomy effluent: a unique microbial ecology. Gastroenterology. 1967 Dec;53(6):874–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Editorial: Bile acid breath test: extremely simple, moderately useful. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):743–744. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James O. F., Agnew J. E., Bouchier I. A. Assessment of the 14C-glycocholic acid breath test. Br Med J. 1973 Jul 28;3(5873):191–195. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5873.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz K. An evaluation of the 'breath test' in Crohn's disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(6):665–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A., Peltokallio P. Bile salt, fat, water, and vitamin B 12 excretion after ileostomy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1971;6(6):543–552. doi: 10.3109/00365527109181671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin D. M., O'Moore R. R., Cussons D. J., Warwick R. R., Rooney P., Percy-Robb I. W., Shearman D. J. Evaluation of the "breath test" in the detection of bacterial colonisation of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Lancet. 1972 Oct 14;2(7781):777–780. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen L., Arnfred T., Thaysen E. H. Rapid screening of increased bile acid deconjugation and bile acid malabsorption by means of the glycine-l-(14C) cholylglycine assay. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1973;8(7):665–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percy-Robb I. W., Jalan K. N., McManus J. P., Sircus W. Effect of ileal resection on bile salt metabolism in patients with ileostomy following proctocolectomy. Clin Sci. 1971 Nov;41(5):371–382. doi: 10.1042/cs0410371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILLING R. F. Intrinsic factor studies II. The effect of gastric juice on the urinary excretion of radioactivity after the oral administration of radioactive vitamin B12. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Dec;42(6):860–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpello J. H., Sladen G. E. 14C-Glycocholate test in Crohn's disease--its value in assessment and treatment. Gut. 1977 Sep;18(9):736–741. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.9.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr H. P., Sasaki Y., Newman A., Banwell J. G., Wagner H. N., Jr, Hendrix T. R. Detection of bacterial deconjugation of bile salts by a convenient breath-analysis technic. N Engl J Med. 1971 Sep 16;285(12):656–661. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197109162851204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


