Abstract
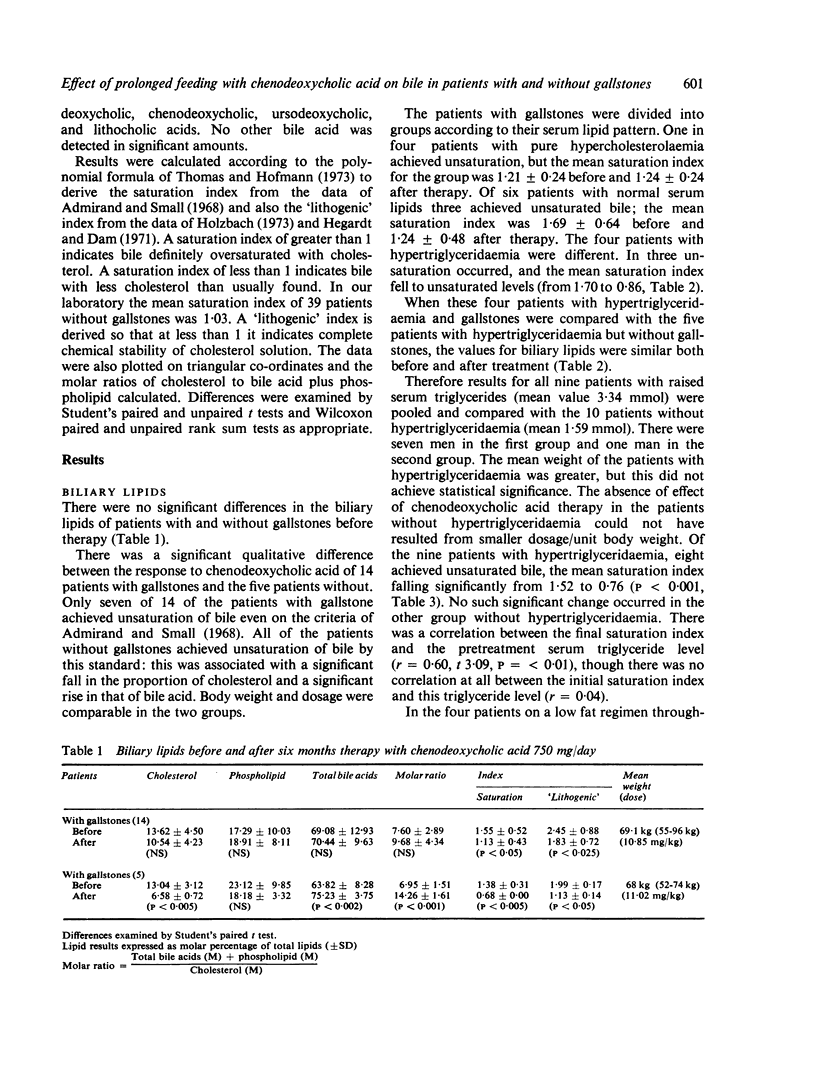
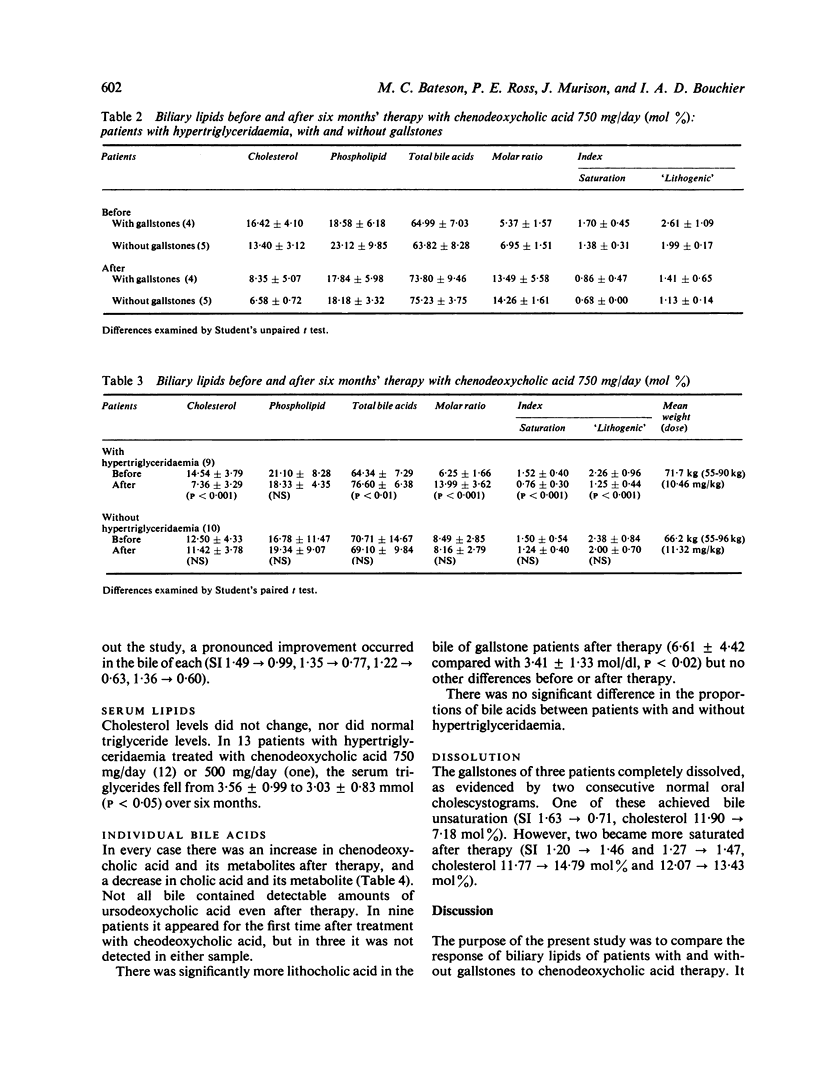
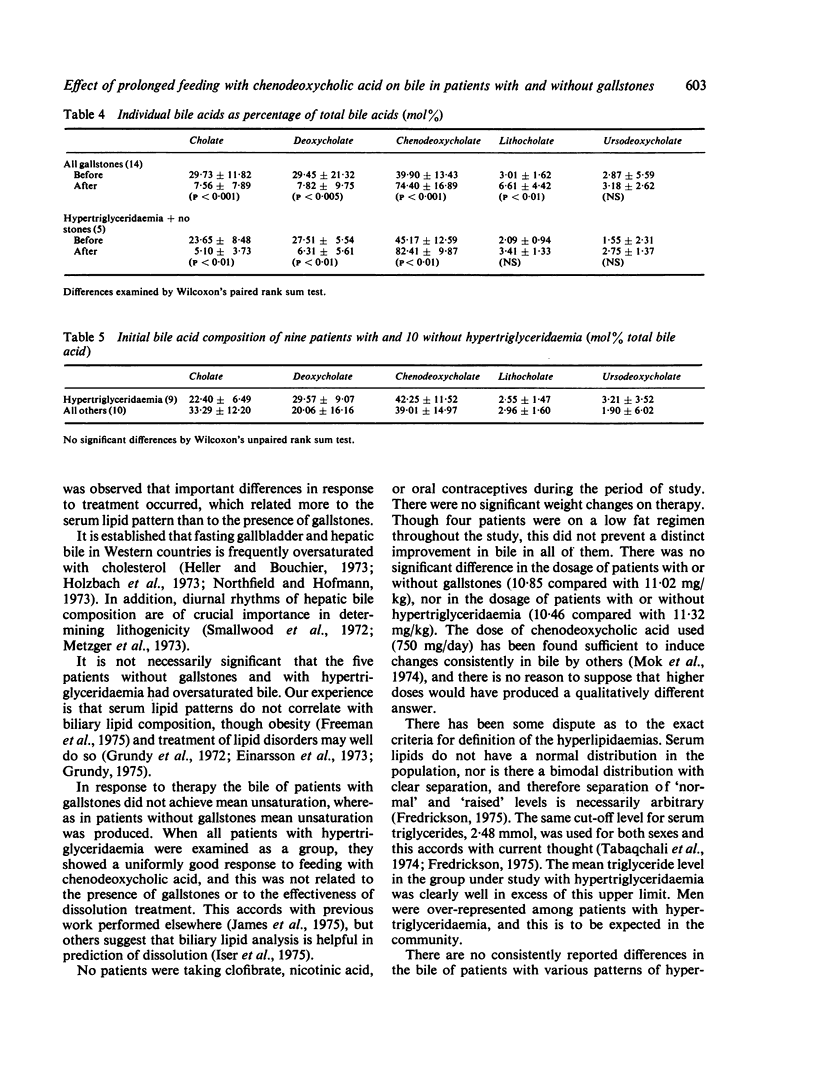
Nineteen patients who received chenodeoxycholic acid 750 mg/day for six months had duodenal bile aspirated before and after treatment. In five patients with hypertriglyceridaemia but no gallstones cholesterol saturation was reversed in every case, the mean cholesterol saturation index (SI +/- standard deviation) changing from 1-38 +/- 0-31 to 0-68 +/- 0-06 (P less than 0-005). In 14 patients with gallstones there was also an improvement in bile cholesterol content, but this was not sufficient to produce mean unsaturation, saturation index changing from 1-55 +/- 0-52 to 1-13 +/- 0-43 (P less than 0-05). Only seven of 14 patients with gallstone achieved cholesterol unsaturation. In four patients with hypertriglyceridaemia and gallstones, mean unsaturation was produced and the saturation index changed from 1-70 +/- 0-45 to 0-86 +/- 0-47 (P less than 0-05). When all nine patients with hypertriglyceridaemia were grouped, the mean saturation index fell from 1-52 +/- 0-40 to 0-76 +/- 0-30 after therapy (P less than 0-001). In contrast the 10 patients without hypertriglyceridaemia showed no significant fall in saturation index which was 1-50 +/- 0-54 before and 1-24 +/- 0-40 after therapy. The ability of chenodeoxycholic acid feeding to improve bile saturation with cholesterol correlated with the presence of hypertriglyceridaemia whether or not gallstones were present. It did not correlate with gallstone dissolution or body weight.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Admirand W. H., Small D. M. The physicochemical basis of cholesterol gallstone formation in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1043–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI105794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelin B., Einarsson K., Hellström K. Evidence for the absorption of bile acids in the proximal small intestine of normo- and hyperlipidaemic subjects. Gut. 1976 Jun;17(6):420–425. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.6.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L., Carlson L. A., Cooper G. R., Fejfar Z., Fredrickson D. S., Strasser T. Classification of hyperlipidaemias and hyperlipoproteinaemias. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(6):891–915. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. D., Lewis B., Petrie A., Dowling R. H. Serum lipids in cholelithiasis: effect of chenodeoxycholic acid therapy. Br Med J. 1973 Sep 8;3(5879):520–523. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5879.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahlin E., Jönsson J., Nilsson S., Scherstén T. Biliary lipid composition in normalipidemic and prebeta hyperlipoproteinemic gallstone patients. Influence of sucrose feeding of the patients on the biliary lipid composition. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1973;8(5):449–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzinger R. G., Hofmann A. F., Schoenfield L. J., Thistle J. L. Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by chenodeoxycholic acid. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 6;286(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201062860101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Hellström K., Kallner M. Bile acid kinetics in relation to sex, serum lipids, body weights, and gallbladder disease in patients with various types of hyperlipoproteinemia;. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1301–1311. doi: 10.1172/JCI107876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Hellström K., Kallner M. The effect of clofibrate on the elimination of cholesterol as bile acids in patients with hyperlipoproteinaemia type II and IV. Eur J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;3(4):345–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1973.tb00361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Hellström K. The formation of bile acids in patients with three types of hyperlipoproteinaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;2(4):225–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1972.tb00648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S. It's time to be practical. Circulation. 1975 Feb;51(2):209–211. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.51.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Levy R. I., Lees R. S. Fat transport in lipoproteins--an integrated approach to mechanisms and disorders. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jan 26;276(4):215–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196701262760406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman J. B., Meyer P. D., Printen K. J., Mason E. E., DenBesten L. Analysis of gallbladder bile in morbid obesity. Am J Surg. 1975 Feb;129(2):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(75)90292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Salen G., Schreibman P. H., Nestel P. J. Mechanisms of action of clofibrate on cholesterol metabolism in patients with hyperlipidemia. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jul;13(4):531–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M. Effects of polyunsaturated fats on lipid metabolism in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):269–282. doi: 10.1172/JCI107930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegardt F. G., Dam H. The solubility of cholesterol in aqueous solutions of bile salts and lecithin. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1971 Apr;10(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02020933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller F., Bouchier I. A. Cholesterol and bile salt studies on the bile of patients with cholesterol gallstones. Gut. 1973 Feb;14(2):83–88. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.2.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbach R. T., Marsh M., Olszewski M., Holan K. Cholesterol solubility in bile. Evidence that supersaturated bile is frequent in healthy man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1467–1479. doi: 10.1172/JCI107321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAKSSON B. On the lipid constituents of bile from human gallbladder containing cholesterol gallstones; a comparison with normal human bladder bile. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1954 Sep 30;59(5-6):277–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iser J. H., Dowling H., Mok H. Y., Bell G. D. Chenodeoxycholic acid treatment of gallstones. A follow-up report and analysis of factors influencing response to therapy. N Engl J Med. 1975 Aug 21;293(8):378–383. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197508212930804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James O., Cullen J., Bouchier I. A. Chenodeoxycholic acid therapy for gallstones: effectiveness, toxicity and influence on bile acid metabolism. Q J Med. 1975 Apr;44(174):349–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaassen C. D. Gas-liquid-chromatographic determination of bile acids in bile. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Nov;35(1):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C., Crook J. N., Smith D. C., McAllister R. A. The composition of hepatic and gallbladder bile in patients with gallstones. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):759–762. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.10.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger A. L., Adler R., Heymsfield S., Grundy S. M. Diurnal variation in biliary lipid composition. Possible role in cholesterol gallstone formation. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 15;288(7):333–336. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302152880702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A. Cholesterol production in obesity. Circulation. 1971 Nov;44(5):842–850. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.44.5.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok H. Y., Bell G. D., Dowling R. H. Proceedings: The effects of different doses of chenodeoxycholic acid and of withdrawing treatment on bile lipid composition and liver function in patients with gallstones. Gut. 1974 Apr;15(4):340–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murison J., Festi D., Ross P. E., Bouchier I. A. The estimation of phospholipids in bile. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Apr 15;68(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90415-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P. P., Gordon M., Reback J. The enzymatic cleavage of the carbon-nitrogen bond in 3-alpha, 7-alpha, 12-alpha-trihydroxy-5-beta-cholan-24-oylglycine. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 10;242(1):7–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northfield T. C., Hofmann A. F. Biliary lipid secretion in gallstone patients. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):747–748. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smallwood R. A., Jablonski P., Watts J. M. Intermittent secretion of abnormal bile in patients with cholesterol gall stones. Br Med J. 1972 Nov 4;4(5835):263–266. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5835.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodhi H. S., Kudchodkar B. J. Correlating metabolism of plasma and tissue cholesterol with that of plasma-lipoproteins. Lancet. 1973 Mar 10;1(7802):513–519. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehl A., Raedsch R., Kommerell B. Increased sulfation of lithocholate in patients with cholesterol gallstones during chenodeoxycholate treatment. Digestion. 1975;12(2):105–110. doi: 10.1159/000197660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Chait A., Harrison R., Lewis B. Experience with simplified scheme of treatment of hyperlipidaemia. Br Med J. 1974 Aug 10;3(5927):377–380. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5927.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. J., Hofmann A. F. Letter: A simple calculation of the lithogenic index of bile: expressing biliary lipid composition on rectangular coordinates. Gastroenterology. 1973 Oct;65(4):698–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


