Abstract
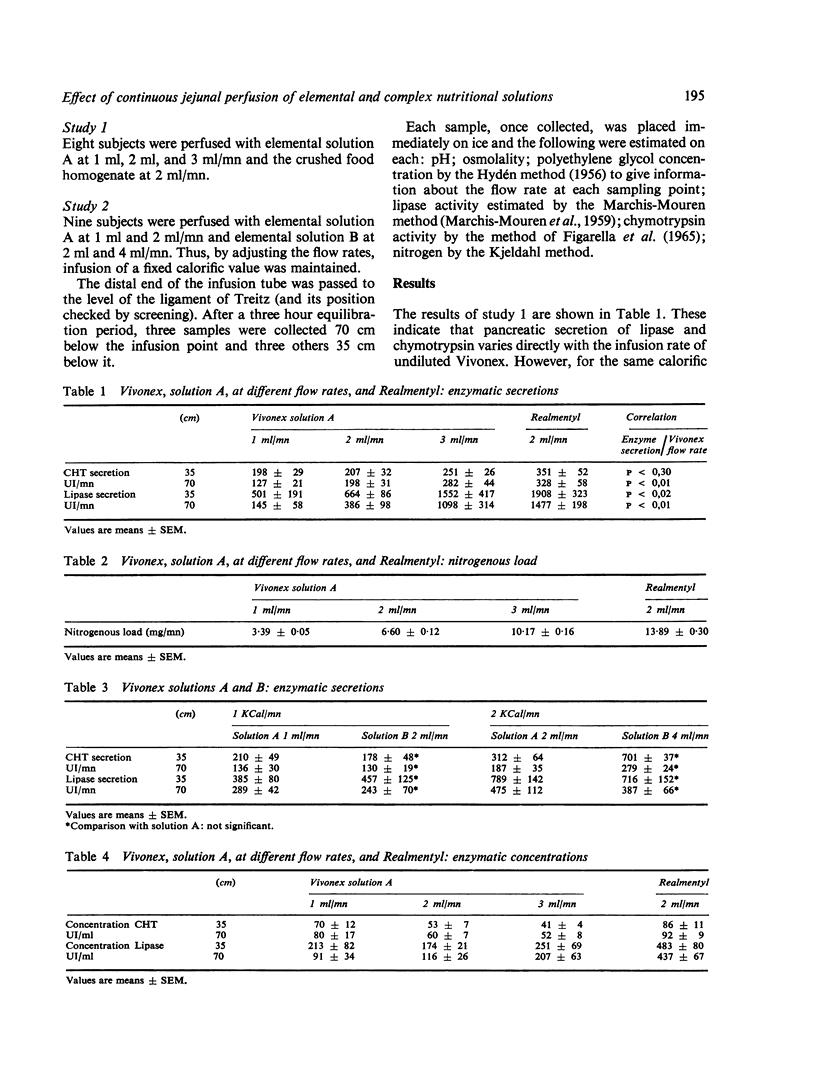
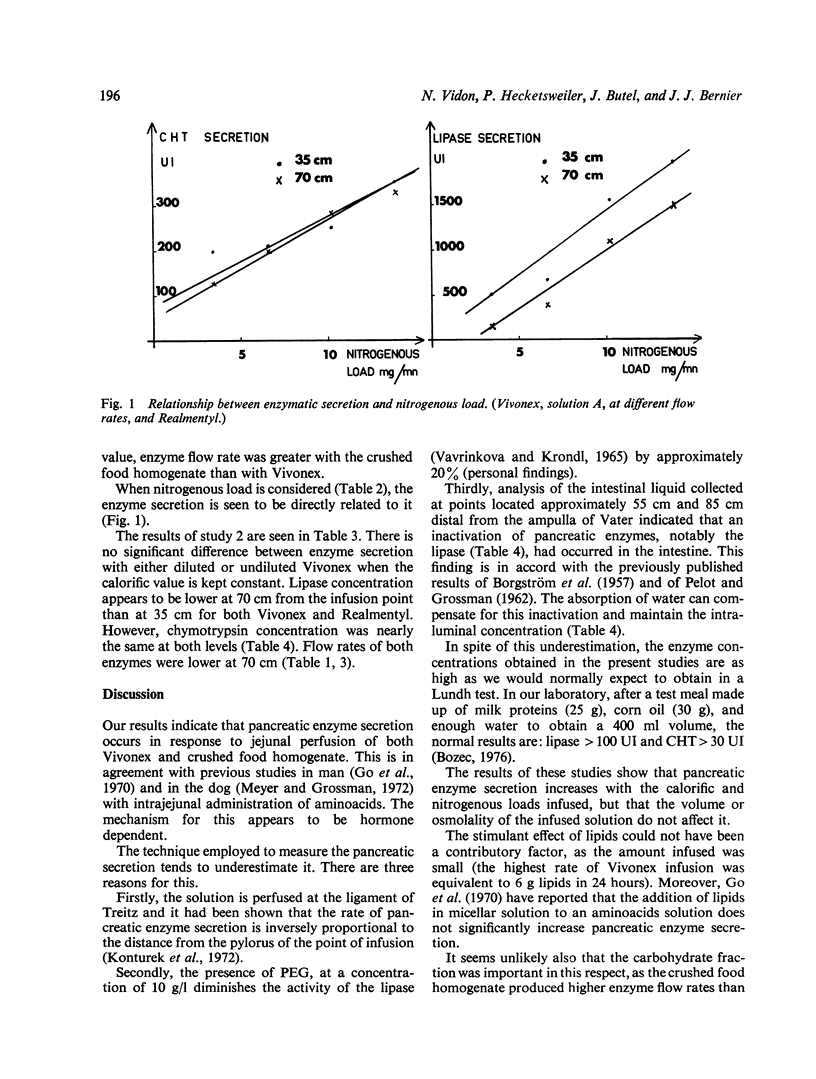
Pancreatic secretion of lipase and chymotrypsin in response to elemental diets and a crushed food homogenate was studied in normal subjects. The solutions were infused at constant flow rates at the ligament of Treitz with polyethylene glycol as a nonabsorbable marker. A triple lumen tube was used, enabling collection of secretions at 35 and 70 cm from the infusion point. The results show that a crushed food homogenate has a greater stimulative effect on pancreatic enzyme secretion than the elemental solutions and that this can be directly related to its greater nitrogen content. The osmolality of the infused solutions does not appear to be important. The relative merits of the solutions tested and total parental nutrition in reducing pancreatic enzyme secretion are discussed.
Full text
PDF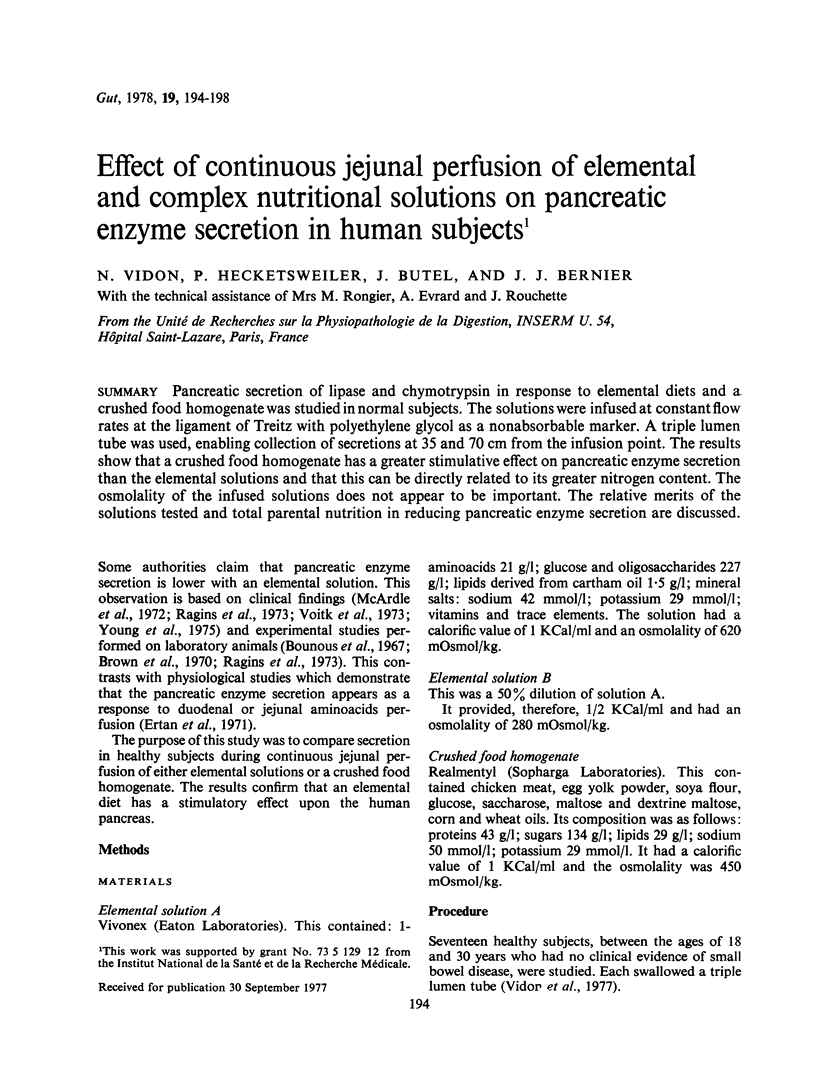


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORGSTROM B., DAHLQVIST A., LUNDH G., SJOVALL J. Studies of intestinal digestion and absorption in the human. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1521–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI103549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bounous G., Sutherland N. G., Mcardle A. H., Gurd F. N. The prophylactic use of an "elemental" diet in experimental hemorrhagic shock and intestinal ischemia. Ann Surg. 1967 Sep;166(3):312–343. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196709000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. A., Thompson A. G., McArdle A. H., Gurd F. N. Alteration of exocrine pancreatic storage enzymes by feeding on an elemental diet: a biochemical and ultrastructural study. Surg Forum. 1970;21:391–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund K., Johansson C. Output of bilirubin and pancreatic enzymes in response to different liquid test meals in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(5):507–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertan A., Brooks F. P., Ostrow J. D., Arvan D. A., Williams C. N., Cerda J. J. Effect of jejunal amino acid perfusion and exogenous cholecystokinin on the exocrine pancreatic and biliary secretions in man. Gastroenterology. 1971 Nov;61(5):686–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIGARELLA C., TAULIER J., SARLES H. DOSAGE DE LA CHYMOTRYPSINE ET DE LA TRYPSINE DANS LE SUC DUOD'ENAL. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1965;47:679–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go V. L., Hofmann A. F., Summerskill W. H. Pancreozymin bioassay in man based on pancreatic enzyme secretion: potency of specific amino acids and other digestive products. J Clin Invest. 1970 Aug;49(8):1558–1564. doi: 10.1172/JCI106373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONG S. S., CHIN D. S., HUR K. B. Influences of hexamethonium and some dietary factors on human pancreatic and bile secretion. J Appl Physiol. 1961 Sep;16:810–814. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1961.16.5.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Tasler J., Obtulowicz W. Localization of cholecystokinin release in intestine of the dog. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jan;222(1):16–20. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHIS-MOUREN G., SARDA L., DESNUELLE P. Purification of hog pancreatic lipase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Jul;83(1):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. H., Grossman M. I. Comparison of D- and L-phenylalanine as pancreatic stimulants. Am J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(4):1058–1063. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.4.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PELOT D., GROSSMAN M. I. Distribution and fate of pancreatic enzymes in small intestine of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1962 Feb;202:285–288. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.2.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragins H., Levenson S. M., Signer R., Stamford W., Seifter E. Intrajejunal administration of an elemental diet at neutral pH avoids pancreatic stimulation. Studies in dog and man. Am J Surg. 1973 Nov;126(5):606–614. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(73)80007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütz H. B., Andersson S., Lagerlöf H. Pancreatic exocrine secretion in normal subjects studied by continuous infusion of pancreozymin and secretin. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1969;4(7):597–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavrinková H., Krondl A. Use of polyethylene glycol in investigations of absorption of fat. Nature. 1965 Oct 16;208(5007):293–294. doi: 10.1038/208293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidon N., Hecketsweiler P., Cortot A., Bernier J. J. Etude de l'absorption d'une solution nutritive élémentaire sous perfusion jéjunale continue: influence du débit et de la concentration sur l'absorption des nutriments. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1977 Mar;1(3):257–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voitk A., Brown R. A., Echave V., McArdle A. H., Gurd F. N., Thompson A. G. Use of an elemental diet in the treatment of complicated pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1973 Feb;125(2):223–227. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(73)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG C. C., GROSSMAN M. I. Physiological determination of release of secretin and pancreozymin from intestine of dogs with transplanted pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1951 Feb;164(2):527–545. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.164.2.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe B. M., Keltner R. M., Kaminski D. L. The effect of an intraduodenal elemental diet on pancreatic secretion. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975 Feb;140(2):241–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. A., Heuler N., Russell P., Weser E. Comparative nutritional analysis of chemically defined diets. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1338–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


