Abstract
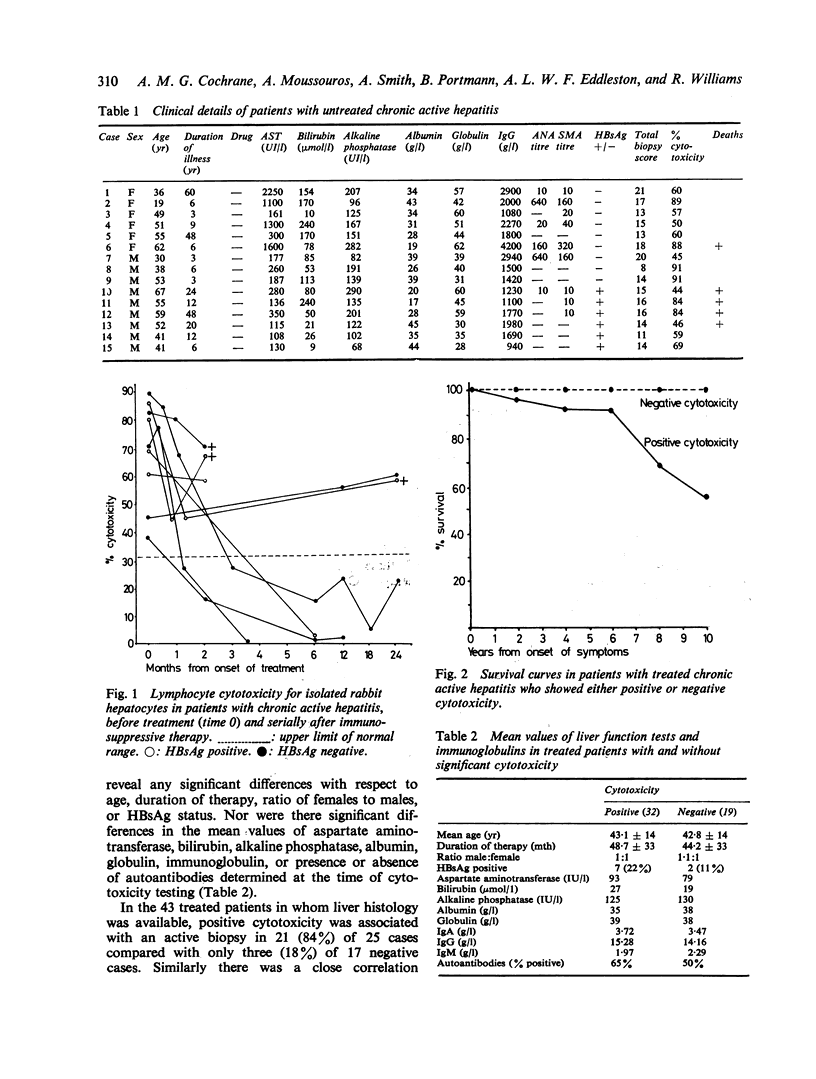
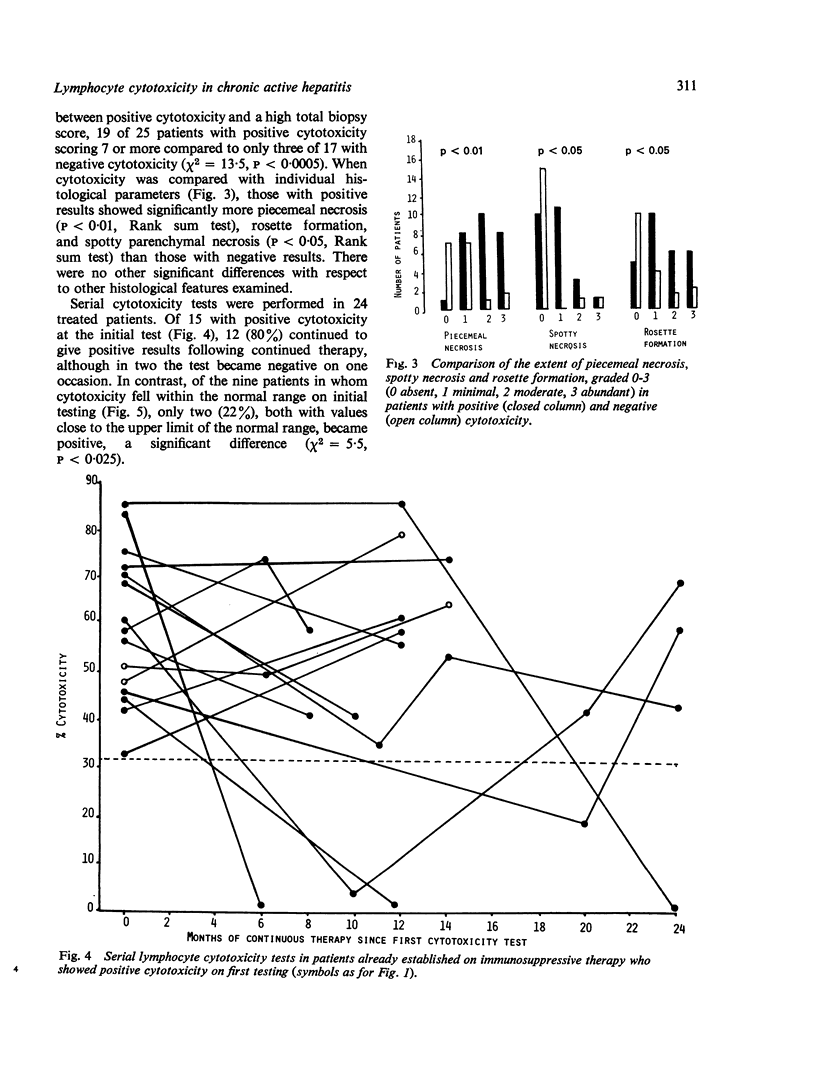
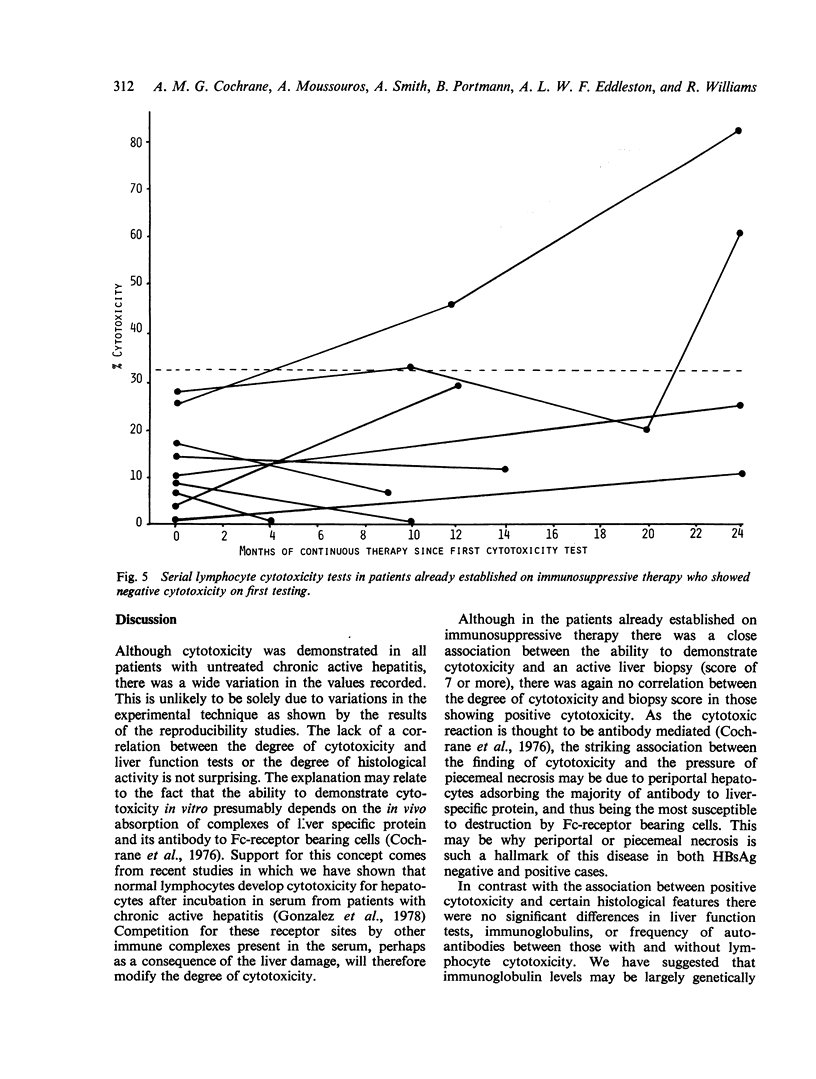
A study of lymphocyte cytotoxicity for rabbit hepatocyte cultures in 15 patients with untreated chronic active hepatitis showed positive results in all cases, both HBsAg positive and negative. After immunosuppressive therapy cytotoxicity became negative and remained negative, in four of nine patients followed serially. In 51 patients established on therapy for periods from three months to 12 years, cytotoxicity was negative in 19 and all patients are currently alive. However, in the remaining 32 patients in whom cytotoxicity was positive there has been a 34% mortality. Cytotoxicity remained persistently positive in 12 of 15 patients followed serially, and persistently negative in seven of nine. Cytotoxicity showed a significant association with histological disease activity, especially the extent of piecemeal necrosis, but not with biochemical tests of liver function, immunoglobulins, or autoantibodies. The basis of this cytotoxicity test is an antibody dependent cell-mediated autoimmune reaction directed against a liver specific protein, and the results suggest that in some cases immunosuppressive therapy is followed by control of this reaction. It may be possible to stop therapy in these patients, but in those in whom the reaction continues, as shown by continuing cytotoxicity, the prognosis is not as good and the use of other drug schedules would seem worthy of trial.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Denman A. M., Barnes R. D. Cooperating and controlling functions of thymus-derived lymphocytes in relation to autoimmunity. Lancet. 1971 Jul 17;2(7716):135–140. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büschenfelde K. H., Kössling F. K., Miescher P. A. Experimental chronic active hepatitis in rabbits following immunization with human liver proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):99–108. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Portmann B., McFarlane I. G., Thomson A. D., Eddleston, Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity for isolated hepatocytes in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1977 May;72(5 Pt 1):918–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. M., Moussouros A., Thomsom A. D., Eddleston A. L., Wiiliams R. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated (K cell) cytotoxicity against isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1976 Feb 28;1(7957):441–444. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook G. C., Mulligan R., Sherlock S. Controlled prospective trial of corticosteroid therapy in active chronic hepatitis. Q J Med. 1971 Apr;40(158):159–185. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.qjmed.a067264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groote J., Desmet V. J., Gedigk P., Korb G., Popper H., Poulsen H., Scheuer P. J., Schmid M., Thaler H., Uehlinger E. A classification of chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1968 Sep 14;2(7568):626–628. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90710-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denman E. J., Denman A. M., Greenwood B. M., Gall D., Heath R. B. Failure of cytotoxic drugs to suppress immune responses of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 May;29(3):220–231. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.3.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Inadequate antibody response to hBAg or suppressor T-cell defect in development of active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1974 Dec 28;2(7896):1543–1545. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith R. M., Eddleston A. L., Williams R., Webster A. D., Pattison J., Doniach D., Kennedy L. A., Batchelor J. R. Enhanced antibody responses in active chronic hepatitis: relation to HLA-B8 and HLA-B12 and porto-systemic shunting. Lancet. 1976 May 1;1(7966):930–934. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geubel A. P., Keller R. H., Summerskill W. H., Dickson E. R., Tomasi T. B., Shorter R. G. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity and inhibition studied with autologous liver cells: observations in chronic active liver disease and the primary biliary cirrhosis syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1976 Sep;71(3):450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. D., Cochrane A. M., Thomson A. D., Murray-Lyon I. M., Williams R. The cytotoxicity of plasma from patients with acute hepatic failure to isolated rabbit hepatocytes. Br J Exp Pathol. 1976 Jun;57(3):348–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Smith M. G., Mitchell C. G., Reed W. D., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Cell-mediated immunity to a human liver-specific antigen in patients with active chronic hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet. 1972 Aug 12;2(7772):296–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92904-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray-Lyon I. M., Stern R. B., Williams R. Controlled trial of prednisone and azathioprine in active chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):735–737. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Meyers O. L., David J. R. An in vitro assay for cellular hypersensitivity in man. J Immunol. 1970 Jan;104(1):95–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloway R. D., Summerskill W. H., Baggenstoss A. H., Geall M. G., Gitnićk G. L., Elveback I. R., Schoenfield L. J. Clinical, biochemical, and histological remission of severe chronic active liver disease: a controlled study of treatments and early prognosis. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):820–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tage-Jensen U., Arnold W., Dietrichson O., Hardt F., Hopf U., Meyer Zum Büschenfelde K. H., Nielsen J. O. Liver-cell-membrane autoantibody specific for inflammatory liver diseases. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 22;1(6055):206–208. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6055.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thestrup-Pedersen K., Ladefoged K., Andersen P. Lymphocyte transformation test with liver-specific protein and phytohaemagglutinin in patients with liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Apr;24(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. D., Cochrane M. A., McFarlane I. G., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active hepatitis. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):721–722. doi: 10.1038/252721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Perrotto J. L., Alpert E., Isselbacher K. J. Cell-mediated immunity in acute and chronic hepatitis. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):921–929. doi: 10.1172/JCI108021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands K. R., Isselbacher K. J. Lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous liver cells in chronic active hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1301–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


