Abstract
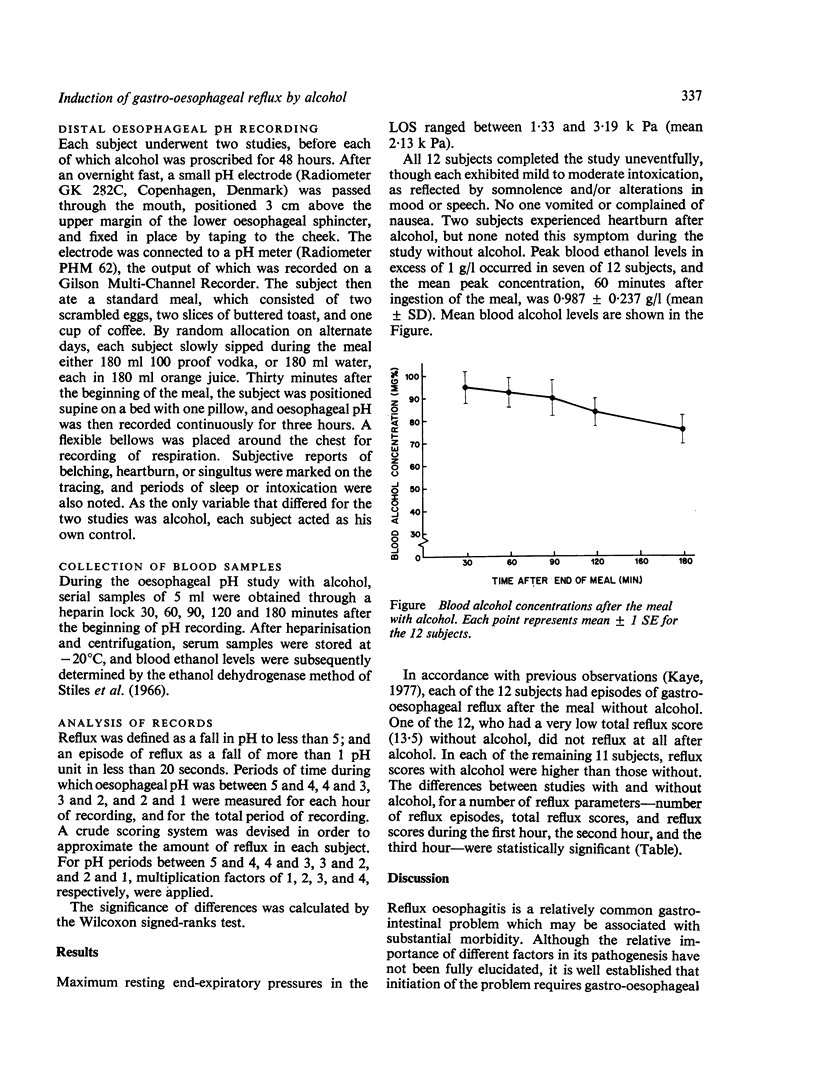
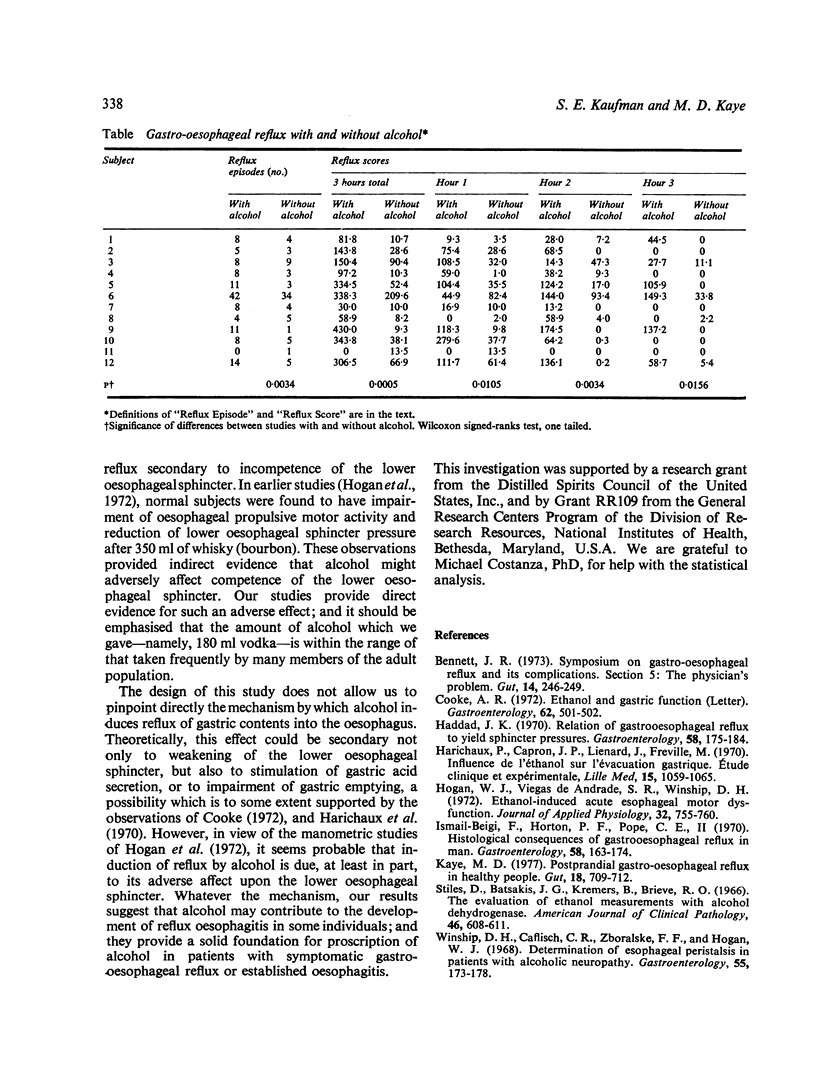
In order to establish whether alcohol in amounts in amounts customarily imbibed during social drinking causes gastro-oesophageal reflux, 12 healthy young individuals, without symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux, were studied twice. Each time, distal oesophageal pH was monitored continuously for three hours after a standard meal which included either 180 ml 100 proof vodka or 180 ml water. The order of studies with and without alcohol was random. Peak blood alcohol concentrations ranged between 0.63 and 1.29 g/l. Eleven of the 12 subjects refluxed more after alcohol; and the difference in mean reflux scores for studies with and without alcohol was highly significant. We conclude that relatively modest quanttities of alcohol induce gastro-oesophageal reflux in healthy people.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. R. Symposium on gastrooesophageal reflux and its complications. 5. The physicians's problem. Gut. 1973 Mar;14(3):246–249. doi: 10.1136/gut.14.3.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke A. R. Ethanol and gastric function. Gastroenterology. 1972 Mar;62(3):501–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. K. Relation of gastroesophageal reflux to yield sphincter pressures. Gastroenterology. 1970 Feb;58(2):175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harichaux P., Capron J. P., Lienard J., Freville M. Influence de l'éthanol sur l'évacuation gastrique: étude clinique et expérimentale. Lille Med. 1970 Aug-Sep;15(7):1059–1065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan W. J., Viegas de Andrade S. R., Winship D. H. Ethanol-induced acute esophageal motor dysfunction. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Jun;32(6):755–760. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.32.6.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail-Beigi F., Horton P. F., Pope C. E., 2nd Histological consequences of gastroesophageal reflux in man. Gastroenterology. 1970 Feb;58(2):163–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye M. D. Postprandial gastro-oesophageal reflux in healthy people. Gut. 1977 Sep;18(9):709–712. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.9.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles D., Batsakis J. G., Kremers B., Briere R. O. The evaluation of ethanol measurements with alcohol dehydrogenase. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Dec;46(6):608–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship D. H., Caflisch C. R., Zboralske F. F., Hogan W. J. Deterioration of esophageal peristalsis in patients with alcoholic neuropathy. Gastroenterology. 1968 Aug;55(2):173–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


