Abstract
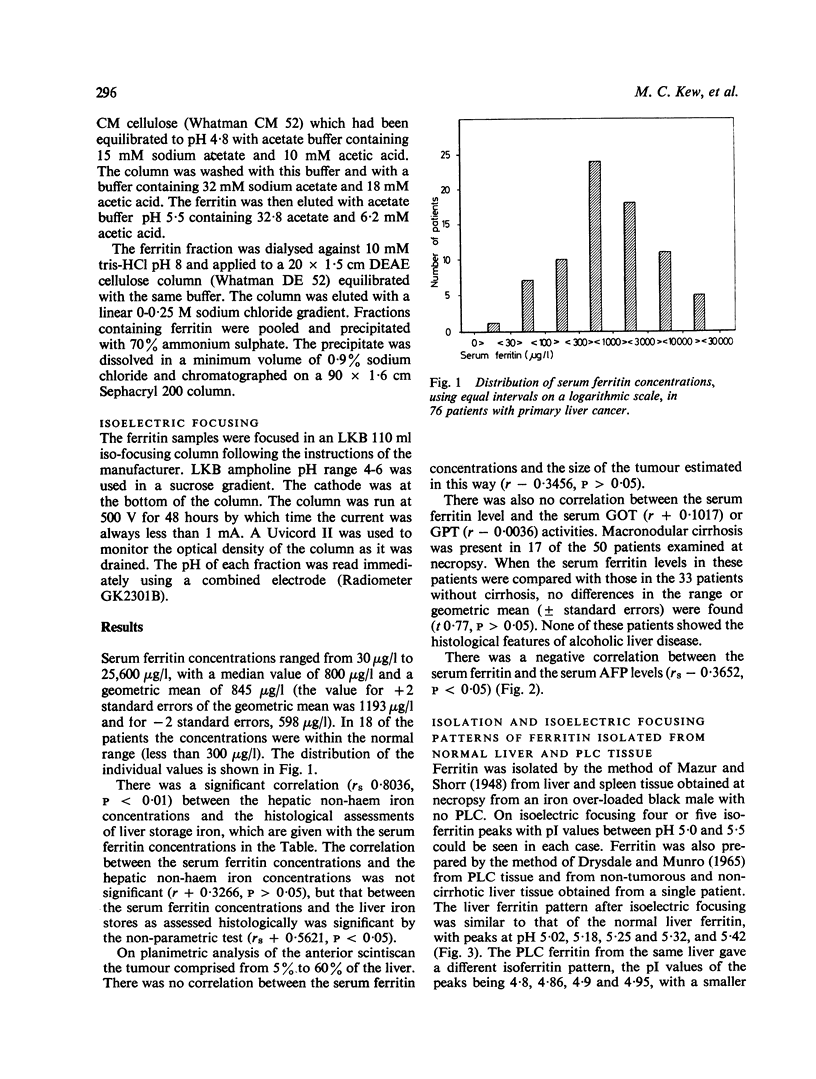
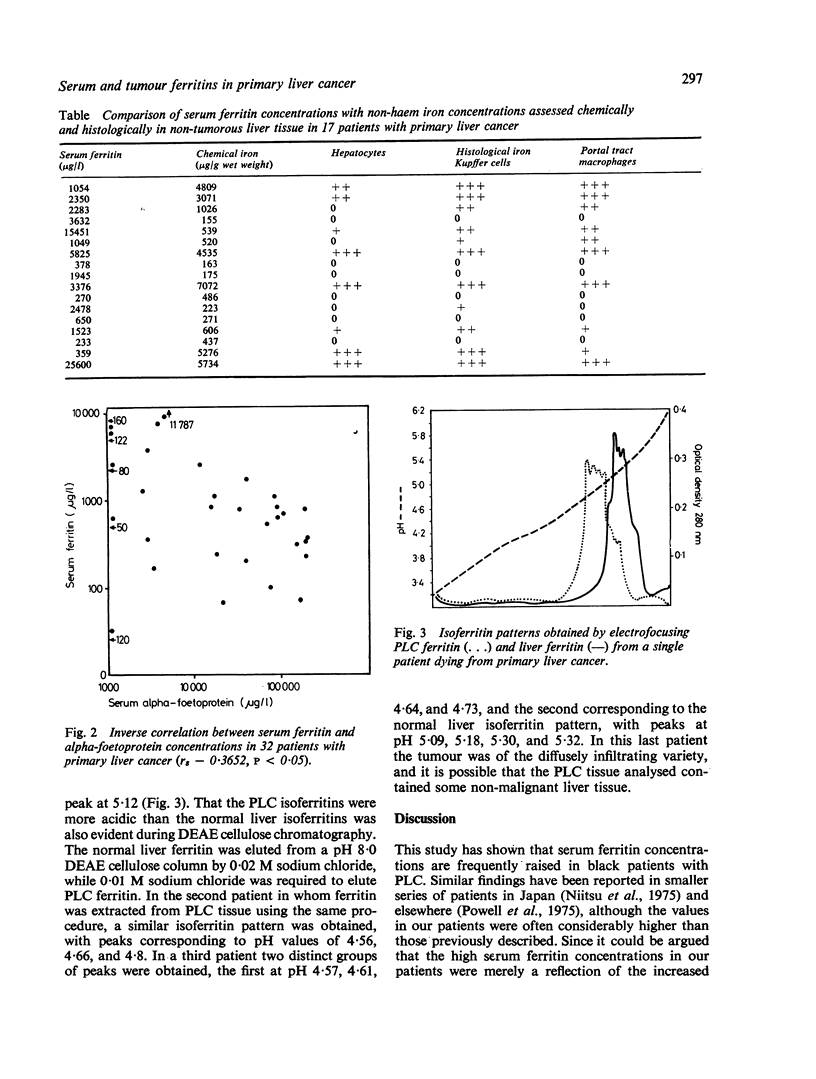
Serum ferritin concentrations were found to be raised, often considerably, in 58 of 76 black patients with primary liver cancer (PLC). No correlation could be demonstrated between the serum ferritin concentration and several other measurements, including the following: hepatic iron stores measured chemically, the size of the tumour, serum transaminase values, and the presence or absence of cirrhosis in the non-tumorous liver. There was, however, a negative correlation between serum ferritin and alpha-foetoprotein concentrations. Ferritin was purified from PLC tissue obtained from three patients at necropsy and the distribution of isoferritins was determined by isoelectric focusing. Acidic isoferritins similar to those previously found in PLC tissue were obtained. Their acidic nature was confirmed chromatographically using DEAE cellulose. Because the serum ferritin in patients with PLC probably consists of a mixture of normal and acidic isoferritins, it is likely that the serum assay used in the present study underestimated the actual concentrations present. With the development of an assay which utlises a specific antibody against acidic PLC isoferritins, serum ferritin may prove to be a second marker for PLC.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert E. Characterization and subunit analysis of ferritin isolated from normal and malignant human liver. Cancer Res. 1975 Jun;35(6):1505–1509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert E., Coston R. L., Drysdale J. W. Carcino-foetal human liver ferritins. Nature. 1973 Mar 16;242(5394):194–196. doi: 10.1038/242194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOTHWELL T. H., BRADLOW B. A. Siderosis in the Bantu. A combined histopathological and chemical study. Arch Pathol. 1960 Sep;70:279–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. D., Lipschitz D. A., Miles L. E., Finch C. A. Serum ferritin as a measure of iron stores in normal subjects. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Jul;27(7):681–687. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.7.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRYSDALE J. W., MUNRO H. N. SMALL-SCALE ISOLATION OF FERRITIN FOR THE ASSAY OF THE INCORPORATION OF 14C-LABELLED AMINO ACIDS. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:851–858. doi: 10.1042/bj0950851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazard J. T., Yokota M., Arosio P., Drysdale J. W. Immunologic differences in human isoferritins: implications for immunologic quantitation of serum ferritin. Blood. 1977 Jan;49(1):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A., Miller F., Worwood M., Beamish M. R., Wardrop C. A. Ferritin in the serum of normal subjects and patients with iron deficiency and iron overload. Br Med J. 1972 Oct 28;4(5834):206–208. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5834.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A., Worwood M. Ferritin in serum. Clinical and biochemical implications. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 1;292(18):951–956. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505012921805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew M. C., Geddes E. W., Macnab G. M., Bersohn I. Hepatitis-B antigen and cirrhosis in Bantu patients with primary liver cancer. Cancer. 1974 Sep;34(3):538–541. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197409)34:3<539::aid-cncr2820340310>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew M. Alpha-fetoprotein in primary liver cancer and other diseases. Gut. 1974 Oct;15(10):814–821. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.10.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipschitz D. A., Dugard J., Simon M. O., Bothwell T. H., Charlton R. W. The site of action of desferrioxamine. Br J Haematol. 1971 Apr;20(4):395–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD R. A. Cirrhosis and primary carcinoma of the liver; changes in their occurrence at the Boston City Hospital, 1897-1954. N Engl J Med. 1956 Dec 20;255(25):1179–1183. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195612202552503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus D. M., Zinberg N. Measurement of serum ferritin by radioimmunoassay: results in normal individuals and patients with breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Oct;55(4):791–795. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. E., Lipschitz D. A., Bieber C. P., Cook J. D. Measurement of serum ferritin by a 2-site immunoradiometric assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Sep;61(1):209–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieto J., Barry M., Sherlock S. Serum ferritin in patients with iron overload and with acute and chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):525–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Seppälä M. Studies of carcino-fetal proteins. 3. Development of a radioimmunoassay for -fetoprotein. Demonstration of -fetoprotein in serum of healthy human adults. Int J Cancer. 1971 Nov 15;8(3):374–383. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrance J. D., Bothwell T. H. A simple technique for measuring storage iron concentrations in formalinised liver samples. S Afr J Med Sci. 1968 Apr;33(1):9–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters G. O., Miller F. M., Worwood M. Serum ferritin concentration and iron stores in normal subjects. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Oct;26(10):770–772. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.10.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


