Abstract
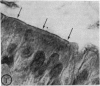
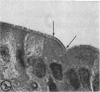
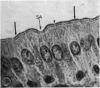
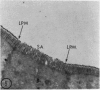
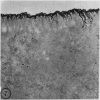
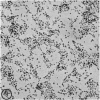
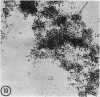
Utilizing colloidal iron staining to localize acid mucosubstances both at light and electron microscopic levels it has been observed that, in the strain of mice studied, there is a distinct variation in the cell-to-cell disposition of the so-called `glycocalyx', ie, the enteric surface coat. It has been inferred that this glycoprotein surface coat is not—analogous to lubricious mucous secretion—a uniform smearing of the epithelial cells by goblet cell mucus. It is also found that each cell possesses and synthesizes its own individual surface coat, with some cells exhibiting more, others less, and still others deficient in surface coat at a given time. It is suggested that these observed variations could well reflect the maturity and functional state of the absorptive cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett G., Leblond C. P. Formation of cell coat material for the whole surface of columnar cells in the rat small intestine, as visualized by radioautography with L-fucose-3H. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):409–416. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. Migration of glycoprotein from golgi apparatus to cell coat in the columnar cells of the duodenal epithelium. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jun;45(3):668–673. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.3.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran R. C., Clark A. E., Lovell D. Acid mucopolysaccharides in electron microscopy. The use of the colloidal iron method. J Anat. 1965 Jul;99(Pt 3):427–434. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S. The enteric surface coat on cat intestinal microvilli. J Cell Biol. 1965 Dec;27(3):475–491. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.3.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent P. W. Structure and function of glycoproteins. Essays Biochem. 1967;3:105–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee T. M., Staehelin L. A. The fine-structural organization of the brush border of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 1971 May;8(3):573–599. doi: 10.1242/jcs.8.3.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee T. M., Williams A. W. A comparative study of the ultrastructure of microvilli in the epithelium of small and large intestine of mice. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):447–461. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTEROVILARDEBO L. R., LANE N., GODMAN G. C. LOCALIZATION OF PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITIES IN COLONIC GOBLET AND ABSORPTIVE CELLS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:486–490. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockerman P. A. Glucose-6-phosphatase in human jejunal mucosa properties demonstrating the specific character of the enzyme activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 29;105(1):22–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A. Recent functional interpretations of intestinal morphology. Fed Proc. 1962 Nov-Dec;21:873–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambourg A., Leblond C. P. Electron microscope observations on the carbohydrate-rich cell coat present at the surface of cells in the rat. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jan;32(1):27–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPICER S. S. The use of various cationic reagents in histochemical differentiation of mucopolysaccharides. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Nov;36:393–407. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.5.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Glycoproteins: their biochemistry, biology and role in human disease (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1969 Oct 30;281(18):991–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196910302811806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Glycoproteins: their biochemistry, biology and role in human disease. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 6;281(19):1043–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911062811905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUMP B. F., ERICSSON J. L. THE EFFECT OF THE FIXATIVE SOLUTION ON THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF CELLS AND TISSUES. A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS WITH PARTICULAR ATTENTION TO THE PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE OF THE RAT KIDNEY. Lab Invest. 1965 Jun;14:1245–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel M. G., Wetzel B. K., Spicer S. S. Ultrastructural localization of acid mucosubstances in the mouse colon with iron-containing stains. J Cell Biol. 1966 Aug;30(2):299–315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]