Abstract
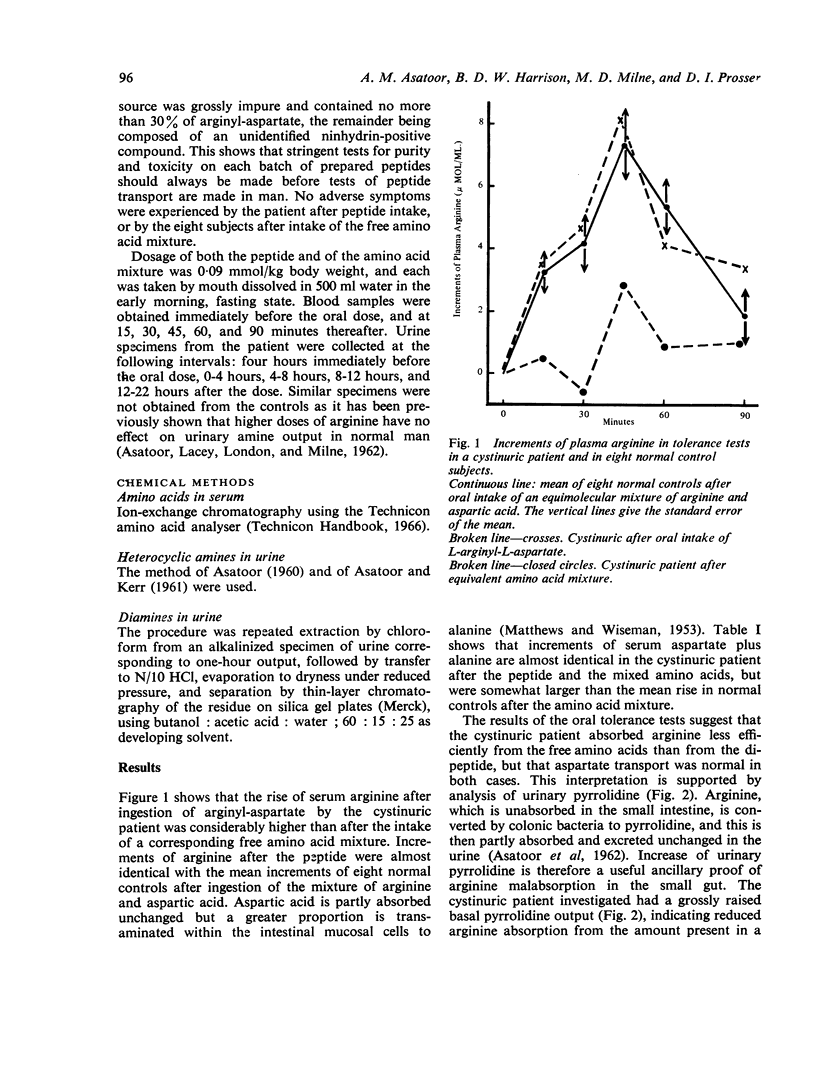
Separate tolerance tests involving oral intake of the dipeptide, L-arginyl-L-aspartate, and of a corresponding free amino acid mixture, were carried out in a single type 2 cystinuric patient. Absorption of aspartate was within normal limits, whilst that of arginine was normal after the peptide but considerably reduced after the amino acid mixture. The results are compared with the increments of serum arginine found in eight normal subjects after the oral intake of the free amino acid mixture.
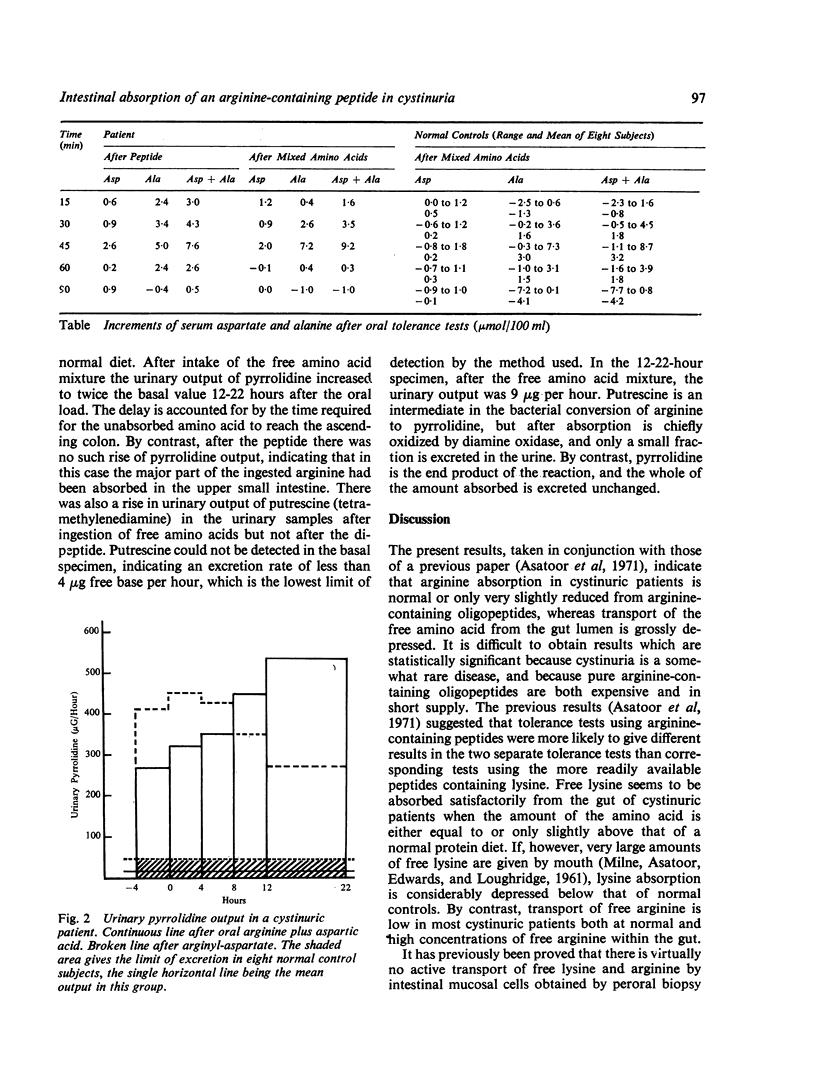
Analyses of urinary pyrrolidine and of tetramethylenediamine in urine samples obtained after the two tolerance tests in the patient support the view that arginine absorption was subnormal after the amino acid mixture but within normal limits after the dipeptide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASATOOR A. M., KERR D. N. Amines in blood and urine in relation to liver disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1961 Mar;6:149–156. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(61)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASATOOR A. M., LACEY B. W., LONDON D. R., MILNE M. D. Aminoacid metabolism in cystinuria. Clin Sci. 1962 Oct;23:285–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asatoor A. M., Cheng B., Edwards K. D., Lant A. F., Matthews D. M., Milne M. D., Navab F., Richards A. J. Intestinal absorption of two dipeptides in Hartnup disease. Gut. 1970 May;11(5):380–387. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.5.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asatoor A. M., Crouchman M. R., Harrison A. R., Light F. W., Loughridge L. W., Milne M. D., Richards A. J. Intestinal absorption of oligopeptides in cystinuria. Clin Sci. 1971 Jul;41(1):23–33. doi: 10.1042/cs0410023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer H. J., Kohne E. The excretion of diamines in human urine. II. Cadaverine, putrescine, 1,3-diaminopropane, 2,2'-dithiobis(ethylamine) and spermidine in urine of patients with cystinuria and cystinlysinuria. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 May;32(3):407–418. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellier M. D., Perrett D., Holdsworth C. D. Dipeptide absorption in cystinuria. Br Med J. 1970 Dec 26;4(5738):782–783. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5738.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS D. M., WISEMAN G. Transamination by the small intestine of the rat. J Physiol. 1953 Jun 29;120(4):55P–55P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY C. F., BORLAND J. L., Jr, LYNCH H. J., Jr, OWEN E. E., TYOR M. P. DEFECTIVE UPTAKE OF BASIC AMINO ACIDS AND L-CYSTINE BY INTESTINAL MUCOSA OF PATIENTS WITH CYSTINURIA. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1518–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI105028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne M. D., Asatoor A. M., Edwards K. D., Loughridge L. W. The intestinal absorption defect in cystinuria. Gut. 1961 Dec;2(4):323–337. doi: 10.1136/gut.2.4.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navab F., Asatoor A. M. Studies on intestinal absorption of amino acids and a dipeptide in a case of Hartnup disease. Gut. 1970 May;11(5):373–379. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.5.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon S. E., Mawer G. E. The digestion and absorption of protein in man. 2. The form in which digested protein is absorbed. Br J Nutr. 1970 Mar;24(1):241–258. doi: 10.1079/bjn19700024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. E., Downing S., Durant J. L., Segal S. Cystinuria: biochemical evidence for three genetically distinct diseases. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):365–371. doi: 10.1172/JCI105351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIER S. O., SEGAL S., FOX M., BLAIR A., ROSENBERG L. E. CYSTINURIA: DEFECTIVE INTESTINAL TRANSPORT OF DIBASIC AMINO ACIDS AND CYSTINE. J Clin Invest. 1965 Mar;44:442–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI105157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


