Abstract
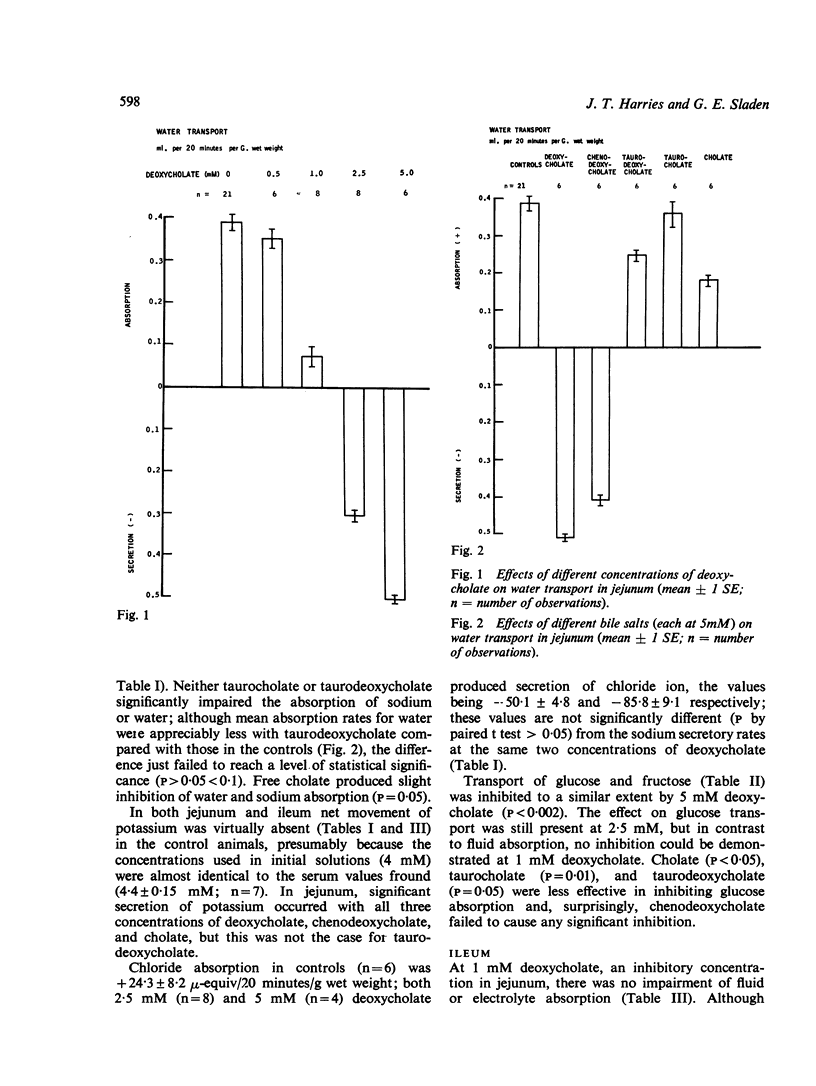
The effects of different bile salts on the absorption of fluid, electrolytes, and monosaccharides have been investigated in the rat small intestine in vivo. In the jejunum, deoxycholate (1 mM) impaired absorption of water and potassium, but not of sodium or glucose; at higher concentrations (2·5 and 5 mM) secretion of fluid and electrolytes occurred, and glucose and fructose absorption was impaired. By contrast, in the ileum, 1 mM deoxycholate failed to inhibit fluid and electrolyte absorption, and a concentration of 10 mM was required completely to inhibit absorption; secretion was not observed in the ileum.
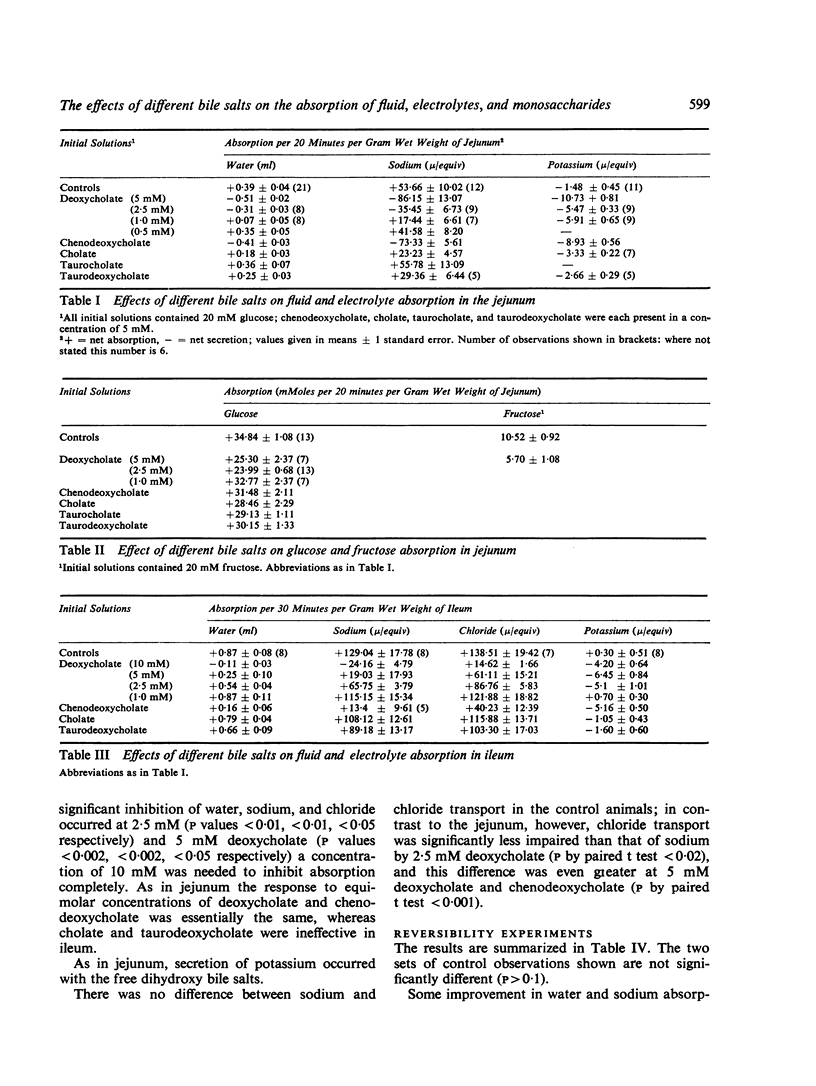
Chenodeoxycholate (5 mM) produced a similar effect to deoxycholate on fluid and electrolyte absorption in both jejunum and ileum, but taurocholate (5 mM) and taurodeoxycholate (5 mM) were ineffective.
In jejunum, cholate, taurocholate, and taurodeoxycholate, each at a concentration of 5 mM, were less effective inhibitors of glucose transport than deoxycholate; chenodeoxycholate failed to inhibit glucose absorption.
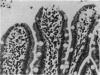
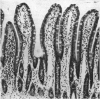
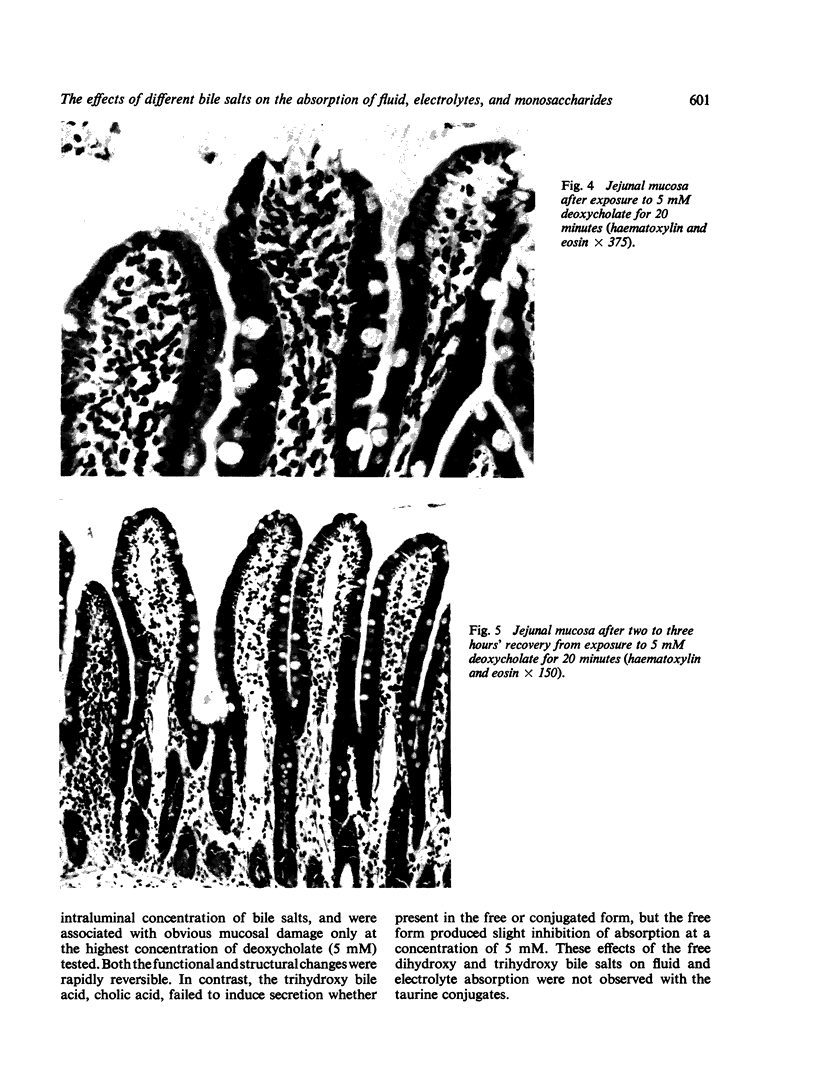
Deoxycholate produced histological damage at 5 mM, but not at lower concentrations. The functional and structural abnormalities were shown to be reversible phenomena.
These findings may be relevant to the pathogenesis of diarrhoea in patients with bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAWSON A. M., ISSELBACHER K. J. Studies on lipid metabolism in the small intestine with observations on the role of bile salts. J Clin Invest. 1960 May;39:730–740. doi: 10.1172/JCI104090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M. Effects of bile salts on intermediate metabolism of the intestinal mucosa. Fed Proc. 1967 Nov-Dec;26(6):1589–1598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr Studies on the pathogenesis of steatorrhea in the blind loop syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1815–1825. doi: 10.1172/JCI105289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRY R. J., STAFFELDT E. EFFECT OF A DIET CONTAINING SODIUM DEOXYCHOLATE ON THE INTESTINAL MUCOSA OF THE MOUSE. Nature. 1964 Sep 26;203:1396–1398. doi: 10.1038/2031396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forth W., Rummel W., Glasner H. Zur resorptionshemmenden Wirkung von Gallensäuren. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol Exp Pathol. 1966;254(4):364–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Anderson C. A. Association of monosaccharide malabsorption with abnormal small-intestinal flora. Lancet. 1969 Aug 16;2(7616):384–385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92734-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Oshin A., Barker J., Glasgow E. F. Bacteria, bile salts, and intestinal monosaccharide malabsorption. Gut. 1971 Sep;12(9):683–692. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.9.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Oshin A. Influence of bile salts on intestinal sugar transport in vivo. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1971;6(3):273–276. doi: 10.3109/00365527109180707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Oshin A. Reversible inhibition of intestinal active sugar transport by deconjugated bile salt in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;225(2):308–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M. Intestinal absorption in the "contaminated small-bowel syndrome". Gut. 1971 May;12(5):403–410. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.5.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G., BEAUFAYS H., DE DUVE C. L'analyse simultanée des hexoses, des trioses et de leurs esters phosphorés. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jul;11(3):416–426. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harries J. T., Sladen G. E. Effects of bile acids on small intestinal absorption of glucose, water, and sodium. Gut. 1971 Oct;12(10):855–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel K. A. Bicarbonate secretion in rat ileum and its dependence on intraluminal chloride. Am J Physiol. 1967 Dec;213(6):1409–1413. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.6.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Schneider R. E., Dobbins W. O. Morphological changes of the small-intestinal mucosa of guinea pig and hamster following incubation in vitro and perfusion in vivo with unconjugated bile salts. Gut. 1970 Jun;11(6):486–492. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.6.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHY B. W., ROWSON K. E., SALAMAN M. H. PLASMA ENZYME LEVELS IN VIRUS-INFECTED MICE. Virology. 1964 Aug;23:528–541. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90237-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekhjian H. S., Phillips S. F. Perfusion of the canine colon with unconjugated bile acids. Effect on water and electrolyte transport, morphology, and bile acid absorption. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jul;59(1):120–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekjian H. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Colonic secretion of water and electrolytes induced by bile acids: perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1569–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI106644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Hatzioannou J., Booth C. C. Bile-salt deconjugation and steatorrhoea in patients with the stagnant-loop syndrome. Lancet. 1968 Jul 6;2(7558):12–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92888-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem M. V., Phillips S. F. Perfusion of the hamster jejunum with conjugated and unconjugated bile acids: inhibition of water absorption and effects on morphology. Gastroenterology. 1972 Feb;62(2):261–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]