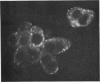
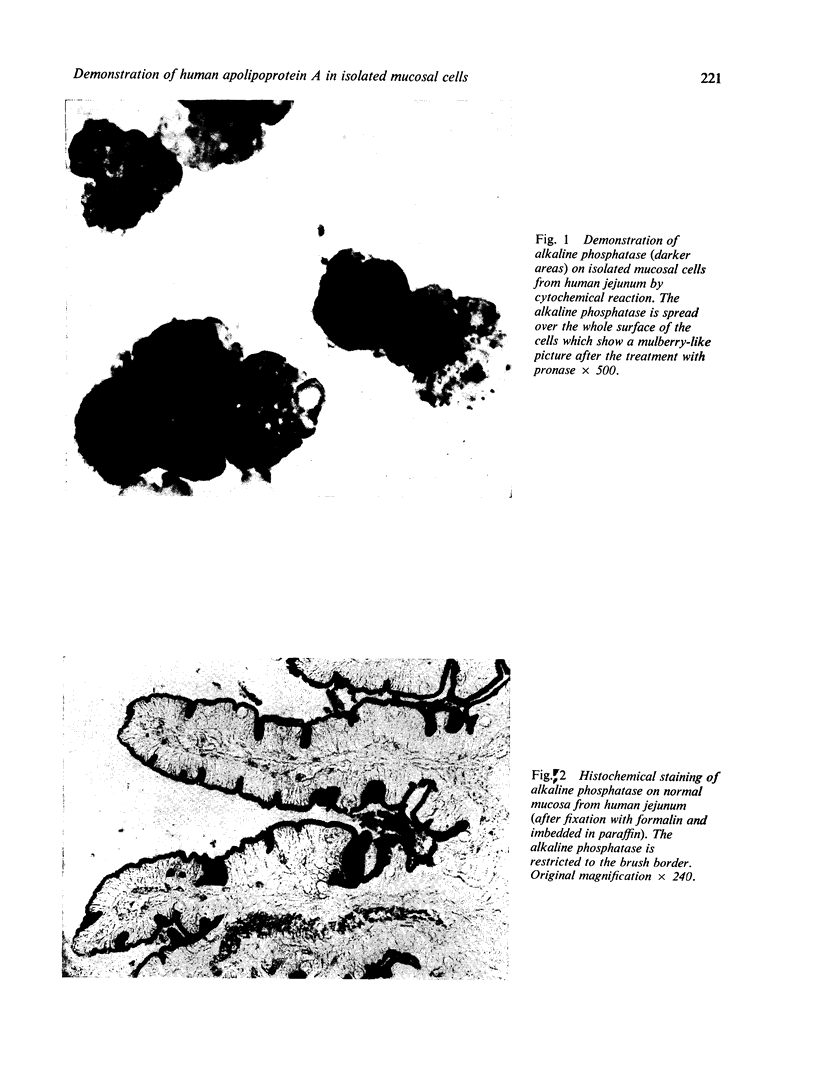
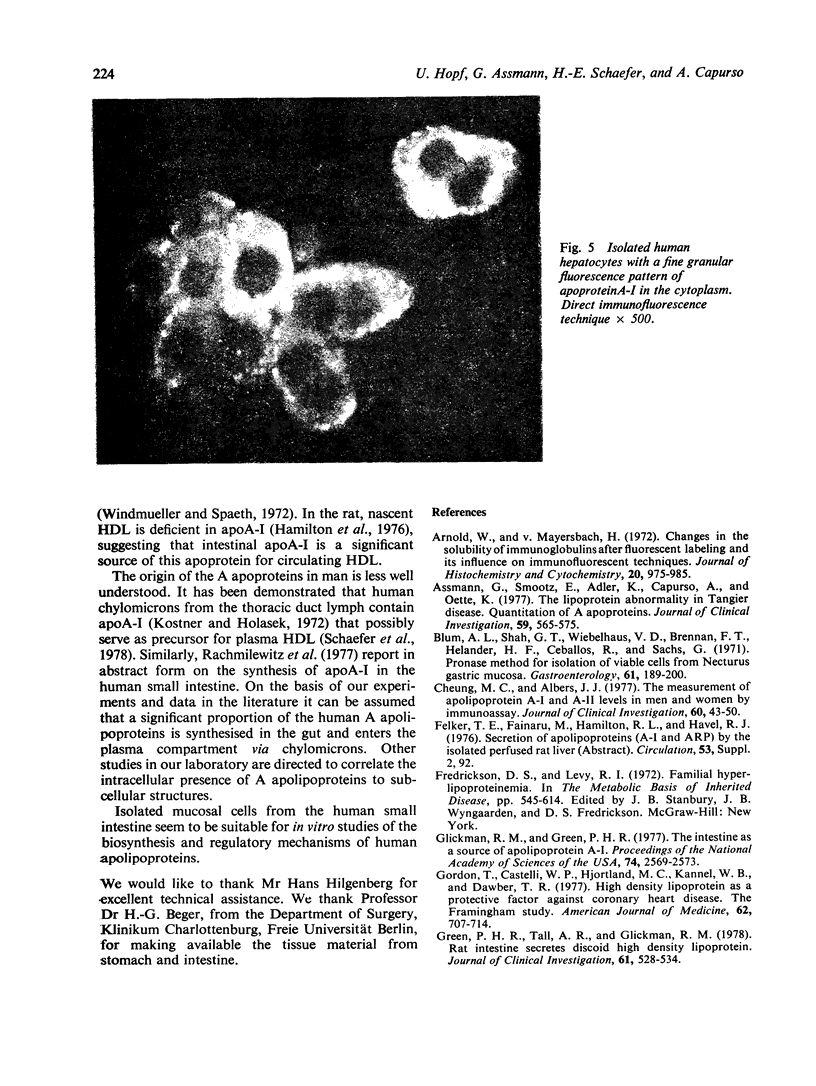
Abstract
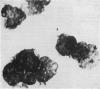
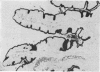
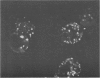
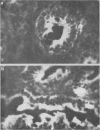
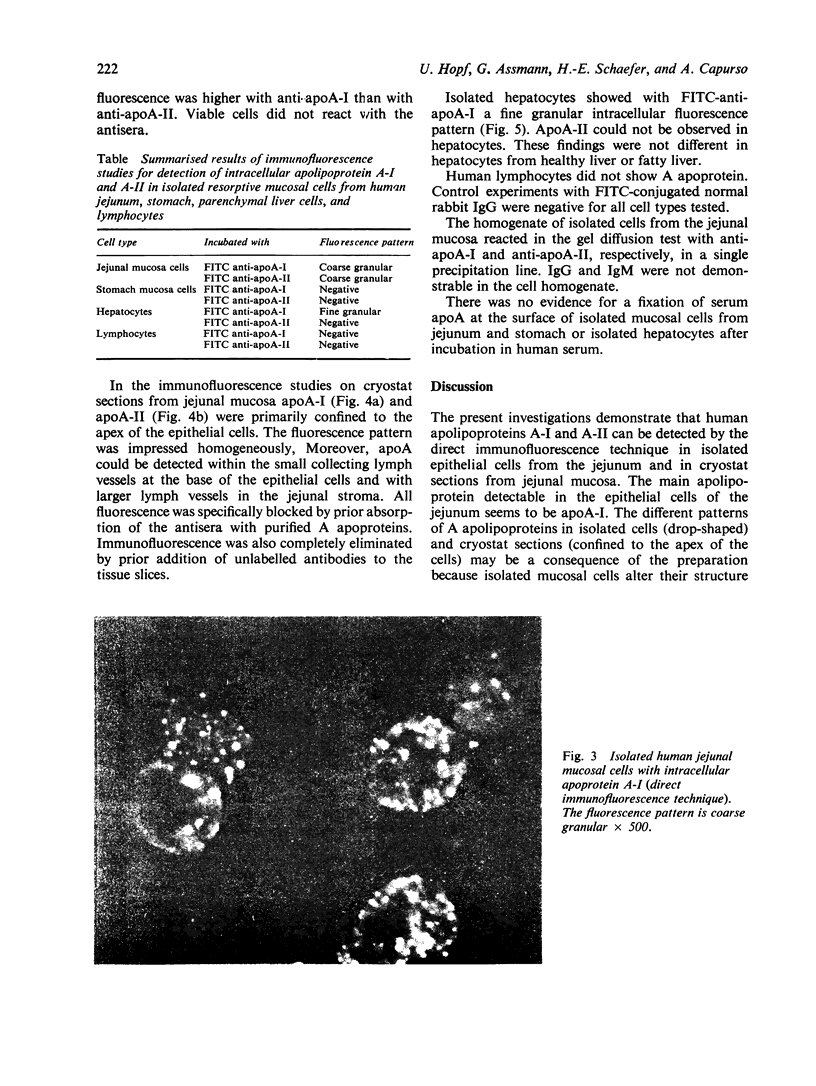
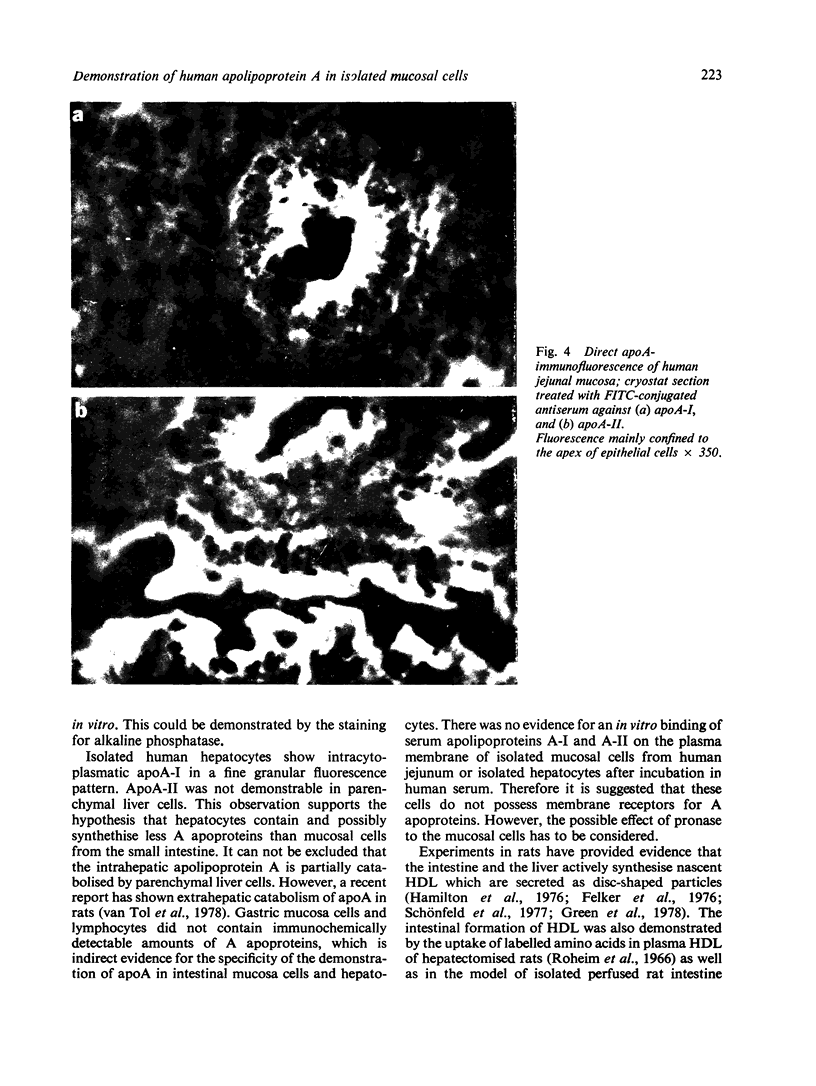
Isolated mucosal cells from the human jejunum and stomach, cryostat sections from the jejunum, isolated parenchymal liver cells and lymphocytes were investigated for the presence of apolipoprotien A (apoA). Antisera against purified human apoA-I and apoA-II were raised in rabbits and conjugated with fluorescein-isothiocyanate (FITC). Mucosal cells from jejunum and stomach were isolated with pronase from tissue obtained from operated patients. ApoA-I and apoA-II could be demonstrated in isolated mucosal cells as well as in cryostat sections from the jejunum. The fluorescence pattern in isolated jejunal cells was coarse granular. In the radial gel diffusion test the homogenate from mucosal cells of jejunum showed a single precipitation line with anti-apoA-I and with anti-apoA-II, respectively. The reaction was more intensive with anti-apoA-I than with anti-apoA-II. Isolated gastric cells were negative for apoA. Hepatocytes incubated with FITC anti-apoA-I showed a fine granular fluorescence pattern in the cytoplasm. Anti-apoA-II did not react with hepatocytes. There was no evidence for an in vivo fixation of serum-apoA at the surface of isolated mucosal cells from jejunum or isolated hepatocytes. The results support the hypotheses that in man apoA is synthesised in the epithelial cells of the small intestine and in parenchymal liver cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold W., von Mayersbach H. Changes in the solubility of immunoglobulins after fluorescent labeling and its influence on immunofluorescent techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1972 Dec;20(12):975–985. doi: 10.1177/20.12.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann G., Smootz E., Adler K., Capurso A., Oette K. The lipoprotein abnormality in Tangier disease: quantitation of A apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):565–575. doi: 10.1172/JCI108672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum A. L., Shah G. T., Wiebelhaus V. D., Brennan F. T., Helander H. F., Ceballos R., Sachs G. Pronase method for isolation of viable cells from Necturus gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1971 Aug;61(2):189–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. The measurement of apolipoprotein A-I and A-II levels in men and women by immunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):43–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI108767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Green P. H. The intestine as a source of apolipoprotein A1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2569–2573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T., Castelli W. P., Hjortland M. C., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am J Med. 1977 May;62(5):707–714. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90874-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. H., Tall A. R., Glickman R. M. Rat intestine secretes discoid high density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):528–534. doi: 10.1172/JCI108963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L. Synthesis and secretion of plasma lipoproteins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;26(0):7–24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7547-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Williams M. C., Fielding C. J., Havel R. J. Discoidal bilayer structure of nascent high density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):667–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI108513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf U., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Arnold W. Detection of a liver-membrane autoantibody in HBsAg-negative chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1976 Mar 11;294(11):578–582. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197603112941103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. A histochemical procedure for localizing and evaluating leukocyte alkaline phosphatase activity in smears of blood and marrow. Blood. 1955 Oct;10(10):1023–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin J. B., Juhn D. J., Starr J. I., Scanu A. M., Rubenstein A. H. Measurement of human high density lipoprotein apolipoprotein A-1 in serum by radioimmunoassay. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jan;17(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G., Holasek A. Characterization and quantitation of the apolipoproteins from human chyle chylomicrons. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 28;11(7):1217–1223. doi: 10.1021/bi00757a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roheim P. S., Gidez L. I., Eder H. A. Extrahepatic synthesis of lipoproteins of plasma and chyle: role of the intestine. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):297–300. doi: 10.1172/JCI105343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Jenkins L. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Human chylomicron apolipoprotein metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 30;80(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90691-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol A., Van Gent T., Van 't Hooft F. M., Vlaspolder F. High density lipoprotein catabolism before and after partial hepatectomy. Atherosclerosis. 1978 Apr;29(4):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(78)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Spaeth A. E. Fat transport and lymph and plasma lipoprotein biosynthesis by isolated intestine. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jan;13(1):92–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]